Английский язык : учебник / И. Ю. Марковина, З. К. Максимова, М. Б. Вайнштейн; - 4-е изд., испр. и перераб. - 2010. - 368 с.
|
|
|
|
II. PHYSIOLOGY
LESSON SEVEN
BLOOD. CIRCULATION
1. Причастия I и II в функции определения (?? 20, 21)
2. Согласование времен (? 18)
3. Функции слов after, before (? 37)
Часть I Слова к части I

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Найдите в следующих сочетаниях слов формы причастий I и II. Переведите их.
a) the
urinary system consisting of two kidneys; the ureters conducting the
urine from the kidneys; a tube leading from the bladder; tubules making
up the parenchyma of the kidneys
b) a thin capillary network called glomerulus; urea dissolved in water; blood vessels straped like a ball
Упражнение 2. Раскройте скобки, используя причастия I и II. Переведите данные предложения.
1. The system (вьгаодящая) the largest part of the waste products of the body is called the urinary system. 2. The capsule (окруженная) by perirenal fat is called the adipose capsule. 3. The urethra is a tube (ведущая) from the bladder. 4. Each renal artery branches into many small arteries (которые называют) arterioles. 5. Ureters are muscular tubes (выстланные) with mucous membrane. 6. The agents (увеличивающие)
the resistance of the organism to an inflammatory process are:
rational diet, balneoand vitaminotherapy as well as immunotherapy.
Упражнение 3. Сравните следующие предложения. Объясните употребление правила.
1. She thinks she will pass her winShe thought she would pass her ter exams successfully. winter exams successfully.
2. We
know the urinary system We knew the urinary system conconsists of
two kidneys, ureters, sisted of two kidneys, ureters, the the
bladder and the urethra. bladder and the urethra.
3. The
doctor says that in this case The doctor said in that case the
the operation on the right kid- operation on the right kidney was
ney is necessary. necessary.
4. The
patient asks whether stones The patient asked whether stones in
the kidneys (or in the bladder) in the kidneys (or in the bladder)
are a very common condition. were a very common condition.
Упражнение 4. Определите, в каких предложениях прошедшее время глагола-сказуемого переводится настоящим временем. Переведите данные пред- ложения.
1.
It was found that after ligation of the common duct in dogs a rise in
the bilirubin concentration of the blood did not occur. 2. The patient
said that he felt better. 3. Many authors stated that the new methods
of treatment of gastric ulcer had been used successfully. 4. It was
proved that saliva varied according to metabolic status and changes in
diet. 5. Mechnikov thought that the extreme age attained by Bulgarian
peasants resulted from the use of sour goat milk and the growth in the
colon of the milk-souring bacterium «Bacillus bulgaricus». 6. Galen
thought that the heart was the source of the body's heat.
Упражнение 5. Прочтите и переведите предложения со словами after, before.
1.
Will you return your textbooks to the library before your examinations
start? 2. The animal died on the 3rd day after inoculation. 3. The
patient felt bad before the operation on his kidney. 4. The blood after
circulation in the glomerulus emerges into capillaries on the walls of
the uriniferous tubes.
5. He never met the man before. 6. After the food leaves the stomach it is acted on by several digestive enzymes.
Упражнение 6. Прочтите и переведите следующие слова.
Упражнение 7. Запомните значение нижеприведенных суффиксов. Про- чтите и переведите следующие слова.
1. Глагол + -ег = существительное, обозначающее а) деятеля; б) аппарат: to write писать - writer писатель.
a) to teach - teacher, to observe - observer, to invade - invader;
b) to intensify - intensifier, to amplify - amplifier, to magnify - magnifier
2. Глагол + -ment = существительное, обозначающее действие, состояние, результат действия: to move двигаться - movement движение.
to improve - improvement, to involve - involvement, to manage - management
Упражнение 8. Прочтите и переведите следующие гнезда слов.
1.
(to) increase, increasing, increased; 2. to invade, invader, invading;
3. (to) wound, wounded; 4. to succeed, success, successive,
succession, successively; 5. to attract, attraction, attractive; 6.
(to) dye, dyeing, dyed; 7. (to) stain, stained, staining, stainless
Упражнение 9. Просмотрите текст А и скажите, что говорится в тексте о двух типах клеток.
Text A
Leucocytes and Lymphocytes
1. Leucocytes. About
65 per cent of all white cells are leucocytes. Their protoplasm
contains granules. Those leucocytes that stain neutral dyes - as the
majority do - are called neutrophils. About 1.5 per cent of the total
stain with acid dyes and are called eosinophils. And a still smaller
number, 0.5 per cent, have granules that stain with basic dyes; these
are called basophils. The percentage of oesinophils increases greatly
when parasites invade the body.
2. One
characteristic of leucocytes is the irregular, or lobed, appearance of
the nucleus. The number of lobes is an index to the cell's age.
Ordinarily, about 45 per cent of all leucocytes have a nucleus of three
lobes. The life span1 of a leucocyte is short, from four to twelve days.
3. The
function of leucocytes is primarily that of protection against
infection. After the skin is pierced and the wound becomes infected,
leucocytes from all the body are attracted to this place. Just what
attracts them is not known - the process is called chemotaxis -
probably some by-product of bacterial metabolism. When they arrive at
the wound, they leave the blood stream. They wage war on the invaders,
engulfing the bacteria within their own protoplasm, a process called
phagocytosis (literally «cell-eating»). Before the infection is not too
overwhelming, the victory usually goes to the leucocytes.
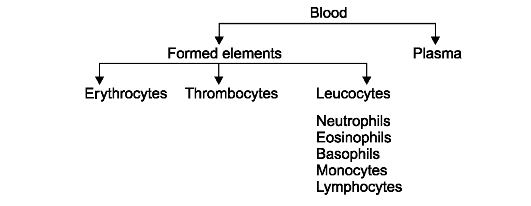
Fig. 7. The formed elements of blood.
4. Lymphocytes. These
cells, which comprise about 35 per cent of the white cells, have a
nucleus which practically fills the cell. They are produced in lymph
nodes scattered throughout the body; the tonsils are examples of lymph
nodes. They live only a few hours after they leave the blood stream.
They are incapable of movement and thus cannot pursue bacteria and have
little cytoplasm so that phagocytosis is practically out of the
question. Bacteria trapped in lymph nodes provoke the formation of
them. Unfortunately if the infection is overwhelming, the lymph nodes
themselves become infected. Thus in guinea pigs it has been possible to
trace the route of tubercle bacilli from the intestines to the lungs,
as the route is marked by successively infected lymph nodes.
Notes
1. life span продолжительность жизни
Упражнение 10. 1) Прочтите и переведите текст А. Абзац 3 переведите письменно. 2) Найдите в тексте А ответы на следующие вопросы.
1.
What is the difference between neutrophils, basophils and eosinophils?
2. When does the percentage of eosinophils increase? 3. The process of
chemotaxis means «cell-eating», doesn't it? 4. What stimulates the
formation of lymphocytes? 5. When do the lymph nodes become infected?
6. What kind of experiment is performed to prove this statement?
Упражнение 11. Подберите пары синонимов.
ordinarily, primarily, to consist of, all over, about, chiefly, throughout, usually, approximately, to comprise
Упражнение 12. Подберите пары антонимов.
regular, to arrive, usually, fortunately, to leave, irregular, unfortunately, unusually
Упражнение 13. Переведите следующие предложения c причастиями I и II.
1.
One of the most important functions served by blood cells is the
ingestion of foreign particles. 2. The blood is not the only fluid
transporting material to different parts of the body. 3. The blood
plasma contains among other things a soluble protein known as
fibrinogen.
4. Blood
and lymph are composed of cells dispended and carried within a watery
fluid. 5. Leucocytes are divided into two major types: granulocytes,
containing large granules in their cytoplasm and granulocytes lacking
granules in their cytoplasm.
Упражнение 14. Переведите следующие предложения. Определите, в каких предложениях используются правила согласования времен.
1.
Galen thought that the heart was the source of the body's heat and
that the blood was the oil which fed the flame. 2. It was established
that the exact form of the corpuscle was dependent upon the osmotic
pressure of the fluid in which it is immersed for examination. 3. Fry
considered that the blood platelets in man arose from the erythrocytes.
4. It has been commonly stated that the hemoglobin served as the
carrier of oxygen. 5. It was demonstrated that rhythmic contractions
would not continue long when sodium chloride was absent.
Упражнение 15. Переведите следующие предложения, определите функции слов after, before.
1.
Anaemia is a medical condition which occurs after the reduction in the
number of erythrocytes or amount of hemoglobin in the circulating
blood. 2. Reticulocytes contain hemoglobin and after they are stained
with a dye, their cytoplasm reveals a dense network of granules. 3. The
granules in the eosinophils turn red, or a rosy colour, after the
addition of an acid dye. 4. Neutrophils increase in number after
pyrogenic (fever-producing) infections and in certain forms of
leukemia.
5. It
is known that the heart is beating in the embryo before it is supplied
with nerves and it will continue to beat in experimental animals even
if the nerve supply is cut.
Упражнение 16. Переведите на английский язык.
1. Лейкоциты составляют около 65% всех белых клеток. 2. Около 45% лейкоцитов имеют ядра, состоящие из трех долек. 3. Лим- фоциты составляют около 35% белых клеток. 4. Они вырабатываются в лимфатических узлах, разбросанных по всему телу.
Упражнение 18. Опишите форменные элементы крови, используя рис. 7.
Часть II Слова к части II

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Подберите пары синонимов.
soon, which, readily, heart, quickly, that, easily, cardiac Упражнение 2. Расшифруйте следующие сокращения.
e.g., i.e., etc., mm, cm
Упражнение 3. Переведите следующие пары слов.
till - until, some - same, to effect - to affect, because - because of, few - a few, to expand - to expend
Упражнение 4. Просмотрите текст В (10 мин). 1) Найдите в нем информацию: а) о природе сердечного удара; б) об особенностях мышечной ткани сердца; в) работе желудочков сердца; г) факторах, которые характеризуют работу левого желудочка. 2) Найдите и переведите предложения: а) с причастиями I и II в функции определения; б) со словами after, before.
Упражнение 5. Прочтите данные суждения. Найдите в тексте В предло- жения, более полно выражающие мысль данного суждения, и прочтите их.
1.
The heart beat is automatic and perfectly rhythmic. 2. Cardiac muscle
tissue has a special property. 3. Both ventricles expel the same volume
of blood. 4. The pressure in the aorta is about six times as great as
in the pulmonary artery. 5. The inhibition of the vagus and sympathetic
centres influences the work of the heart. 6. The stroke volume depends
upon the «venous return». 7. The chambers of the heart are able to
supply additional blood.
Text В Nature of the Heart Beat
The
fact that the heart, completely removed from the body, will go on to
beat for a time shows that its beat is «automatic», i.e. does not
require nerve impulses.
The beat is
rhythmic: it is not jerky; the ventricles relax fully before the next
contraction. This is explained by a special property of cardiac muscle
tissue. The period of time during which the muscle is not responsive to
a stimulus is called the refractory period. It is characteristic of
the heart muscle to have a long refractory period. When the heart
muscle is stimulated, it will contract but will not respond again to
that stimulus (though it may respond to a stronger one) until it has
relaxed. This rest period is occupied by the heart filling with blood,
in preparation for the next beat. Even the heart forced to beat rapidly
maintains a perfectly rhythmic beat; although the beats come closer
together, there is always that little rest period in between.
The
heart is a pump, but a double pump; the volume expelled by the right
ventricle is the same as that expelled by the left. When exercise is
suddenly undertaken, the «venous return», i.e. the blood returned to
the heart through the veins, is suddenly increased. For a few beats the
right ventricle does put out more blood than the left, but soon the
additional blood has passed through the lungs and is entering the left
ventricle. From then on, both put out the same amount.
The Cardiac Output
Cardiac
output refers to the volume of blood which the left ventricle forces
into the aorta per minute of time. It must be noted that this term
refers to the output of the left ventricle only, and that the total
output is twice as much. The reason that the output of the left
ventricle is given this special name is that it supplies the entire
body (except the lungs) with the blood. Another reason is that it does a
much greater amount of work than does the right, and consequently is
more likely to fail.
Cardiac
output is the product of two factors: heart rate (the number of beats
per minute) and stroke volume (the volume expelled per beat).
1. The
heart rate is normally controlled by a balance between impulses
reaching it over the vagus and over the sympathetics. Thus, inhibition
of the vagus centre speeds up the heart. And inhibition of the
sympathetic centre slows down the heart. It seems that in the human
most of the effect is achieved by inhibition of the vagal centre of the
sympathetic region.
2. The
second factor affecting cardiac output is the stroke volume, that is,
the amount of blood which the left ventricle ejects per beat. The
stroke volume depends upon the «venous return». The normal heart is
capable of a considerable degree of enlargement; after the venous
return is increased - as it is in exercise - the chambers of the heart
are able to supply the additional blood. The walls of right atrium and
the great veins are thin and stretch readily; therefore the heart rate
is increased.
The
increased venous return in exercise is brought about in the following
manner: 1) after muscles contract, they exert a «milking» effect on the
blood vessels which they contain. With each contraction, blood is
squeezed out1 into the veins; it cannot be squeezed back
into the arteries because the arterial pressure is high - and with each
relaxation the blood vessels of the muscle again fill up with blood;
2) in exercise, breathing becomes deeper. The heart lies within the
thorax; when the thorax expands, blood is «sucked2 into» the heart.
The
two factors, working together, lead to the increase of the blood
amount returned. First the right side of the heart, and within a few
beats the left, are dilated and take bigger «bites» of blood. Thus the
stroke volume is increased.
Notes
1. to squeeze out просачиваться
2. to be sucked всасываться
Часть III
Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 7
Упражнение 1. Укажите и переведите придаточные предложения, где сказуемые переводятся настоящим временем.
1.
Early Greeks considered that it was possible to transfuse animal blood
to people. 2. The doctor was sure that the patient's blood belonged to
the first group. 3. It is written that the blood was taken yesterday.
4. Landsteiner showed that people possessed different kinds of blood.
5. They are informed that conserved blood was brought two days ago.
(Ответ: 1, 2, 4. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 18 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 2. Укажите и переведите предложения, где after и before
являются союзами.
1.
After the blood was exposed to the air, the process of clotting began.
2. Before blood transfusion, it is ideal to have donor and recipient
of the same blood group. 3. The clot shrinks after its formation. 4.
Lavoisier found that consumption of oxygen was greater after the
ingestion of food than before. 5. After haemoglobin combines with
oxygen, oxyhemoglobin is formed. 6. Human serum must be diluted about
one-third with water before the cup-shaped corpuscles will predominate.
(Ответ: 1, 5, 6. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 37 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 3. Укажите и переведите предложения, где причастия I и II являются определением.
1.
The clotting mechanism is extremely complex. 2. Fibrin is formed in
long, interlacing threads. 3. Fibrin is derived from fibrinogen, which
is ordinarily quite stable. 4. Blood platelets rupture readily when
they are exposed to any other environment. 5. There is a substance in
the blood called prothrombin. 6. The heart rate is controlled by a
balance between impulses reaching it over the vagus and the
sympathetics.
(Ответ: 1, 2, 5, 6. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 20 Грамматического справочника.)
LESSON EIGHT
RESPIRATION
1. Причастия I-II в функции обстоятельства (?? 20, 21)
2. Независимый причастный оборот (? 22)
3. Функции и перевод слов both, both ... and ( ? 40)
Часть I Слова к части I

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Переведите следующие предложения с причастиями I-II. Определите функции причастий.
1.
Examining coagulating blood upon a slide by means of the
ultramicroscope, it is possible to see small masses of coagulum. 2.
Lymphocytes fight disease producing antibodies and thus destroying
foreign material. 3. Methoxamine and phenylephrine are vasopressors
that, when given intravenously, elevate systemic vascular resistance.
4. The contraction and relaxation processes in vascular smooth muscle
display more differences than similarities when compared with those in
skeletal and cardiac muscle. 5. The patient examined complained of
severe headache.
Упражнение 2. Замените следующие придаточные предложения причаст- ными оборотами, оставив союзные слова when, while, if. Переведите эти предложения.
Образец 1: When the ward doctor examines his patients, he usually checks up their blood pressure.
When examining his patients the ward doctor usually checks up their blood pressure.
1.
When leucocytes arrive at the wound, they leave the blood stream. 2.
While leucocytes engulf the bacteria within their own protoplasm, they
wage war on the invaders. 3. When muscles contract, they exert a
milking effect on the blood vessels which they contain.
Образец 2: When people are hospitalized, they undergo a thorough medical examination.
When hospitalized, people undergo a thorough medical examination.
1.
When the heart muscle is stimulated, it contracts. 2. Medical
treatment must be more useful if it is applied immediately. 3. Certain
drugs may cause serious harm if they are used without doctor's
permission.
Упражнение 3. Определите независимый причастный оборот в следующих предложениях. Переведите предложения.
1.
There is a great deal of difference in the phagocyte activity of
corpuscles concerning such substances as carbon and quartz particles,
the former being ingested much more rapidly than the latter. 2. During
the experiment the node and all efferent vessels were cleaned, care
being taken to avoid trauma to the structures. 3. The heart is a double
pump, the volumes expelled by the right and left ventricles being the
same.
4. The experiment having been finished, we were ready to discuss it.
5. Diastole is the relaxation phase of the heartbeat, the atria and ventricles filling with blood.
Упражнение 4. Переведите следующие предложения. Определите, какую функцию выполняют слова both, both ... and.
1.
When performing a transfusion, it is ideal to have both donor and
recipient of the same blood group. 2. The teacher showed us the picture
of the heart in both systolic and diastolic phases. 3. The pleural
surface normally has the tissue on both sides. 4. Heart rate, arterial
pressure and cardiac output were examined in both groups of patients.
5. Both blood and lymph protect the body carrying disease-fighting
cells (phagocytes) and protein substances called antibodies which
combat infection.
6. Both the diaphragm and the ribs move rhythmically and regularly during respiration.
Упражнение 5. Напишите глаголы, от которых образованы следующие существительные. Переведите их.
inhalation, exhalation, respiration, expansion, exertion, contraction, construction, action, acceleration
Упражнение 6. Прочтите и переведите следующие гнезда слов.
1.
to decrease, to increase, decreased, increasing; 2. to participate,
participation, participant, participating; 3. to accelerate,
acceleration, accelerated, accelerating; 4. to assist, assistance,
assistant, assisting; 5. to contract, contraction, contractility,
contractile, contracted
Упражнение 7. Прочтите и переведите следующие сочетания слов.
increasing
the size of smth, the increased capacity, the contraction of certain
muscles, an expansion of the lung, accelerated respiration, to assist
in producing inspirations
Упражнение 8. Просмотрите текст А и скажите, что в нем сказано о движении мышц при дыхании.
Text A
Movements of Breathing Mechanism of Inhalation and Exhalation
1.
Respiration consists of rhythmically repeated inhalations and
exhalations. Inhalation takes place as follows: the muscles
participating in inhalation contract under the influence of nerve
impulses. While contracting the diaphragm descends (flattens)
increasing the vertical size of thoracic cavity. Contraction of the
external intercostal and certain other muscles elevates the ribs
increasing both the anteroposterior and transverse size of the thoracic
cavity. Thus muscular contraction increases the capacity of the
thorax. Since the pleural cavity contains no air and the pressure in it
is negative both lungs expand
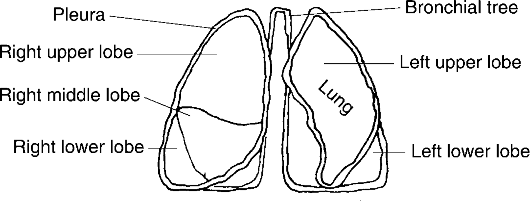
Fig. 8. Diagram of lungs
simultaneously
with the increase in capacity of the thorax. The lungs expanding, the
air pressure in them drops and atmospheric air rushes into the lungs
through the air passages. Hence an inhalation involves a contraction of
muscles, an increase in the capacity of the thorax, an expansion of
the lungs, and entrance of atmospheric air into the lungs through the
air passages.
2. Inhalation
is followed by exhalation. The muscles participating in inhalation
relax, the diaphragm rising. The ribs drop as a result of contraction
of the internal intercostal and other muscles and because of their own
weight. The capacity of the thorax decreasing, the lungs become
compressed, the pressure in them rises and the air rushes out through
the air passages.
3. The
respiratory movements are rhythmic. An adult at rest makes 16-20
respiratory movements per minute, children make more movements (a
newborn child makes up to 60 movements a minute). Physical exertion,
particularly in untrained people, is usually accompanied by faster
respiration. Accelerated respiration is also observed in many diseases.
Sleep is accompanied by a slowing of respiration.
4. Movements of breathing. Changes
in the volume of air in the lungs are brought about by movements both
of the diaphragm and ribs. Contraction of the diaphragm increases the
length of the capacity of the chest, while the upward movement of the
ribs increases the cross section of the chest. Inspiration is due to
contraction of the diaphragm and of the muscles attached to the ribs.
These contractions are induced by nervous impulses. Expiration is a
less active process than inspiration, for when the muscles relax the
elasticity of the lungs themselves tends to drive out the air
previously inhaled. Any impediment to breathing due to pressure or
constriction in the respiratory passages is especially noticeable
during expiration, because it is usually of a passive character. When
the volume of breathing is increased by physical exercise many
assessory muscles are involved while producing deeper inspirations.
Expiration also involves a vigorous action of the abdominal muscles.
Упражнение 9. 1) Прочтите и переведите текст А. Первый абзац переве- дите письменно. 2) Найдите в тексте А ответы на следующие вопросы и зачитайте их.
1.
How is contraction of the muscles participating in inhalation
regulated? 2. Why does the size of the thoracic cavity increase? 3.
When is impediment to breathing especially noticeable? 4. What
processes does
the inhalation (exhalation) involve? 5. What do the movements of the diaphragm and ribs bring about?
3) Составьте письменно план текста А.
Упражнение 10. Подберите пары синонимов.
inspiration,
to take place, to induce, per minute, respiration, breathing, to
cause, to produce, inhalation, to occur, a minute
Упражнение 11. Подберите пары антонимов.
to
compress, inhalation, to contract, to increase, to drop, upward, to
decrease, to rise, downward, exhalation, to expand, to relax
Упражнение 12. Переведите следующие предложения, определите функции причастий.
1.
For mechanical analysis the respiratory system may be divided into
three parts: the gas (in the airways and air spaces), the lung
structure, containing the gas, and the thorax containing the lungs. 2.
Dynamic increases in airway resistance during expiration set the limit
on the ventilatory capacity of the respiratory system in normal and
diseased lungs. 3. While flowing through the capillaries the blood
accepts the oxygen from the alveolus and deposits carbon dioxide into
the alveolus. 4. Airway pressures are not everywhere equal, being most
negative in the alveoli. 5. During inspiration pleural pressures become
more negative, the widening tendency increasing.
Упражнение 13. Опишите анатомическое строение легких, используя текст и рис. 8.
Часть II Слова к части II

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Используя суффиксы -tion, -ate, -ly, -al, -ing, образуйте производные от следующих слов. Переведите их.
to inhibit, stimulus, automatic, reflex, spine, to relax, to excite, to cough, to sneeze, to alter
Упражнение 2. Просмотрите текст В (10 мин). 1) Выделите 4 основные фактора в процессе дыхания, описанные в тексте. 2) Найдите и переведите: а) предложения, где причастия выполняют функцию обстоятельства; б) предложения с независимым причастным оборотом; в) предложения со словами both, both...and.
Text В
Regulation of Respiration. Nervous Control of Breathing
The
mechanism of regulation of respiration is very complex. Schematically
it is as follows. In the medulla oblongata there is the respiratory
centre. In the respiratory centre both excitation and inhibition
continuously alternate. When excited it transmits impulses to the
spinal cord and hence along nerves to the respiratory muscles; the
latter contract and an inhalation takes place. When the respiratory
centre is in a state of inhibition the transmission of impulses to the
respiratory muscles ceases, the muscles relax and an exhalation re-
sults.
The
specific stimulus of the respiratory centre is carbon dioxide. As soon
as the blood accumulates a certain amount of carbon dioxide, the
respiratory centre becomes excited and an inhalation takes place.
During inhalation the lungs expand, which stimulates the endings of the
vagus nerve embedded in the tissue of the lungs. While arising in the
receptors the excitation is transmitted along the vagus nerve to the
respiratory centre and inhibits it, and an exhalation results. Thus
respiration is automatically regulated; an inhalation stimulates an
exhalation, and the exhalation brings about an accumulation of carbon
dioxide which stimulates an inhalation.
Respiration
is subjected to the control of the cerebral cortex; this being
demonstrated by the fact that a person can voluntarily hold his breath
for a very short time or change both the rate and depth of respiration.
Cortical regulation of respiration is also evident in the acceleration
of respiration during emotional states. Protective acts, such as
coughing and sneezing, are associated with respiration. Both of them
are performed reflexly; the centres of the reflexes are situated in the
medulla oblongata.
Nervous control of breathing. The
muscles of breathing have no independent or automatic rhythm, they
contract only responding to impulses from the brain down the spinal
cord. These impulses arise and are coordinated in a specialised area in
the brain, the respiratory centre, which is in the medulla. The medulla
is at the base of the brain and is a bulbous continuation of the
spinal cord within the skull. The respiratory centre has to adjust the
volume of air breathed and to maintain a uniform alkalinity of the
blood; the centre effects the reciprocal alteration both of inspiration
and expiration.
Упражнение 4. Прочтите данные суждения. Найдите в тексте В предложе- ния, более полно выражающие мысль суждений, и прочтите их.
Часть III
Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 8
Упражнение 1. Найдите и переведите предложения, где причастие I выполняет функцию обстоятельства.
1.
We were talking about coming exams. 2. When the ribs are elevated by
the inspiratory muscles they are drawn toward a horizontal plane thus
increasing the anteroposterior diameter of the thorax. 3. Having
obtained the nesessary results the scientists used them in their future
works. 4. When considering neurogenic factors that regulate local
blood flow one thinks of sympathetic non-adrenergic nerves.
(Ответ: 2, 3, 4. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 20 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 2. Найдите и переведите предложения, где причастие II выполняет функцию обстоятельства.
1. When excised the lungs were not allowed to collapse completely.
2. Any
pressure applied to a body is opposed by an equal pressure developed
by the body. 3. The stability of the lung tissues is indicated by their
behaviour when freed by surface influences. 4. As mentioned at the
previous lecture next theme will be devoted to nervous control of
breathing. 5. Inspiration enlargement of the anteroposterior and
lateral diameters of the chest is accomplished through the contraction
of muscles.
(Ответ: 1, 3, 4. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 21 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 3. Найдите и переведите предложения с независимым причастным оборотом.
1.
Respiration is usually either an automatic or a reflex act, each
expiration sending up afferent, sensory impulses to the central nervous
system. 2. It is impossible to cause death voluntarily holding the
breath.
3. The
air passes rhythmically into and out of the air passages, and mixes
with the air already in the lungs, these two movements being known as
inspiration and expiration. 4. The increase of the chest in size is due
to the diaphragm, whose muscular fibres by their contraction are
pushing down the abdominal organs.
(Ответ: 1, 3. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 22 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 4. Укажите и переведите предложения, где слово both является а) частью составного союза; б) местоимением.
1.
Modern scientists have been successful in the use of fibrinolytic
therapy in both ball and disc mitral prosthesis. 2. When the diaphragm
is released both lungs collapse by their own elasticity and expel the
air. 3. The decrease in thoracic size during expiration is accomplished
both by release of physical stresses and by active participation of
contracting muscles. 4. Both these methods of examining the lungs are
frequently used. 5. During forced expiration the contraction of the
abdominal muscles allows both external and internal intercostals to act
as expiratory muscles.
(Ответ: a) 1, 3, 5; б) 2, 4. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 40 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 5. Выберите правильное значение выделенных слов.
(Ответ: la, б; 2а; За; 4а; 5б.)
LESSON NINE
DIGESTION
1. Инфинитив в функции подлежащего и обстоятельства (? 25)
2. Сравнительная конструкция the ... the ... (? 4)
3. Функции и перевод слов due, due to (? 39)
Часть I
Слова к части I


Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Найдите формы инфинитива в следующих предложениях. Переведите предложения.
1.
Spontaneous respiration was chosen to permit the development of
pulmonary edema and alveolar collapse. 2. To determine progressive lung
damage in this case was rather difficult. 3. To give first aid one
must learn the basic first aids rules. 4. It is useful to summarize
very briefly what is known about the elastic properties of elastin and
collagen. 5. Experiments were done to observe the effects of
temperature upon the respiratory process.
Упражнение 2. Заполните пропуски подходящими по смыслу прилага- тельными sooner, less, more. Переведите данные предложения.
1.
The ... people are physically trained, the ... oxygen they have in
their blood. 2. The ... appetizing the food is, the ... amount of
secretion it causes. 3. The ... time you spend in the sanatorium, the
... you will recover after the illness. 4. The ... capacity of the
thorax decreases, the ... the lungs become compressed.
Упражнение 3. Переведите следующие предложения со словами due, due to.
Упражнение 4. Отработайте чтение следующих слов, переведите их.
Упражнение 5. Запомните значение следующих суффиксов. Образуйте слова согласно данным моделям. Переведите эти слова.
1. Прилагательное (существительное) + -ify = глагол, имеющий значение «производить действие»: class класс - to classify классифицироват ь.
pure, intensive, solid, note, sign
2. Прилагательное + -ty (-ity, -ety) = существительное, обозначающее состояние, положение: extreme крайний - extremity конечность.
equal, proper, human, dense, immune, certain
Упражнение 6. Прочтите и переведите данные гнезда слов.
1. nutrient (n, a), nutritive,
nutrition, nutritional; 2. to dissolve, solution, soluble, insoluble,
solvent; 3. to vary, variant, various, variable, variability; 4.
bacterium, bacterial, bacteriology, bacteriologist; 5. (to) vomit,
vomiting, vomitive; 6. to digest, to ingest, digestive, digestion
Упражнение 7. Просмотрите текст А. Разделите текст на 3 части и озаглавьте их.
Text A
The Digestive System and the Process of Digestion and Absorption
1. The
present text is given to explain the processes of digestion and
absorption. The more we know about them, the better we shall understand
how important these processes are.
2. Every
cell of the human body requires certain chemical nutrients in the
fluids that surround it. In order to supply these nutrients, the body
must break down complex foods into molecules small enough to pass
through tissues, enter the blood stream or lymphatic systems, and be
delivered in a soluble form to the various body cells. This break of
insoluble forms is known as digestion; the passage of such substances
into the blood stream or lymph is known as absorption.
3. The human digestive tract is a long, muscular tube (up to
4. Several
glands, located outside the digestive tract, are also important in the
digestive process. Our tast is to describe them in detail.
These glands, known as accessory glands, are connected by ducts to the digestive tube. These accesory glands include the salivary glands,
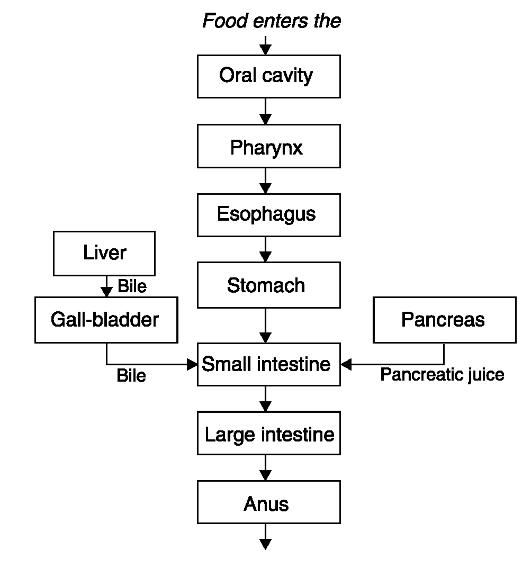
Feces leave the body
Fig. 9. Pathway of food through the digestive tract
liver,
gall-bladder and the pancreas. Each gland produces secretions that
function in the digestive process, and each is therefore part of the
digestive system.
5. The
process of digestion is due to the activity of many enzymes,
chemicals, and physical processes within the digestive tract. According
to the area in which digestion is carried on, these digestive
processes may be classified as salivary digestion, when occurring in
the mouth; gastric digestion in the stomach; and intestinal digestion
in the small intestine. In the large intestine (the last section of the
digestive tube) no digestion takes place. Here water is absorbed,
bacteria grow, and the unabsorbed solid-residue wastes of digestion
collect and are excreted as feces.
6. The
absorption means the passage of digested foods through the lining of the
intestines into the blood or lymph. Practically all absorption takes
place in the small intestine. A few drugs and alcohol are absorbed
through the walls of the stomach, but no foods. Glucose is an
exception, but it must be present in such high concentrations as to
cause vomiting. Furthermore, we eat very little glucose, which is
formed mainly in the small intestine due to the action of the
dissaccharide-
splitting enzymes. Therefore, absorption of food does not normally occur through the stomach walls.
7.
Water is absorbed throughout the length of the small intestine and
also, as has been noted, in the ascending limb of the colon. With
normal digestion, between 95 and 100 per cent of all carbohydrates,
fats, and animal proteins are absorbed. Plant proteins, such as beans
or peas, are protected by the plant cell membrane, so that only 60 to
70 per cent are absorbed. The remaining 30 to 40 per cent undergo
bacterial decomposition in the intestine, which results in the
formation of large amounts of intestinal gas («flatus»).
To study the pathway of food through digestive tract is very important for explanation of the process of digestion.
Упражнение 8. 1) Прочтите и переведите текст А. Второй абзац переведите письменно. 2) Найдите в тексте ответы на следующие вопросы и про- чтите их.
1.
How are nutrients supplied to the body? 2. What processes are known as
digestion and absorption? 3. What do we call the parts of the
digestive tube from the mouth up to the anus? 4. Is glucose absorbed
from the stomach or the small intestine? 5. Water and drugs arc
absorbed through the stomach walls, aren't they?
3) Найдите в каждом абзаце предложения, выражающие основную мысль первого абзаца.
4) Составьте письменно план текста А.
Упражнение 9. Найдите в каждом ряду слово, противоположное по значению первому слову ряда.
1.
soluble - decomposed, dissoluble, diluted, insoluble; 2. to include -
to conclude, to exclude, to leave out; 3. solid - hard, weak, soft,
firm, soluble; 4. ascending - going up (down), descending, sitting down
Упражнение 10. Переведите следующие предложения, определите функции инфинитива.
1.
The present investigation is carried out to determine the liver
functions in experimental dogs. 2. An attempt was made to correlate
metabolism with humidity, light, or average daily temperature. 3. One
of the purposes of this work is to prevent the action of the
dissaccharide-splitting enzymes.
Упражнение 11. Определите в следующих предложениях конструкцию сравнения the ... the. Переведите предложения.
1.
The greater amount of the substance was added to the nutrient, the
more significant change in three or four experiments was produced. 2.
The more specialized the animal is, the more differentiated its enzymes
become. 3. The more food with an appetizing smell you digest, the more
digestive juices will be poured out. 4. The greater the difference in
temperature is, the more rapidly will heat be lost from the body. 5.
The younger the individual is, the higher the caloric requirement -
i.e. the more nutrition is needed.
Упражнение 12. Переведите следующие предложения; определите функции слов due, due to.
1.
Jaundice is the yellow colour of skin sclerae and mucous membranes due
to an increase of bilirubin in the plasma. 2. Some patients' digestive
systems react more intensely to emotional stress due to hypersensitive
nerve endings in their intestinal tract. 3. The secondary rise in
oxygen consumption in normal cats may be due to the reconversion of
lactic acid to glicogen in the liver. 4. It has been shown that the
decrease in resistance across the stomach wall of the experimental dog
is due to a decrease in the resistance across the external muscle
layers. 5. Physiologists have raised the question as to whether the
rhythmic activity of the heart muscle is due to some rhythmic power
located within the heart muscle fibre.
Упражнение 13. Опишите прохождение пищи по пищеварительному тракту, используя текст и рис. 9.
Часть II Слова к части II


Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Отработайте чтение следующих слов, переведите их.
baruim sulphate, substance, process, human, limited, especially, resistance, contract, peristalsis, series, mix, axial, origin
Упражнение 2. Напишите исходные слова к данным производным и переведите их.
movement, observation, constriction, shapeless, interference, tubular, muscular, insufficient, digestion
Упражнение 3. Прочтите текст В (10 мин). 1) Разделите текст на 4 части и назовите тему каждой из них. 2) Найдите в тексте предложения, где: а) инфинитив выполняет функцию подлежащего; б) обстоятельства; в) употребляются слова due, due to. 3) Переведите эти предложения.
Text В
The Movements of the Stomach
It
is advisable to study the movements of the stomach by direct
observation by means of the X-rays. In order to make the shape of the
stomach visible the food - bread and milk - is mixed with a quantity of
barium sulphate. The presence of this substance does not interfere
with the processes of digestion, but renders the gastric contents to
the Rontgen rays.
In
the human stomach the term fundus is limited to that part of the
stomach situated above the cardiac orifice (in the erect position). The
body of the stomach is marked off from the pyloric part by the
incisura angularis on the lesser curvature represented in many animals
by a strong «transverse band». The pyloric portion consists of the
pyloric vestibule (or antrum) and the pyloric canal, the latter being a
tubular portion with thick muscular walls about
forced them
towards the pylorus. Peristalsis begins almost at once, each
constriction starting near the middle of the stomach, and deepening as
it slowly progresses towards the pylorus. These waves succeed one
another, so that the pyloric part may present a series of
constrictions. Their effect is to force towards the pylorus the food
which has been mixed with gastric juice. The longer the pylorus remains
closed the longer the food cannot escape and therefore is squeezed
back, forming an axial reflux stream towards the body. These
contractions last throughout the whole period of gastric digestion, and
become more marked as it proceeds. Due to their action a thorough
mixture of food and gastric juice results.
Movements
of the stomach may be observed even on a stomach which has been
excised and placed in warm water-salt solution. They must therefore
have their origin in the walls of the stomach itself.
Упражнение 5. Прочтите данные суждения. Найдите в тексте В предложе- ния, более полно выражающие мысль суждений, и прочтите их.
1.
It is advisable to study the movements of the stomach by means of
X-rays. 2. The pyloric portion consists of the pyloric vestibule. 3.
When food has been swallowed some of it passes to the pyloric part of
the stomach. 4. Peristalsis begins near the middle of the stomach. 5.
The contractions last throughout the whole period of gastric digestion.
Часть III
Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 9
Упражнение 1. Найдите и переведите предложения, в которых инфинитив выполняет функцию а) подлежащего; б) обстоятельства.
1.
To render surgical assistance, a surgeon should have a lot of
knowledge and skill. 2. It is difficult to analyse the natural
movements of the stomach in the empty and full states. 3. Since all
parts of the stomach are not in the same transverse position it is
therefore almost impossible to speak of a normal position or shape of
the stomach. 4. Enterokinase increases the activity of all ferments in
the pancreatic juice but acts as a co-ferment to activate trypsin
secreted in inactive form.
(Ответ: а) 2, 3; б) 1, 4, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 25 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 2. Найдите предложения с конструкцией сравнения the ... the. Переведите предложения.
1.
When a small quantity of liquid is swallowed into the empty
contracting stomach, the liquid passes at once into the antrum. 2. The
sooner he finishes his experiment on mechanical action of smooth muscle
contraction, the sooner we start a new one. 3. The emptying rate of
the stomach increases progressively from the onset of the completion of
digestion. 4. The more high vitamin diet you try, the sooner you will
recover. 5. The more appetizing smell the food has the more digestive
juices will be poured.
(Ответ: 2, 4, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 4 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 3. Найдите и переведите предложения с составным предлогом due to.
1.
Pancreatic juice is a clear alkaline secretion due to the presence of
sodium bicarbonate. 2. The gastric secretion begins with food in the
stomach due partly to mechanical distension, partly to chemical
stimulation. 3. Nervous mechanisms permit due communication between
widely separated portions of the gastro-intestinal tract. 4. The effect
of stimulation of the splanchnic nerves is explained by the
complication of asphyxia due to simultaneous vasoconstriction. 5.
Disturbances of digestion may be due either to absence of certain
secretions or to their presence in insufficient amounts.
(Ответ: 1, 2, 4, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 39 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 4. 1) Подберите к англо-американским единицам измерений соответствия в метрической системе.
1) inch, 2) foot, 3) ounce, 4) pound
1) 28.35 г, 2)
2) Переведите в метрическую систему.
Упражнение 5. Опишите процесс пищеварения, используя рис. 9.
LESSON TEN
NUTRITION
1. Инфинитив в функции определения (? 25)
2. Бессоюзные придаточные предложения (? 32)
3. Функции и перевод слова for (? 37)
Часть I
Слова к части I

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Переведите на русский язык следующие словосочетания; скажите, чем выражено определение.
attempts
to increase the endogenous iron; the observations to be described;
capacity to clear blood ammonia; an analysis based on; blood vessels
surrounding the wall of the small intestine; the proteins to be
absorbed; protein diet; complex foods to be broken down; obesity to be
prevented; food absorption
Упражнение 2. Переведите следующие предложения. Определите: а) вид бессоюзных придаточных предложений; б) какой союз пропущен.
1.
Studies in vivo we discuss here indicate that intestinal absorption is
an important pathway to regulate the quantity of iron in the body. 2.
The methods we present here were modified and gave satisfactory
reproducible results. 3. Mechnikov thought old age was brought on by
the absorption of the products of the proteolytic group of organisms.
4. We know digestive enzyme of the stomach is pepsin. 5. I.P. Pavlov
showed that the digestive juices flow at the sight and especially at
the smell of food.
Упражнение 3. Переведите следующие предложения co словом for.
1.
For the assay of enzyme activity the animals were killed, the liver
quickly removed, washed thoroughly with cold distilled water and placed
in a beaker with cracked ice. 2. Protein is essential for growth and
repair. 3. Heart pain persisted for half an hour so we had to dial 03
for the doctor to come. 4. The patient is to keep the bed, for his
disease may affect the heart.
Упражнение 4. Прочтите и переведите данные гнезда слов.
1.
oxide, to oxidize, oxidation, oxygen, to oxygenate; 2. to distribute,
distribution, distributing; 3. equal, equally, equality; 4. abundant,
abundantly, abundance
Упражнение 5. Просмотрите текст А и определите тему каждого абзаца.
Text A Foods
Foods
are substances which when taken into the body yield energy on
oxidation, build new tissue, repair old tissue and play an essential
role in growth and nutrition. We know the oxidation of foods produces
heat thus maintaining the body temperature and providing kinetic energy
for work. Supplying bodily heat and energy and leaving waste materials
behind the food is «burned up» in combination with the oxygen to be
furnished by the air we breathe.
Scientists
have studied the problem of food classification for many years. Foods
are to be divided into two general classes. These are inorganic and
organic foods. The former class includes inorganic salts and water. The
latter class includes carbohydrates, fats and proteins. There are
accessory foodstuffs called vitamins which are essential to growth and
freedom from deficiency diseases1.
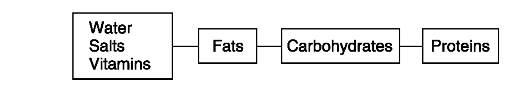
Fig. 10. Composition of food
The
overall composition of the body is about 59 per cent water, 18 per
cent protein, 18 per cent fat and 4.3 per cent minerals. At any time
there is less than 1 per cent carbohydrate in the make-up of the body.
These
substances which make up the body are not distributed equally in all
organs. For example, the percentage of water varies from 90-92 per cent
in blood plasma to 72-78 per cent in muscles, 45 per cent in bone, and
only 5 per cent in tooth enamel. Proteins are found most abundantly in
muscles. Fat is concentrated in the adipose (fat) cells under the skin
and around the intestines. Carbohydrates are found mainly in the
liver, muscles and blood. Carbohydrates are known as the chief source
of energy. The absence of carbohydrates upsets the fat and protein
metabolism. As for the minerals, high levels of calcium and phosphorus
form part of the bones and teeth, sodium and chloride are found mainly
in the body fluids (blood plasma and lymph), potassium is the main
mineral in mus- cles, iron is essential to red blood cells, and
magnesium is found throughout the body. These are the main minerals to
be supplied to the body as food but many other minerals are essential
to the human body in proportionally smaller amounts. They too must be
ingested with our food. Other types of food (vitamins) needed in very
small amounts for various functions of the body are essential.
You determine
how you will feel throughout each day by the type of breakfast you
eat. Your breakfast establishes how readily your body can produce energy
that day or, more specifically, the amount of sugar in your blood.
Your energy production, which corresponds to the quantity of sugar
available, determines how you think, act and feel. Energy is produced
in your body when sugar alone or sugar and fat together are burned
(oxidized).
It
should be noted, sixty more nutrients are needed to build health. For
example, cheese is an excellent source of protein but is largely
lacking in carbohydrate. Black currants provide a rich source of
ascorbic acid though they make little contribution to the calorie
intake of the body. Milk we usually use is regarded as the most
excellent food, for it contains much protein but little sugar.
Therefore,
it is neccessary to select a well balanced diet containing all the
essential nutritional substances to maintain health and to prevent
illness.
Notes
1. deficiency diseases авитаминоз
Упражнение 6. 1) Прочтите и переведите текст А. Абзац 3 переведите письменно. 2) Найдите в тексте А ответы на следующие вопросы и зачитайте их.
1.
Does the oxidation of foods produce heat or energy? 2. How is the food
burnt up? 3. What substance is the most abundant one in the body?
4. What substances are present in the body? 5. What is the percentage of different substances in different organs?
3) Найдите в каждом абзаце предложение, выражающее основную мысль абзаца.
Упражнение 7. Найдите в каждом ряду слово, синонимичное по значению первому слову ряда.
1.
to supply - to give, to furnish, to support, to provide; 2. to upset -
to set up, to disturb, to improve, to distress; 3. food - nourishment,
foodstuff, provision; 4. deficiency - need, luck, shortage,
imperfection;
5. to yield - to send, to give, to submit, to produce
Упражнение 8. Найдите в каждом ряду слово, противоположное по значению первому слову ряда.
1.
the former - the last, the latest, the latter; 2. general -
particular, local, definite, in detail; 3. deficiency - efficacy,
efficiency, efficient, effectiveness; 4. essential - unimportant,
unnecessary, vital, dispensable
Упражнение 9. Переведите на русский язык следующие предложения, определите функции инфинитива.
1.
The most convenient approach to understand metabolism is to examine
the properties of different sorts of foods. 2. It is interesting to see
the apparatus used to determine the caloric value of different
foodstuffs. 3. From the intestines glucose is absorbed and carried to
the liver to be converted into a form of carbohydrate, glycogen or
animal starch. 4. To reduce weight in an obese patient is an important
problem. 5. Fat yields 9 calories of heat per gram instead of the 4
calories to be yielded by sugar.
6. Muscle fibres have the power to store glycogen.
Упражнение 10. Переведите предложения с бессоюзными придаточными.
1.
Many substances the organism absorbs may be harmful, and many harmless
substances may be difficult for the organism to handle. 2. We know
proteins are absolutely essential to the proper nourishment of the
human body. 3. There is some evidence vitamin A plays a part to protect
the body against rickets. 4. It is known vitamin С
occurs abundantly in the juices of the citrus fruits, tomatoes,
germinated seeds, cabbages, carrots, beans, apples, turnips, rutabagas,
raspberries, liver. 5. The carbohydrates animals most commonly ingest
consist of a variety of sugars.
Упражнение 11. Переведите следующие предложения и определите функции слова for.
1. The young
animals are practically porkilothermic at birth and continue to be so
for some days. 2. They could not translate the article for it was
written in French. 3. Each organism establishes for itself a level of
nitrogen metabolism which is modified only with difficulty. 4.
Carbohydrates and fats are food substances which do not contain
nitrogen; they have high fuel value, and so are able to serve for the
production of heat.
Упражнение 12. Заполните пропуски подходящими по смыслу словами for, as, since, after, before.
1.
... it is commonly stated one of the chief distinctions between
animals and plants lies in the fact that the animals depend upon highly
organized foodstuffs ... their source of supply. 2. The protozoa are
considered ... very primitive organisms, rudimentary ancestors of
higher animals, ... they are unicellular. 3. ... the discovery of
streptomycin, a great deal of information has been accumulated
concerning its use. 4. Rats deprived of vitamin D ... 35 to 40 days
become unable to use their hind legs.
Упражнение 13. Переведите на английский язык.
1. Продукты питания, которые мы используем, можно разделить на два общих класса. Это органические и неорганические вещества. 2. Дополнительные вещества, которые должны присутствовать в нашей диете, - это витамины. 3. Отсутствие или недостаток углеводов в организме нарушает жировой и белковый обмен.
Часть II Слова к части II

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Прочтите следующие слова и переведите их на русский язык.
actually, crystalline, substance, combination, essential, series, difference, isolation, synthesis, diet, to produce, product, spinach, cream, capsule, calcium, protein
Упражнение 2. Найдите в данном ряду слово, перевод которого дан в начале ряда. Переведите данные слова.
1. вылечивать - curare, curative, curable, cure; 2. источник - sour, south, resource, source; 3. проводить - conclude, conduct, convey, convoy; 4. означать - means, meaning, mean, main
Упражнение 3. Прочтите
текст В (10 мин). 1) Выделите три основных момента, обсуждаемых в
тексте по теме «Витамины». 2) Найдите предложения, где: а) инфинитив
выполняет функцию определения; б) употребляется слово for; в) бессоюзные придаточные предложения. 3) Переведи- те предложения.
Text В
Vitamin
means life. The story of vitamins actually begins in 1911, when a
Polish chemist by the name of Kazimir Punk extracted from rice
polishings1 a crystalline substance. This substance was
capable to cure beri-beri. Analyses of these crystals revealed the
presence of nitrogen in basic combination, i.e. the «amino»-nitrogen;
Punk therefore called this substance «vita-mine». The root «vita»
indicates that the substance is essential to life and health. In this
way, the word vitamin was born. For four years before Punk's discovery a
series of studies had begun in the
Today
the successful isolation and synthesis of many of the substances has
proved that vitamins are organic chemical compounds to be present in
the diet for the maintenance of growth and health.
Vitamins
are substances to be found in certain foods which are necessary for
the growth, development and general health of the body. There are
several different kinds of these protective substances to be provided
in the diet. To make sure our bodies get all the vitamins they need, it
is best to include several different vitamin-containing foods in the
diet. Such foods include milk and many of the products made from
it, all the
green leafy vegetables like spinach, cabbage, lettuce, other fresh
vegetables, fruit and fruit juices, whole-grained cereals, eggs and a
number of others.
When
we plan a nutrition program for any person, young and old, well and
ill, we must know certain foods are the best sources each body
requires.
1. Vitamin A: fruits and vegetables, cream, butter or margarine, eggs and liver.
2. The В vitamins: yeast, liver, whole-grained breads and cereals, milk, meat.
3. Vitamin C: orange or grapefruit juice, any fresh raw fruit or vegetable, ascorbic acid tablets if needed.
4. Vitamin D: fish-liver oil or vitamin-D capsule.
5. Vitamin E: soy-bean oil, vegetables oils.
6. Vitamin
K: is produced by intestinal bacteria. The diet must be adequate in
milk and unsaturated fatty acids and low in refined carbohydrates;
intestinal bacteria are increased by eating yogurt.
7. Vitamin P (rutin): citrus fruits, especially lemons.
8. Calcium: milk, yogurt.
9. Phosphorus: milk, eggs, cheese, meat.
10. Iron: liver, yeast, meat, bread and cereals.
11. Proteins: yeast, milk, yogurt, cheese, meat, fish, eggs.
12. Liquids: milk, fruit, juices, soup, water.
Experts
in the study of foods are constantly conducting experiments. They are
making their discoveries public from time to time for such knowledge
enables us to select the proper foods in order to protect us against
the diseases.
Notes
1. rice polishings шелуха риса
Упражнение 4. 1) Найдите в тексте предложения, более полно выражающие мысль данных суждений, и прочтите их.
1. К. Punk has extracted a substance capable to cure beri-beri. 2. Vitamins are organic chemical compounds to be present in the diet. 3. Vitamins are found in certain foods. 4. Certain foods are the best sources each body requires. 5. Vitamin К is produced by intestinal bacteria.
2) Передайте основное содержание текста, используя предыдущее упражнение в качестве плана.
Часть III
Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 10
Упражнение 1. Найдите и переведите предложения, в которых инфинитив выполняет роль определения.
1.
The secret of a proper diet depends much on the ability of the cook or
dietician to prepare and serve meals which are palatable and tasty to
the individual. 2. Average intake of protein to maintain nitrogen
equilibrium is
(Ответ: 1, 2, 3, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 25 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 2. Найдите и переведите бессоюзные придаточные предложения: а) определительные; б) дополнительные.
1. When the man smells something he likes to eat, the gastric juice is poured out in large quantities. 2. We know vitamin B1
is widely distributed in nature occurring in most foods. 3. The cells
select the amino acids they need and use them to construct new body
tissue and such vital substances as antibodies, hormones, enzymes and
blood cells. 4. The food we take and the air we breathe often contain
poisonous substances and pathogenic microorganisms. 5. Chemical studies
have shown vitamin D is exceedingly stable as regards oxidation and
heating. 6. The four parts the pituitary consists of perform several
functions and produce several secretions.
(Ответ: a) 1, 3, 4, 6; б) 2, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 32 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 3. Укажите, в каких предложениях for: а) союз; б) предлог. Переведите эти предложения.
1. The ordinary intake of vitamin A by most adults is sufficient to maintain their health in good condition for administration of this vitamin decreases the susceptibility to the «common cold» (or lessens its severity). 2. Scientists have studied the deficiency diseases for many years. 3. The importance of vitamin D for growth and nutrition was established as a result of a series of discoveries. 4. The cell is not isolated
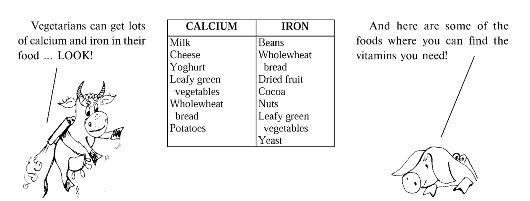
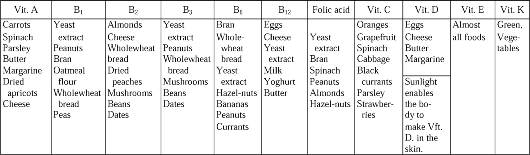
Fig. 11. Vitamins you need and the food where you can find them
from the outer world by its membrane, for it is entirely dependent on this outer world. 5. Cotton thread is used for ligatures.
(Ответ: a) 1, 4; б) 2, 3, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 37 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 4. Переведите производные от данных слов.
1. oxide - окислять, окисление, кислород, насыщать кислородом; 2. provide - обеспеченный, при условии, что..., временный; 3. distribute - распределение, распределительный
(Ответ: 1. oxidize, oxidation, oxygen, oxygenate; 2. provided, provided that, provisionary; 3. distribution, distributing.)
Упражнение 5. Дайте синонимы к следующим словам.
1. to supply; 2. to upset; 3. foods; 4. deficiency; 5. to yield (Ответ: 1. to furnish, to provide; 2. to disturb, to distress; 3. foodstuffs; 4. lack, shortage; 5. to produce.)
Упражнение 6. Дайте антонимы к следующим словам.
1. general; 2. deficiency; 3. around; 4. essential
(Ответ: 1. particular; 2. efficiency; 3. within; 4. unimportant, unnecessary.)
Упражнение 7.
1. Расскажите, какие вещества входят в состав пищи, используя рис. 10 на с. 128.
2. Расскажите, в каких продуктах содержатся те или иные витамины, используя рис. 11 на с. 135.
LESSON ELEVEN
THE EXCRETORY ORGANS
1. Сложное подлежащее (? 27)
2. Функции и перевод слов as well as, as well (? 40)
Часть I
Слова к части I

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Переведите следующие предложения, определите сложное подлежащее.
1.
The body is known to utilize six kinds of food-stuffs - carbohydrates,
proteins, fats, water, mineral salts and vitamins. 2. When burned, the
carbohydrates, proteins and fats are sure to yield a certain definite
and measurable amount of heat energy. 3. Many substances which are
readily absorbed by the organism prove to be harmful, and many harmless
substances prove to be difficult for the organism to absorb. 4.
Proteins are found to be absolutely essential to the proper nourishment
of the human body. 5. Vitamin С appears to be
lacking in seeds, white bread, fats, yeast, purified proteins and
carbohydrates. 6. Vitamin D is known to be the antirachitic substance.
Упражнение 2. Переведите следующие предложения, определите, какую функцию выполняют слова as well и as well as.
Упражнение 3. Дайте исходные слова к следующим производным. Переведите их.
various, harmful, excretory, namely, greater, evaporation, frequency
Упражнение 4. Познакомьтесь со значениями данных ниже приставки over и суффикса ful. Образуйте слова согласно модели. Прочтите и переведите их.
1. over- + различные части речи = соответствующая часть речи со значением избыточности. Соответствует русским приставкам сверх-, над-, пере-: heating нагревание - overheating перегрев.
to work, busy, to feed, to build, work, production, weight
2. Существительное (глагол) + -ful = прилагательное со значением «обладающий качеством, выраженным основой»: harm вред - harmful вредный.
success, care, beauty, joy, use, help
Упражнение 5. Прочтите и переведите данные гнезда слов.
1.
empty, to empty, emptiness; 2. average, to average; 3. vapour, to
evaporate, evaporation, evaporable; 4. frequent, frequency, frequently;
5. urea, urine, urination, urinary, ureter, urethra, urology, uremia
Упражнение 6. Просмотрите текст А, разделите его на 3 части и назовите тему каждой части.
Text A Excretory Organs
1. Various
harmful and unnecessary substances are continually being formed in the
human body. These substances entering the blood are eliminated from
the body by the excretory organs, namely the kidneys, the skin and the
lungs; the latter are passing out carbon dioxide and water vapour. The
quantity of water lost through the lungs probably varies within small
limits only. The quantity lost through the sweat varies, of course,
with temperature as well as with exercise. It may be said that the
amounts of water secreted through the kidneys and skin are of an
inverse proportion to each other, that is, the greater the amount lost
through the skin, the less will be secreted by the kidneys.
2. Through
these three organs but mainly through the kidneys blood is being
continuously depleted of water and the loss must be made up by the
ingestion of new water.
3. Most
of the body wastes are found to be eliminated in the urine by the
urinary organs. The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters,
urinary bladder and urethra. Urine is formed in the kidneys, which are
the main organ of excretion. It then passes through the ureters into
the urinary bladder which serves as a reservoir. The bladder is emptied
through the urethra, which leads to the exterior of the body. The
wastes are excreted as urine, which is normally composed of
approximately 96 per cent water, plus urea and various salts. The
density of urine appears to
vary from 1.015 to 1.020; the pH averages about 6. The healthy adult seems to excrete an average of about
4. The
combination of a warm, rainy day, increased liquid intake as well as
moist air that prevents evaporation from the skin is likely to result
in great frequency of urination.
5. The
urine is being formed in the kidneys from many waste and harmful
substances contained in the blood. Blood flows into the kidneys through
the blood vessels. In the kidneys the blood is cleansed of these
substances. Thus, the blood leaving the kidneys is pure while urine
formed in the kidneys flows down special ducts - the ureters, passing
into the bladder from which it is eliminated.
6. An
excretory function is also performed by the skin. The skin being the
cover of the body protects it from harmful external influence and
serves at the same time as an excretory organ passing the sweat out.
7. Sweat
is formed in tiny perspiration glands found in the skin. It consists
of water in which substances similar to those in the urine are formed
but in smaller quantities. The evaporation of perspiration is known to
cool the body and protect it from overheat as well.
Упражнение 7. Прочтите и переведите текст А. Первый абзац переведите письменно. Найдите и запомните значение слов the latter, through, only, that is, the greater ... the less.
Упражнение 8. Найдите в тексте А ответы на следующие вопросы и прочтите их.
1.
How are harmful substances eliminated from the body? 2. What organs
pass out carbon dioxide and water vapor? 3. What are the organs of the
urinary system? 4. How is water eliminated from the body? 5. When is
the volume of urine increased or reduced? 6. What process takes place
in the kidneys?
Упражнение 9. Найдите в каждом ряду слово, противоположное по значению первому слову ряда.
1.
various - sum, some, same, seem; 2. the latter - former, the former,
formal; 3. greater - lessen, lesson, lesser, less; 4. to increase -
to decrease, to decide, to decree, to demand; 5. to cool - to want, to water, to warm, to warn
Упражнение 10. Найдите в каждом ряду слово, перевод которого дан в начале ряда.
1. внешний, наружный - exterior, interior, exteriorly, exteriority; 2. в норме - normal, normality, normally; 3. посредством, путем - throughout, through, though, throw; 4. очищать, дезинфицировать - to clean, to claim, to cleanse, to clear
Упражнение 11. Прочтите следующие предложения. Определите, какой частью речи являются выделенные слова. Переведите предложения.
1. Most of the body wastes are eliminated in the urine by the urinary organs. 2. The bladder is emptied through the urethra which leads to the exterior of the body. 3. The wastes are excreted as urine which is normally composed of approximately 96 per cent of water plus urea and various salts.
Упражнение 12. Определите, чем выражено подлежащее в следующих предложениях. Переведите данные предложения.
1.
The rate of urinary flow is known to be increased by various agents
known in medicine as diuretics. 2. Three hours after injection 38-45%
of the injected mercury was found in the kidneys. 3. Renal tubular
excretory transport of selected sulfonamides is assumed to require a
physicochemical interaction. 4. Under these conditions it was difficult
to estimate the actual rate of tubular excretory transport. 5. The
bladder is more likely to be affected with a direct pus-forming
infection than by any other disease. 6. It is found that the process of
urine secretion goes on constantly at the rate of about a drop every
thirty seconds from each kidney.
Упражнение 13. Переведите следующие предложения со словами as well as и as well.
1.
The most important function of the kidneys is to remove urea from the
blood as well as to maintain the proper balance of water, salts and
acids in the body fluids. 2. Urinalysis is an examination of urine to
determine the presence of abnormal elements as well as the presence of
diabetes mellitus. 3. The purpose of this study is to determine the
simultaneous rates of bronchial and renal urea excretion as well. 4.
Any doc-
tor is responsible for the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases as well.
Упражнение 14. Нарисуйте схему органов выделения. Опишите систему органов выделения, используя схему.
Часть II Слова к части II

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Прочтите и запомните перевод следующих слов и словосо- четаний. Переведите предложения с этими словами и словосочетаниями.
1. except (that, for) за исключением (того, что); exception исключение; with few exceptions за редким исключением: The elements which compose the urine, with few exceptions, exist in the blood plasma.
2. regard n отношение; взгляд; in (with) regard to относительно, в отношении; regarding что касается, с точки зрения; regardless независимо от, несмотря на; v считать, рассматривать: Kidney must be regarded as the chief controller of chemical balance in the organism.
Упражнение 2. Напишите исходные слова к данным производным. Переведите все слова на русский язык.
constituent, precisely, glomeruli, distinguishable, regardless, excessive, composition, exception
Упражнение 3. Прочтите текст В (10 мин). 1) Разделите его на 2 части и назовите тему каждой части. 2) Найдите предложения: а) со сложным подлежащим; б) со словами as well, as well as. 3) Переведите эти предложения.
Text В
The Excretory Function of the Kidney
It
has long been known that the kidney does not manufacture fully the
elements which compose the urine. It is known only to extract them
unchanged from the blood plasma where, with very few exceptions, they
already exist. In other words, the urinary function is the excretion,
but the kidney is found to exercise a choice among the numerous organic
substances present in the circulating blood. Some substances, such as
the proteins, are wholly retained in the organism, although the blood
plasma contains a high concentration of them (70 to
Finally,
we may ask ourselves what internal instrument may change at every
moment the rate at which each constituent of the blood plasma is taken
away by the kidney.
The
basic instrument of this mechanism seems to be the nephron. Each
kidney is formed of about a million nephrons, joined by an interstitial
tissue through which the blood vessels as well as nerves pass. Thus
the nephron is the morphological and functional unit of the system
determining the composition of the urine. Its structure is not very
simple. The glomerulus, a small bundle of arterial capillaries enclosed
in a small round capsule, forms the head of the nephron. Although the
glomeruli are small and hardly distinguishable by the naked eye1,
the total quantity of blood which passes through them every minute is
very great: over a litre for the two kidneys of an adult, which
is a quarter of the total blood distributed to all the rest of the organism in the same time.
This is the first stage in the production of urine, known as glomerular filtration.
Physiologically
the kidney must not be regarded as just an organ for the formation of
urine, wastes. The kidney appears to be the chief controller of the
delicate chemical balance necessary to life.
Notes
1. by the naked eye невооруженным глазом
Упражнение 4. Найдите в тексте В предложения, более полно выражающие мысль данных суждений, и прочтите их.
1.
The kidney doesn't manufacture the elements which compose urine. 2.
The urinary function is that of excretion. 3. Some substances are
retained in the organism. 4. Penicillin is eliminated through the
urine. 5. The basic instrument of the kidney is the nephron.
Часть III
Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 11
Упражнение 1. Найдите и переведите предложения со сложным подлежащим.
1.
The chief function of the kidneys is to separate fluid and certain
solids from the blood. 2. The excretion of urine is thought to be
possible by the selective action of the cells of the kidney tubules. 3.
When the kidneys fail to act solid waste substances accumulate in the
blood. 4. The formation of urine is found to begin in the glomerulus as
water salts, sugar, urea and other wastes. 5. Streptococci do not seem
to cause glomerular inflammation by direct invasion. 6. After the
first two weeks of acute nephritis patients usually appear to make a
complete recovery.
(Ответ: 2, 4, 5, 6. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 27 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 2. Укажите, в каких предложениях as well as, as well: а) составной союз; б) наречие. Переведите предложения.
1.
Acute glomerular nephritis may involve various systems of the body as
well as the glomerular tufts. 2. Specific gravity is a measurement that
reflects the amount of wastes as well as minerals in the urine. 3.
Acids as
well as other
substances which the body does not need are secreted into the distal
renal tubules from the blood stream. 4. Drugs can be obtained from
plants, animals and chemical substances as well. 5. While examining a
patient the doctor was asking him about his previous and present
condition as well.
(Ответ: а) 1, 2, 3; b) 4, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 41 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 3. Переведите на английский язык производные от данных слов.
1. excrete - выделение, выделительный, экскреция; 2. active - активность, активно, деятельность; 3. constitute - составная часть, телосложение; 4. urine - мочевой, мочеиспускание, урология; 5. sweat - потеть, потение, потный, потовые (железы)
(Ответ: 1.
excretion, excretory, excretion; 2. activity, actively, activities; 3.
constituent, constitution; 4. uric (urinary), urination, urology; 5.
to sweat, sweating, sweaty, sweat (glands).)
Упражнение 4. Дайте синонимы к следующим словам.
1. to eliminate; 2. waste products; 3. manner; 4. to take place; 5. quantity (Ответ: 1. to excrete; 2. waste matter (wastes); 3. way; 4. to occur; 5. amount.)
Упражнение 5. Образуйте словосочетания, используя слова из пунктов а) и б). Переведите их.
а) 1. to eliminate; 2. to carry out; 3. to excrete; 4. to get rid of; 5. to throw out; 6. excretory; 7. activity (of);
б) 1.
the excess of water (constituents); 2. organ(s); 3. action; 4. the
kidneys and skin; 5. sweat glands; 6. muscular; 7. the function; 8.
waste products
(Ответ: 1-1, 8; 2-1, 7, 8; 3-1, 8; 4-1, 8; 5-1, 8; 6-2, 3; 7-4, 5, 6.)
LESSON TWELVE
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
1. Сложное дополнение (? 26)
2. Составные союзы either ... or; neither ... nor; so ... that; not only ... but (? 40)
Часть I
Слова к части I

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Переведите следующие предложения с конструкцией «слож- ное дополнение» на русский язык.
1. We know nephron to be the histological kidney unit.
Упражнение 2. Замените следующие придаточные предложения конст- рукцией «сложное дополнение».
1.
We know that glomeruli are absent in certain fishes. 2. Most
physiologists believe that the phenomenon of urinary secretion is due
to filtration of the non-colloid constituents of the plasma through the
glomerulus. 3. Some investigators thought that the rate of flow was a
paramount factor governing renal secretion. 4. The doctor supposed that
the rise of blood pressure caused increased urination. 5. Scientists
consider that a balanced diet is necessary for everybody.
Упражнение 3. Прочтите и переведите следующие предложения с со- ставными союзами either ... or, neither ... nor, not only ... but (also), so ...
that.
1.
Experimental work has shown that removal of one-half, two-thirds and
sometimes three-fourths of the kidney substances in the dog produces
changes neither in urinary volume nor in urinary nitrogen. 2. The
lecturer demonstrated that in the frog's kidney indigo carmine, neutral
red and ferric ammonium citrate not only appear in the glomerular
filtrate but also in proportion to their concentrations in the serum.
3. The decreased rate of glomerular secretion results in its slower
passage through the tubules so that water absorption is more complete.
4. The percentile chloride may either increase or decrease, but the
total excretion is always greater.
Упражнение 4. Заполните пропуски составными союзами either ... or, neither ... nor, not only ... but, so ... that.
1. The cations К and Ca induce diuresis when administered ... together ... in succession. 2. The kidney is an organ capable of altering the
quantity and quality of the urine secreted ......the water balance and
osmotic
relations in the blood and tissues are kept within optimal ranges. 3.
The functions of the kidney are ... numerous ... they require a high
degree of correlation as well. 4. ... our group ... group 5 decided who
will be the first to begin the experimental work on glomerular
filtration.
Упражнение 5. Отработайте чтение следующих слов и словосочетаний.
Упражнение 6. Образуйте слова согласно модели и переведите их. Запомнить значение суффикса -ize и приставки inter-.
1. Прилагательное, существительное + -ize (-ise) = глагол: oxide окись - to oxidize окислять.
active, material, popular, crystal, immune, special
2. inter- + существительное, прилагательное, глагол = производное слово, обозначающее взаимодействие, взаимовлияние, положение между...: to act действовать - to interact взаимодействовать.
change, to connect, coastal, national, action, auricular, cellular, clavical
Упражнение 7. Прочтите и переведите данные гнезда слов.
1.
to act, action, activity, activities, to activize; 2. to emerge,
emergence, emergency, emergent; 3. to fail, failure, failing; 4. to
disturb, disturbance, disturbed; 5. to suffice, sufficient, sufficiency, sufficiently
Упражнение 8. Прочтите и переведите следующие словосочетания.
to
put into action, in case of emergency, emergency case, movable kidney,
heart failure, failing sight, to measure out a spoonful of medicine
Упражнение 9. Просмотрите текст А. Разделите текст на смысловые части.
Text А
Endocrine Glands
1.
There are two organ systems - the nervous system and the endocrines -
which coordinate the activities of all others. Almost nothing can
happen to the body anywhere without appropriate response either motor
or perceptual, voluntary or involuntary. Similarly, various parts of
the endocrine system act upon each other and other organs, stimulating
them to do their special jobs. Thus, the thyroid gland stimulates the
metabolism of all bodily parts. The adrenal medulla mobilizes the
activities of many organ systems in case of the emergency. And the
adrenal cortex exercises control over many body functions, so important
that its removal results in
failure of the functions and
the
death of the animal. 2. Endocrine glands or glands of internal
secretion are ductless glands, that is, they empty their secretions -
chemical substances called hormones (from the Greek word «hormao» -
excite) - directly into the blood stream. The hormones are carried
through out the organism with the blood and are delivered to various
organs whose activity they either stimulate or depress. Neither single
hormone nor endocrine gland acts wholly by itself at any time.
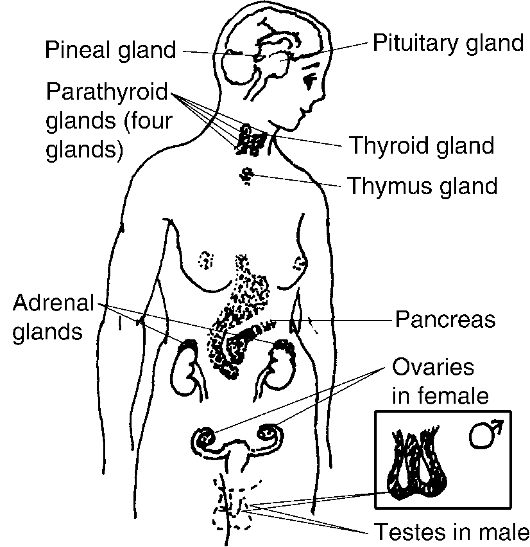
Fig. 12. The endocrine system
3. We
know hormones to play a very important part in the organism. Many of
them affect metabolism and the activity of the cardiovascular and other
systems. A disturbance in the activity of the endocrine glands is
accompanied by changes throughout the organism. These changes may be
not only due to an increase in the function of a gland (hyperfunction)
but to a decrease (hypofunction).
5. The
functions of all the endocrine glands are interconnected so that the
glands make up a single system. Physiologists consider the hypophysis
to be the chief gland of this system; they consider it to produce
special substances which stimulate the activities of other endocrine
glands.
6. The
activities of endocrine glands are regulated by the nervous system. It
is known to exercise direct control over the endocrine glands through
the nerves and neurohumoral control, particularly through the
hypophysis. The hormones in their turn affect the functions of the
different parts of the nervous system.
Упражнение 10. Прочтите и переведите текст А. Первый абзац переведите письменно.
Упражнение 11. Найдите в тексте ответы на следующие вопросы и зачи- тайте их.
1. The functions of various endocrine glands are different, aren't they? What are they? 2. Is the disturbance in the activity of the endocrine glands accompanied by any changes throughout the organism? 3. What is hyperor hypofunction? 4. Why is hypophysis considered the chief gland of the endocrine system? 5. How do the endocrine and nervous systems interact?
Упражнение 12. Найдите ключевые предложения в каждой смысловой части текста А и выпишите их.
Упражнение 13. Найдите в каждом ряду слово, перевод которого дан в начале ряда.
1. деятельность - activator, activities, activation, activity, activist;
2. подобным образом, также - similarity, similar, simple, similarly;
3. таким образом, так - so, then, thus, actually; 4. влиять на... - to effect, to defect, to affect
Упражнение 14. Прочтите и переведите данные предложения. Определите, какой частью речи являются выделенные слова.
1. Thus the thyroid gland stimulates metabolism. 2. Hormones affect metabolism and the function of the cardiovascular system. 3. The functions of endocrine glands are interconnected. 4. The nervous system exercises direct control over the endocrine glands through the nerves and neurohumoral control. 5. The hormones either stimulate or depress the activity of various organs. 6. The activities of endocrine glands are regulated by the nervous system.
Упражнение 15. Переведите следующие предложения. Определите функции инфинитива
1.
The methods developed to establish special aspects of endocrinology
have become diversified and complicated. 2. The existence of many
hormones to be discussed must be regarded as probable rather than
demonstrated with certainty. 3. The hypophysis is believed to be the
chief endocrine gland. 4. The chief action of the thyroid hormone is to
accelerate all oxidations, particularly those of fat and protein. 5.
The discharge of thyroid hormone appears to be guided by a thyrotropic
pituitary hormone. 6. The scientists believe insulin and anterior
pituitary hormones to exert contrary actions on the blood sugar level.
Упражнение 16. Переведите следующие предложения. Запомните значение парных союзов either ... or, neither ... nor, so ... that, not only ... but.
1.
The observations of surgeons on thyroid deficiency revealed that
internal secretions are not only necessary for proper growth and
nutrition but for normal mental development as well. 2. An excess of
the somatotropic hormone, either due to hypersecretion or injection of
extracts, causes gigantism and leads to acromegaly in adults. 3. The
molecular weight of insulin is so great that prospects of its synthesis
seem very remote. 4. While asked the student could neither describe
nor show the pineal gland in figure 12.
Упражнение 17. Переведите данные предложения на английский язык письменно.
1. Нервная и эндокринная системы координируют и стимулируют деятельность организма. 2. Эндокринные железы не имеют про- токов и выделяют свой секрет непосредственно в кровь, которая разносит его по организму. 3. Снижение функции или понижение активности эндокринных желез вызывает изменения в работе всего
организма. 4. Деятельность всех эндокринных желез взаимосвязана и регулируется гипофизом. 5. Нервная система контролирует работу эндокринных желез.
Упражнение 18. Опишите органы эндокринной системы, используя текст и рис. 12.
Часть II Слова к части II

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Прочтите и переведите следующие слова.
hypothalamus,
anterior, intermediate, posterior, microscope, fibre, secretion,
circulation, neurons, neurohumoral, gigantism, acromegaly, oxitocin, to
intensify
Упражнение 2. Найдите в данном ряду слово или словосочетание, значение которого дано в начале ряда.
1. поскольку - in so far as, so far as, as far as; 2. серия, ряд - row, line, series, set; 3. то есть - all that, so that, that is, that is why
Упражнение 3. Найдите в данном ряду слово или словосочетание, синонимичное данному в начале ряда.
1.
fairly - rather, too, enough, actually, completely; 2. to break up -
to believe in, to end, to divide into... ; 3. adults - teenagers,
children, the old, grown-ups; 4. insufficient - enough, lacking,
deficient, excessive
Упражнение 4. Запомните значение сочетаний со словом that.
that is the point в этом суть дела
that is to say то есть
that is why вот почему
now that теперь, когда
Упражнение 5. Прочтите текст В (10 мин). 1) Разделите его на три смысловые части. 2) Найдите предложения: а) с конструкцией «сложное
дополнение»; б) с парными союзами either...or, neither...nor, so ... that, not only...but. 3) Переведите эти предложения.
Text В
The Hypophysis (the Pituitary)
We know the hypophysis to be a small oval body weighing about
The
hypothalamus has been found to secrete special substances which regulate
the secretion of the hypophysical hormones. The activities of the
other endocrine glands are thus subject to neurohumoral regulation
through the hypophysis.
Disfunction
of the anterior lobe of the hypophysis is accompanied by changes
throughout the organism. For example, excessive secretion of the growth
hormone in childhood results in gigantism. Such people may grow to a
height of 2.5-2.6 m. Excessive secretion of this hormone in adults
results not only in excessive growth of the bones of the face, fingers
and toes, but in enlarged nose, tongue and certain other organs. This
disease is called acromegaly. Insufficient secretion of the growth
hormone in childhood is accompanied by retarded growth (dwarfism). It
is a relatively rare condition associated with either early atrophy or
absence of the anterior lobe.
The
posterior lobe of the hypophysis secretes oxytocin and vasopressin.
Physiologists consider oxytocin to intensify the contractions of the
uter-
ine
muscles and it is therefore used to boost weak labour. We know
vasopressin to cause constriction of the blood vessels, especially
those of the uterus.
Упражнение 6. Прочтите следующие суждения. Найдите в тексте В пред- ложения, более полно выражающие мысль данных суждений, и прочтите их.
1.
The hypophysis is connected with hypothalamus. 2. There are two lobes
in the gland. 3. Hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system of blood
vessels supplies blood to the anterior lobe of the hypophysis. 4.
Hypophysis regulates the activity of other endocrine glands. 5.
Disfunction of the anterior lobe of the hypophysis is accompanied by
changes of different kind throughout the organism.
Часть III
Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 12
Упражнение 1. Найдите и переведите предложения со сложным дополне- нием.
1.
Thyroxine is necessary in the body to maintain a normal level of
metabolism in all body cells. 2. Parathyroid hormone causes calcium to
leave bone tissue and enter the blood stream. 3. Removal of the thymus
gland is found to be helpful in treatment of muscular-neurological
disorders. 4. Cells need oxygen to carry on metabolic processes. 5. We
know the pituitary gland to be also called the hypophysis. 6. Pituitary
growth hormone acts on bone tissue to accelerate its growth in the
body.
(Ответ: 2, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 26 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 2. Укажите, в каких предложениях использованы составные союзы.
1. Insulin is necessary in the blood stream so that sugars can pass from the blood into the cells of the body.
hypofunction
of endocrine glands. 6. Overproduction of glucocorticoids leads not
only to obesity, moonlike fullness of the face but also to elevated
blood sugar, high blood pressure and weakness (fatigue).
(Ответ: 1, 3, 5, 6. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 40 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 3. Расшифруйте данные сокращения. i., f., oz(s), g., lb., 1., ml., cm.
(Ответ: inch, foot (pl. feet), ounce(s), gramme (gram), libra (лат. для pound), litre, millilitre, centimetre.)
Упражнение 4. Опишите функции эндокринных желез, используя рис. 12.
LESSON THIRTEEN
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
1. Герундий (? 23)
2. ing-формы в различных функциях (? 24)
Часть I
Слова к части I

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Переведите следующие предложения с герундием.
1.
Stimulating the somatotropic hormone upon growth can be partly
correlated with its acceleration of metabolism. 2. Certain researchers
believe that the hypophysectomized animal differs essentially from the
normal in that it has lost the power of converting fats to
carbohydrates.
are regarded as basic metabolic hormones necessary for maintaining general nutritive conditions.
Упражнение 2. Найдите ing-формы в следующих предложениях. Переведите предложения.
1.
Thyrotropic hormone is of considerable importance not only in
regulating the thyroid secretion but in accounting for many metabolic
effects. 2. Related injections of extracts containing ketogenic
hormones cause fat infiltrations of liver, reduction in fat of other
tissues and ketosis. 3. The stimulating action of the somatotropic
hormone upon growth can be partly correlated with its acceleration of
metabolism. 4. Injecting hormones into normal young animals results in
animals of large size and precocious sexual development. 5. Acromegaly
and gigantism produce overgrowing of bones and there may be an actual
lengthening of the spinal column.
Упражнение 3. Отработайте чтение следующих слов.
Упражнение 4. Прочтите и переведите следующие словосочетания.
1.
to react upon each other, reaction power, the reaction of eye to the
light, Wasserman reaction, reaction of sensibility; 2. to feel one's
pulse, to feel like doing smth, to feel tired, to feel fine, a feeling
of danger; 3. to treat with penicillin, surgical treatment, treatment
by exercises, to try many treatments for pneumonia, to be under
treatment
Упражнение 5. Просмотрите текст А и сравните по содержанию обе части текста.
Text A
The Nervous System. The Brain and Nerves
1. Nerves
lead from the spinal cord or from the brain to each part of the body.
Then they lead from each part of the body back to the brain or spinal
cord. The brain and spinal cord are the centres of this system of
nerves.
2. All parts of your body are connected by nerves. The nerve cells with their fibres make up the nervous system. When we study one
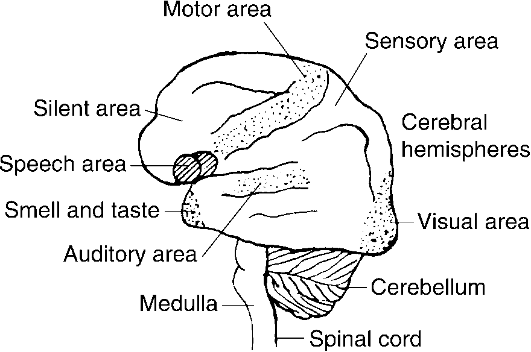
Fig. 13. Diagram to illustrate some of the more important centres in cerebral hemispheres
nerve
cell, we see that it has a long fibre at one end and short fibres at
the other. The nerve cells send impulses to each other by means of the
fibres at their ends. These fibres do not actually touch but are so
close to each other
that an impulse can travel from one fibre to another. Physical agents
become stimuli for nerve terminals by transferring energy from the external world to the nerve terminals.
3. Thus
all nerve cells connect with each other. There are millions of these
connecting nerve cells. Thus a stimulus from any part of the body can
reach any other part of it. In the spinal cord and brain, the nerve
cells connect with each other by their connecting fibres. Outside the
spinal cord and brain, certain long fibres are grouped together forming
nerves. Each nerve is made up of thousands of nerve fibres together in
a bundle, as a cable is made up of separate wires.
The Brain Centre of the Nervous System
4. We
know the nerves to carry impulses to the brain. We know that the brain
sends these impulses along so that they go to the right place. The
brain is made up of three parts. The cerebrum sits like a cap on the
cerebellum. And the medulla is that long portion connecting the brain
with the spinal cord. The cerebrum has certain parts that do certain
work. Studying human beings with accidential injuries of brains helped
scientists to get information about these areas. For instance they have
discovered that the part for thought, memory, and feeling is found in
the front of the cerebrum. The part for hearing is found at the side of
the cerebrum, and the part for sight in the back of the cerebrum.
5. Many
experiments have shown that the brain is the centre of feeling and
understanding. The nerve cells in the brain can be «put to sleep» with
ether or other anesthetics. Then the brain does not feel any impulses
from the part being operated on. Sometimes the nerve cells near the
part of our body being treated may be deadened by novocaine, as
when
the dentist pulls a tooth. What the novocaine does is preventing the
impulses from getting to the brain from the nerve in the tooth.
6.
The cerebellum is the centre for making your muscles work as a team.
The medulla is the centre of certain of our most important acts:
breathing and heartbeat, on which life itself depends. The medulla is
also capable of controlling acts such as swallowing and yawning.
Упражнение 6. Переведите письменно абзацы 5 и 6 текста А.
Упражнение 7. Найдите в тексте А ответы на следующие вопросы и зачи- тайте их.
1.
What do we know about the structure of the nerve cell? 2. How does a
nerve react to a stimulus? 3. How many parts is the brain made up of?
4. What have scientists found out about the brain?
Упражнение 8. Прочтите и переведите следующие предложения, выбрав одну из данных ing-форм, подходящую по смыслу.
reacting, responding, combining, descending, controlling, containing, cooling, warming
Упражнение 9. Переведите следующие предложения c ing-формами на
русский язык, определите их функции.
1.
The intensity of an impulse arising during the relatively refractory
period is less and it decreases when passing through a depressed
stretch of nerve. 2. Functional nerve block can be produced without
cutting or injuring the fibres permanently. 3. Among the outstanding
symptoms found in cerebellar disease, ataxia (i.e. the inability of
maintaining equilibrium through failure of muscular coordination)
received a great deal of attention. Thus, a cigarette may be raised to
the eye or a spoon may reach the ear and the patient (with cerebellar
disease) is quite incapable of easily touching the tip of his nose when
the eyes are closed. 4. Extensive pathological changes or injury of the
brain, including the frontal
lobes,
cause both in man and animal disturbances and abnormalities such as
torpidity, inertia, inattention, indifference to surroundings, etc.
Часть II Слова к части II

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Прочтите и переведите следующие слова.
classification, to classify, equilibrium, cutaneous, to distribute, corpuscle, reflex, stimulus
Упражнение 2. Найдите в данном ряду слово, синонимичное данному в начале ряда.
1.
sense - feeling, sense organs, faculty, sensation; 2. to excite - to
cause, to respond, to arouse, to stimulate; 3. completely - partially,
always, fully, at last, to the end; 4. to augment - to decrease, to
increase, to stop, to stimulate
Упражнение 3. Найдите слово, перевод которого дан в начале ряда.
1. знакомый - famous, known, near, close, familiar; 2. ощущение, восприятие - sense, sensibility, sensation, sensationism; 3. усталость - hunger, thirst, fatigue, tired; 4. спускаться - to ascend, to come down, to go down, to descend
Упражнение 4. Прочтите текст В (10 мин). 1) Скажите, какие органы чувств описаны в тексте. Опишите механизм мышечных ощущений. 2) Найдите и переведите предложения с ing-формами.
Text В Classification of the Senses
Sense organs are specialized endings of the sensory division of the peripheral nerves.
We
are commonly thought to possess five senses. Actually, there are many
more. We may classify them as follows: 1) the cutaneous senses -
touch,
heat, cold and pain; 2) the deeper senses - pressure and muscle sense;
3) the internal senses, or senses from the internal organs of the
body; 4) the special senses, or those in which the receptors lie in
special organs - sight, hearing, equilibrium, taste and smell; and
finally 5) the general body senses - hunger, thirst, fatigue, sexual
sensation, etc.
The cutaneous senses. There
are said to be 500,000 touch receptors in the skin. They are unevenly
distributed, being most numerous in the finger tips, lips and tongue,
and least numerous on the back. Their receptors are specialized
structures called Meissner's corpuscles. The sense-organs for cold
constitute 150,000 receptors; they are the endorgans of Krause. Warmth
has about 16,000 receptors, the end-organs of Ruffini; and pain has
some 3,000,000 receptors. Pain receptors, however, are not specialized;
they are simply the naked ends of the pain nerves, somewhat branched
at their terminals. The Pacinian corpuscles are the receptors for
pressure, and the muscle spindles for muscle sense.
Proprioception. Everyone
knows what pain and touch are, but proprioception («muscle sense») may
be less familiar. It is a very important sense since it is the sensory
link of a reflex controlling muscle tone and contraction; and it also
gives the brain important information about the location or position of
the limbs. Muscle spindles are tiny, spindle-shaped structures
scattered throughout muscles, and they are most numerous around the
tendons and joints. The stimulus exciting them is muscle contraction
and joint movement. Since muscles are never completely at rest - one
portion or another is contracting all the time - there is a constant
flow of nerve impulses into the spinal cord over the muscle sense
fibres. Any activity of muscles, such as walking, augments the flow. Let
us analyze the fact of walking. One foot is lifted from the ground,
moved forward, and, as it descends, the weight of the body is shifted
to this foot. The other foot is then lifted, moved, etc. Once a child
has learned to walk, he accomplishes this action not noticing it; it is
done reflexly, and this reflex is one in which the sensory information
comes over the fibres of proprioception.
At any
instant of time, the spinal cord is receiving information as to the
immediate, present location of the feet and legs, and it is sending
out, over motor fibres, impulses which continue the activity. At any
time, a person knows, without looking, approximately where his feet are
and where his legs are, since this information is also being sent to
the brain.
Упражнение 6. Прочтите данные суждения. Найдите в тексте предложения, более полно выражающие мысль данных суждений.
1.
There are more senses than we are commonly thought to possess. 2.
Besides touch receptors there are cold, warmth and pain receptors.
3.
Proprioception is the sensory link of a reflex. 4. Muscle contraction
and joint movements excite muscle spindles. 5. Walking augments the
flow of impulses. 6. The spinal cord and the brain regulate motor
activity.
Упражнение 7. Передайте основное содержание текста В письменно.
Упражнение 8. Назовите наиболее важные центры головного мозга. Проверьте себя по рис. 13.
Часть III
Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 13
Упражнение 1. Найдите герундий в данных предложениях. Переведите предложения.
1. The brain is the primary centre for regulating and coordinating body activities. 2. Man receives his information
concerning the outside world through his sense organs. 3. We know of
the position of an arm or a leg without looking at it. 4. The nerves
are trunks containing many nerve fibres which are incased in a common
sheath. 5. The conditioned reflexes discovered by I.P. Pavlov are the
mechanism through which the body responds to the outside world in
avoiding injury, obtaining food and performing many more complex acts.
6. The best method in this case is removing one adrenal totally and
rendering the medulla of the other non-functional by cutting the
splanchnic nerves.
(Ответ: 1, 3, 5, 6. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 23 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 2. Найдите в следующих предложениях: а) герундий; б) при- частие; в) отглагольное существительное.
1.
The brain has many different parts controlling different aspects of
the body functions. 2. The cerebellum is located beneath the posterior
part of the cerebrum, its function being to aid in the coordination of
voluntary movements and to maintain balance and muscular tone. 3. The
thalamus monitors the sensory stimuli we receive by suppressing some
and magnifying others. 4. Professor told us about diagnosing the
hypophisis disfunctions. 5. The proprioceptors in the muscles not only
supply information on the condition of the muscles, but aid in
controlling the energy and extent of muscular activity. 6. Paralysis
often results from the plugging up of blood vessels, and consequent
arrest of blood supply to an area of the brain.
(Ответ: а) 3, 4, 5; б) 1, 2; в) 6. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 24 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 3. Переведите следующие пары слов.
(Ответ: 1. плечо-брать на себя, взваливать на плечи; 2. груз - нагружать; 3. взгляд - взглянуть на...; 4. знак - подписывать; 5. мечта (сон) - мечтать (видеть сон); 6. цель - целиться, направлять.)