Английский язык : учебник / И. Ю. Марковина, З. К. Максимова, М. Б. Вайнштейн; - 4-е изд., испр. и перераб. - 2010. - 368 с.
|
|
|
|
LEARNING TO DISCUSS MEDICINE
THE
Упражнение 1. Прослушайте и повторите за диктором (преподавателем) следующие слова. Обратите внимание на ударение.

Упражнение 2. Прослушайте и повторите за диктором (преподавателем) следующие группы однокоренных слов (гнезда слов). Определите, какой частью речи являются слова в каждой группе и переведите их: для этого найдите и проанализируйте словообразовательные суффиксы.
surgery,
surgical, surgeon; therapy, therapeutic, therapeutist; pediatrics,
pediatric, pediatrician; hygiene, hygienic, hygienist; physiology,
physiological, physiologist; chemistry, chemical, chemist; to graduate,
a graduate, graduation
Упражнение 3. Назовите корневые слова, от которых образованы следую- щие производные.
foundation, graduation, preparatory, surgical, therapeutic, scientific, preventive
Упражнение 4. Прочтите и переведите текст.
The
Yesterday, when we had our English lesson, the teacher said: «You are students of the
«Yes,»
said Semenov, one of our students. «I know that our Academy was
founded in 1758 as a faculty of the Moscow University and in 1930 it
was reorganized into an independent higher learning institution».
«You
are quite right,» said the teacher. «The Sechenov Moscow Medical
Academy, one of the oldest and biggest medical schools in Russia, was
formerly the Medical Faculty of the Moscow University, founded by the
great Russian scientist M.V. Lomonosov. The University had three
faculties: Philosophical, Law and Medical and only thirty students
studied at these faculties. Among them were the first medical students:
Sybelin, Veniaminov and Yastrebov. The students were taught by three
professors of natural history, anatomy and chemistry, respectively. At
that time the majority of the staff were foreign professors.The first
Russian professor of medicine was one of the graduates - Professor
Sybelin.
By
the 19th century there were six departments at the Medical Faculty:
the departments of anatomy, physiology, pathology, surgery, internal
medicine and midwifery. The first clinical hospitals were opened in
1805. They were the hospitals of surgery and obstetrics. By the end of
the 19th century 26 departments and 12 clinical hospitals had been
founded and new departments added: the departments of hygiene and
anatomic pathology.
The
professors and students of the Medical Faculty took an active part in
the political and social life of the time. The ideas of Herzen and
Belinsky were very popular among the staff and students. At that time
many outstanding doctors worked at the Faculty. They were: A.A.
Ostroumov, a physician; N.V. Sklifosovsky, A.A. Bobrov, P.I. Dyakonov,
surgeons; A.U. Kozhevnikov, a neurologist; S.S. Korsakov, a
psychiatrist; B.F. Snegirev, an obstetrician-gynecologist; N.F.
Filatov, a pediatrician; I.M. Sechenov, a physiologist; F.F. Erisman, a
hygienist, and others.
At
present there are many more faculties at the Academy: the Medical
Faculty, the Faculty of Preventive Medicine, the Pharmaceutical Faculty
(with an evening division), the Nursing Faculty, the Stomatological
Faculty, the Military Medicine Faculty, as well as the postgraduate
Health Care Management Faculty and the Faculty for Advanced Training of
doctors and pharmacists. The head of each faculty is the Dean.
The
course of training at the Academy is divided into junior and senior
levels (the junior and senior divisions of the faculties, respective-
ly).
There is a six-year course of study at the Medical, Preventive
Medicine, Stomatological and Military Medicine Faculties. At the
Pharmaceutical Faculty the students are trained for five years. The
course of training in the Nursing Faculty is four years. Over 9,000
students study at these faculties.
The Academy
has more than eighty departments in various theoretical and clinical
specialties. The curriculum includes all the basic and clinical subjects
that are necessary for the training of highly qualified physicians,
surgeons, nurses and pharmacists. At the end of each term (or semester)
students take examinations. The undergraduates do a practicum at the
clinics and teaching hospitals of the Academy. The students have all
the facilities to carry on their research under the supervision of
their professors. The students' scientific society plays an important
role in the training of would-be health care specialists.
The
students of our Academy have various facilities for sports and
recreation. Students from other towns are given hostel accommodations».
Then
one of the students said that those who were admitted to the Academy
took the First-Year Student's Oath. They solemnly swear to master the
fundamental medical subjects and to follow the traditions of the oldest
institution of higher medical learning.
During
the graduation ceremony young doctors, graduates of the Academy, take
The Oath of the Russian Doctor. Young doctors solemnly swear that they
will use all their knowledge and abilities to improve the people's
health, and to prevent and cure diseases.
The lesson was very interesting and we enjoyed it very much.
Active Words and Word Combinations

Упражнение 5. Найдите в тексте ответы на следующие вопросы и прочтите их вслух.
1. What faculties were (there) at the
take?
Упражнение 6. Прочтите следующие утверждения и выразите согласие или несогласие.
Начните свои ответы со слов: Yes, you are right...; No, I don' think you are right...; No, I don't think that is correct... .
1. By the end of the 19th century there were 26 departments and 12 clinics at the Medical Faculty of the
3. B.F. Snegirev, one of the famous physicians, worked at the Medical Faculty of the
Упражнение 7. Поставьте специальные вопросы к следующим предложениям и запишите их. Используйте вопросительные слова, данные в скобках.
4. The great Russian writer A.P. Chekhov graduated from the Medical Faculty of the
Упражнение 8. Вас пригласили на встречу со студентами-иностранцами, только что поступившими в ММА им. И.М. Сеченова. Ответьте на вопросы первокурсников об истории Академии.
1. When was the
Упражнение 9. Очередная встреча с иностранцами-первокурсниками по- священа факультетам Московской медицинской академии им. И.М. Сеченова. Расскажите о факультете, на котором вы учитесь. Используйте данные вопросы в качестве плана.
1. What faculty do you study at? 2. How many students study at the faculty? 3. What specialists are trained at the faculty? 4. What is the
course
of study? 5. Who is the dean of your faculty? 6. Students carry on
research work in the Students' Scientific Society, don't they? 7. How
many students of your faculty take part in the annual students'
scientific conferences?
Упражнение 10. Руководитель студенческого научного кружка попросил вас рассказать иностранным студентам-медикам историю Академии. Используйте следующие слова и сочетания слов в своем рассказе.
to be
founded, to be one of the oldest institutions of higher medical
learning, independent institution of higher learning, departments,
medical students, to open a clinical hospital, staff members of the
faculty, outstanding scientist, junior and senior divisions, to
graduate from the Academy
Упражнение 11. Студент из Индии хочет узнать о работе Студенческого Научного Общества. Выступите в роли индийского и российского студентов: опираясь на текст (упр. 4), составьте несколько вопросов о СНО (индийский студент), подготовьте информацию о работе научного общества, чтобы ответить на вопросы (российский студент) Используйте следующие словосочетания в вашей беседе.
Students' Scientific
Society; theoretical and clinical departments; to carry on research; to
devote one's time to research; important problems of modern medicine;
to play an important role in...; training of wouldbe health care
specialists, under the supervision of, to develop one's abilities,
annual students' scientific conferences, to be held
Упражнение 12. Прослушайте (прочитайте) диалог и скажите, между кем идет беседа и какие темы обсуждаются.
Dialogue
Dima: Hello, Jane. I am so glad to see you.
Jane: Hi, Dima. How nice to meet you again. I haven't seen you for ages. How is life?
Dima: I'm a student of the
Dima: Certainly I did. I had to take exams in chemistry and biology and to write a composition.
Jane: What marks did you get?
Dima: Two «excellent» and one «good».
Jane: So, you must be a second year student now.
Dima: Yes, I am in the second year. And what about you?
Jane: I
haven't decided yet what college to choose. Tell me more about your
Academy. I believe the systems of higher learning are very different in
our countries. Is there an evening division at your Academy?
Dima: Yes, there are evening divisions at the pharmaceutical and nursing faculties.
Jane: What subjects do medical students study?
Dima: Oh,
there are a lot of subjects in the pre-clinical years. We study
anatomy, biology, microbiology, general and biological chemistry,
physics, physiology and some other subjects. We also study languages:
Latin focussing on basics of medical terminology and one of the three
foreign languages English, German, or French trying to learn to
understand medical texts.
Jane: What is the course of study at your faculty?
Dima: Six years.
Jane: Well, I guess it takes a lot of time and much effort to become a highly qualified medical professional.
Dima: Yes, it certainly does. But I find all this very interesting.
Упражнение 13.Прослушайте (прочитайте) диалог вторично.
Используя диалог в качестве модели, выступите в роли студента младшего отделения ММА им. И.М. Сеченова и корреспондентов иностранных молодежных изданий, интересующихся вопросами поступления и обучения на младших курсах медицинских вузов России.
Упражнение 14. Вы участвуете в викторине на английском языке «Что я знаю об одном из старейших медицинских институтов нашей страны». Вы правильно ответили на все вопросы. Для того чтобы стать победителем, вам нужно выполнить последнее задание - перевести письменно следующие предложения.
1. Московская медицинская академия была основана в 1758 году как факультет Московского университета. 2. Основателем Московского университета был великий русский ученый М.В. Ломоносов. 3. В 19 веке в Московском университете было шесть ка-
федр. 4. В Московской медицинской академии были открыты два новых факультета: стоматологический и военной медицины. 5. Каждый факультет возглавляет декан. 6. Студенты: младшего отделения изучают разные виды химии.
Упражнение 15. Вы участвуете в юбилейной международной конференции «Московская медицинская академия - старейший медицинский вуз России». а) 4 студента вашей группы подготовили доклады по следующим темам:
1. The Medical Faculty of
б) Прослушайте эти доклады и задайте вопрос каждому выступающему.
MEDICAL EDUCATION IN
Упражнение 1. Прослушайте (прочитайте) и запомните следующие сло- восочетания. Переведите предложения.
1. World Health Organization (WHO) Всемирная организация здравоохранения
World Health Organization promotes the development of health education in all the countries of the world.
The regional WHO office for Europe is situated in
2. to receive nursing training at a specialised secondary school получить среднее медицинское образование (в медучилище)
My sister received nursing training at a specialised secondary school. She works as a nurse at hospital No. 5.
Упражнение 2. Прослушайте и повторите за диктором (преподавателем) следующие слова. Обратите внимание на ударения.

Упражнение 3. Определите, от каких глаголов образованы данные суще- ствительные, и переведите их.
information, achievement, examination, selection, instruction, training, supervision, introduction
Упражнение 4. Прочтите и переведите текст.
Medical Education in
Last year a delegation from the World Health Organization visited
Dr. Conroy: Dr.
Ivanov, my colleagues and I are here by the arrangement with the World
Health Organization. We should like to receive some information on the
training of doctors in your country and about the curricula in the
medical institutions of higher learning, or medical schools as we call
them.
Dean: I'll be happy to answer all your questions.
Dr. Conroy: First of all, would you kindly tell us who has the right to enter a medical school in your country?
Dean: Any citizen of our country who has a complete secondary education may apply to medical school.
Dr. Conroy: Applicants have to take examinations, don't they?
Dean: Yes,
quite so. All the applicants are required to take entrance competitive
examinations in biology, chemistry, and the Russian language. And
those who obtained the highest marks in the examinations are admitted.
Applicants who have finished school with a gold or silver medal are
allowed to take only one examination. If they get an excellent mark,
they are admitted to the medical school.
Dr. Brown: Would you tell us, please, how your students are instructed?
Dean: The instruction at higher schools is given through lectures, group instruction and practical classes.
Dr. Scott: Is the attendance at lectures and classes voluntary?
Dean: No, it is compulsory for all students.
Dr. Conroy: How is the students' knowledge checked?
Dean: Our
academic year begins on September 1st and is divided into two terms of
four months each. At the end of each term the students have to pass a
number of examinations.
Dr. Brown: We should like to know something about your medical curriculum, if we may.
Dean: Well,
the course of study lasts 6 years and covers basic preclinical and
clinical subjects. In the pre-clinical years the curriculum is uniform
for the students of the medical, preventive medicine, stomatological
and pediatric faculties. During the first two years students study
physics, general, organic, inorganic and biological chemistry. The
students also study human anatomy, physiology, histology, microbiology,
Latin, a foreign language, and philosophy. Beginning with the third
year special clinical subjects are introduced - all branches of
internal medicine, surgery, gynaecology, obstetrics, ophthalmology,
infectious diseases and others. At the end of the third year students
take a six-week practical course. They perform the duties of nurses.
After their fourth year students take another practical course during
which they are ex- posed to direct doctor-patient communication at the
department of internal diseases as well as at the surgical department,
and the department of obstetrics and gynaecology. Working as doctor's
assistants, students master a definite number of medical and diagnostic
procedures. Senior students also do a practicum in out-patient
departments. They have to attend lectures, seminars, and clinical
conferences as well.
Dr. Conroy: Dr.
Ivanov, you've told us about undergraduate clinical training in the
Medical Faculty. How does the training course at a medical school end?
And what about specialization?
Dean: You
see, in our country graduate medical students take a final state
examination which includes theoretical questions in internal diseases,
surgery and obstetrics and gynaecology, as well as in clinical cases.
The graduates also have to demonstrate their practical skills. Those
who have passed the examination receive their diploma, which certifies
them as doctors. Having received a diploma they may either take a
one-year internship course qualifying them as general health care
specialists, or a two-year residency course qualifying them as narrow
specialists.
Dr. Brown: Dr. Ivanov, would you kindly tell us what facilities your doctors have for specialization?
Dean: Interns
and residents work under the direct supervision of experienced
specialists in clinics and in major hospitals. Medical graduates can
also apply for the post-graduate training. For three years
postgraduates do research into one of the important problems of modern
medicine, prepare a thesis, defend it, and obtain an academic degree of
Candidate of Medical Science.
Dr. Conroy: Dr. Ivanov, thank you very much for the talk. Dean: You are most welcome. If you like, I'll gladly show you through some of our clinical hospitals and departments. Dr. Brown: We'd be much obliged to you.
Active Words and Word Combinations to apply to a medical school подать to instruct обучать

Упражнение 5. Задайте вопросы, ответами на которые будут следующие предложения:
Model: The course of study at medical schools in
Упражнение 6. Отреагируйте на высказывание собеседника, пользуясь следующей моделью:
Model: I am studing all branches of internal medicine at the
Упражнение 7. Вы беседуете с Раджем Шарма, студентом из Индии. Ответьте на его вопросы.
Raj: Look, when I told my parents that I'd like to become a doctor they advised me to go to
You:
Raj: What subjects shall we study in the first two years?
You:
Raj: What about the textbooks? Where shall I take them? How much money will I have to pay for the books taken from the library?
You:
Raj: Shall we take examinations every year?
You:
Raj: When shall we begin specialization in medicine, surgery or obstetrics and gynaecology?
You:
Упражнение 8. Вы учитесь на 6 курсе лечебного факультета. Расскажите вашим иностранным друзьям о занятиях на выпускном курсе. Исполь- зуйте следующие словосочетания в вашей беседе:
the
final year of medical training, to do a practicum at the hospital, to
specialise in surgery, to assist at operations, to treat patients, to
attend, clinical conferences, lectures, to take final state
examinations
Упражнение 9. Прочтите следующие утверждения и выразите согласие. Начните свои высказывания фразами:
I agree with you that.., I think you are right in saying that...
1.There are many medical schools all over
Упражнение 10. Ознакомьтесь
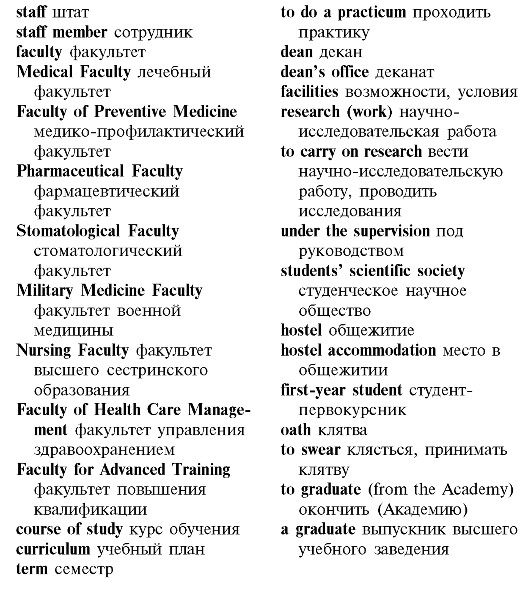
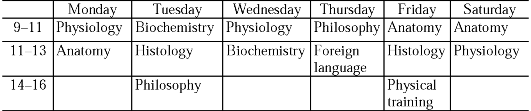
с расписанием занятий студентов 2 курса лечебного факультета
Московской медицинской академии. Скажите, как организован учебный
процесс, сколько семестров занимаются студентымедики? Какие предметы изучают студенты 2 курса?
Year 2. Third Term (17 weeks). September 1 - December 31.
Year 2. FourthTerm (17 weeks). February 7 - May 31.
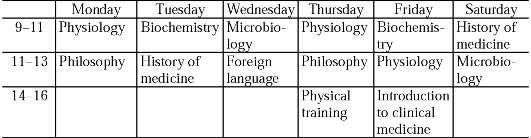
Упражнение 11. а) Прочтите методические указания к курсу гистологии для студентов 2 курса лечебного факультета Московской медицинской академии.
б) Задайте вопрос к каждому предложению. Отвечая на вопросы, расскажите, как организован этот курс в вашем институте.
The
course of histology covers the light and electron microscopic
structure of cells, tissues, and organs in relation to their function.
It is designed 1) to acquaint students with cell and tissue structure
in correlation to their study of biochemistry and physiology and 2) to
provide them with a working knowledge of normal light microscope
morphology as background for their later study of pathology. The
lectures will cover cells and their specialisations in specific tissues
such as muscle, nerve, epithelium, lymphoid and connective tissue.
Descriptions of the structure of various organs will be correlated with
their physiological functions. The laboratory sessions will give
students an opportunity to study the light microscopic structure of
normal cells, tissues, and organs and to review in small group sessions
the concepts covered in the lectures. Students' knowledge will be
evaluated by an oral examination.
Упражнение 12. Прочитайте и переведите диалоги. Выучите диалоги наизусть и разыграйте
1
Kate: Well, it's a higher education establishment, which trains students to be doctors. You would call it a Medical school.
Kate: No,
they are not. The Russian system of academic degrees is different.
Russian graduates are given diplomas which certify them as health care
professionals.
2
Jane: What subjects do students study at your
Dmitry: You know, it depends on the faculty and the year they are in.
Jane: Well, let's say the second year of the Medical Faculty.
Dmitry: Second-year students study anatomy, physiology, histology, microbiology, biochemistry and philosophy.
Jane: And what about Latin and foreign languages?
Dmitry: As for Latin, we study it in the first year. And we study one foreign language - English, French, or German for two years.
Упражнение 13. Студенты вашей группы принимают участие во встрече американских и канадских студентов-медиков. Расскажите гостям о системе высшего медицинского образования в нашей стране, используя следующий план.
1. The rules of admission to a medical institution of higher learning. 2. The instruction of medical students in
HEALTH CARE IN
Упражнение 1. Прослушайте (прочитайте) и запомните следующие сло- восочетания. Переведите предложения.
1. the Medical Workers' Union профсоюз медработников Doctors, nurses, and all health workers of the hospital are members
of the Medical Workers'
2. patient's visit to the doctor (syn. doctor's appointment) прием врача, визит к врачу.
District doctors give consultations to ambulant patients during the
patients' visits to the polyclinic.
3. maternity consultation centre женская консультация
Pregnant women are kept under observation by the doctor of the
maternity consultation centre.
Упражнение 2. Прослушайте и повторите за диктором (преподавателем) следующие слова.

Упражнение 3. Скажите, как с помощью суффикса можно определить, какой частью речи является слово и переведите производные слова следующих лексических гнезд.
to
prevent - prevention, preventive; to practise - practice, practical,
practitioner; to protect - protection, protective; to detect -
detection, detective; to diagnose - diagnosis, diagnostic
Упражнение 4. Назовите признаки, по которым можно определить, что данное слово является производным.
medical, institution, healthy, preventive, curative, examination, infectious, prevention, treatment, arrangement
Упражнение 5. Прочтите и переведите текст.
Health Care in
A group of British doctors came to
Dr. Sharland: During our stay in
Dr. Sharova: Dear
colleagues, as to the character of health care in our country, the
most distinctive feature of it is the attention paid to pro-
phylaxis. One of the main tasks in the fight against various diseases is the early detection of the first signs of disease.
Dr. McDonald: Would you tell us how this is done?
Dr. Sharova: We
pay much attention to the health education of the population. We
believe that is one of the main available methods of preventing the
spread of diseases. For this purpose the press, cinema, radio, and
television are very helpful.
Dr. Kelly: We
were surprised to find out that general practitioners do not exist in
your country. We were told that in your country the primary medical care
is provided by polyclinics. We visited some polyclinics. Your
polyclinics are large medical centres employing many doctors and
nurses. Polyclinics have their own laboratories and X-ray,
physiotherapy, surgical and dental departments. Some have even
radiotherapy units.
Dr. Kruglov: I
would like to add that we have polyclinics for the adult population of
a given area and polyclinics for children. Ambulant patients are seen
at the polyclinic by district doctors. Patients who are seriously ill
are visited by their district doctor at home.
Dr. Sharland: We've
seen that district doctors in your country, like their British
colleagues, are on call part of their working day. And how many hours a
day does your district doctor work?
Dr. Nikitina: The
doctor works 6 hours a day. For the district doctor this is made up of
3 hours seeing patients at the polyclinic and 3 hours in visiting
patients in their homes.
Dr. McDonald: And what about your emergency ambulance service?
Dr. Sharova:. The
emergency ambulance service operates day and night and is free of
charge. In case of an emergency condition one has to dial 03 for a
doctor to come. The ambulances are equipped with diagnostic,
respiratory, and anaesthetic apparatus, as well as blood-transfusion
and other devices, which enable the doctor to give emergency surgical
and medical treatment.
Dr. Kelly: We saw several specialised hospitals in
Dr. Nikitina: I'd
like to add that the main task of this Centre is to ensure the birth
of a healthy baby. That is why the doctors focus on the
problem
of the care for the foetus or «intra-uterine patient» as we say. New
methods of disease prevention, diagnostics and treatment developed at
the Centre are made known to the numerous maternity consultation
centres of our country which provide health care for expectant mothers
starting from the early months of pregnancy.
Dr. Stewart: I for myself, am very much curious to know about private medical practice and medical insurance in
Dr.Napalkov: At
present, there have emerged a number of private diagnostic and
consultation centres, general hospitals and specialised clinics.
Medical and health care is provided in line with compulsory and
voluntary medical insurance programmmes set up by the state via private
insurance companies.
Dr. Sharland: Dear colleagues, we've seen much of the practice of medicine in
Dr. Kruglov: As
for scientific problems, medical research is concerned with the
prevention and treatment of cardiovascular, and oncological diseases, as
well as infections, HIV and TB in particular. Medical scientists are
doing research into the problems of gerontology, medical genetics,
immunology and the development of artificial organs. Modern
non-invasive/minimally invasive techniques of the surgical treatment of
ischemic heart disease have been introduced, among them coronary
artery bypass grafting, percutaneous transloominal coronary angioplasty
or intracoronary stenting.
Dr. Sharland: I'd like to thank you for the warm reception and for the opportunity to get acquainted with the health care system in your country. We hope to see a delegation of Russian doctors in Great Britain in the near future. Thanks very much, again.
Active Words and Word Combinations


Упражнение 6. Ответьте на вопросы вашего товарища. Используйте в ответах слова, данные в скобках.
1.
What were the British doctors acquainted with? (health care,
preventive, curative) 2. What is the characteristic feature of health
care in our country? (to pay attention to; prophylaxis) 3. Where is the
primary medical care provided? (polyclinic, out-patient department,
ambulant patients, district doctor) 4. What do you know about the work
of a district doctor? (to be on call, to visit patients in their homes,
to see 5. What are the problems facing medical science in our country?
(prevention, treatment, cardiovascular diseases, oncological diseases,
artificial organs, to do research into, infectious diseases, HIV, TB,
to introduce, modern minimally invasive surgical techniques).
Упражнение 7. Прочтите следующие утверждения и выразите согласие или несогласие. Начните свои ответы со слов I believe you are right saying that.. или: In my opinion you are not quite right...
1. Prevention of diseases is the main principle of health care
Упражнение 8. Ваш
товарищ работает фельдшером (doctor's assistant) на станции скорой
помощи. Попросите его рассказать, как и кому оказывается скорая
медицинская помощь. Используйте следующие словосочета- ния в вашей беседе.
emergency
medical service, to deal with urgent cases, free of charge, to dial 03
for the doctor to come, blood-transfusion equipment, cases of
myocardial infarction, acute heart disease, to handle any emergency, to
give emergent treatment
Упражнение 9. Прослушайте (прочитайте) диалог. Скажите, какой вопрос обсуждался на занятии по терапии.
Dialogue
Teacher: Dear
colleagues, you know, patients are not used to talking about their
bodily functions and abnormalities. Very often they cannot easily find
the precise words to describe the character of their pain and of the
kind of cough ([kof] кашель) that they have, and so on. Today we'll talk about pain. The words «pain» and «ache» mean the same thing.
Student": If
«pain» and «ache» mean the same thing, then we may ask our patient if
he has an ache in his shoulder, for example. It's correct, isn't it?
Teacher: No,
you are mistaken. The thing is that both of these words are nouns but
the word «ache» can be used only with the following words to form a
compound noun: backache, headache, earache, stomach-ache, toothache.
For the other parts of the body we say: «I have a pain in my shoulder,
chest», etc.
Student: Is it possible to have pain in the back or in the head?
Teacher: Yes,
it is possible to have pain in the back, head and stomach but this
generally refers to a more serious condition than backache, headache
and stomach-ache.
Student: Can we use the word «ache» as a verb? Is it possible to say «My tooth is aching»?
Teacher: Quite
so. The word «ache» can also be used as a verb. And the patient may
say: «My leg aches after much walking», or «My back aches after
gardening».
Student: And what about the word «hurt»? My patient told me: «My chest hurts when I cough».
Teacher: The
word «hurt» is another verb used to express injury and pain. So it's
absolutely correct when patients describe their complaints (жалобы) as: «My chest hurts when I cough» or «My neck hurts when I turn my head». It means that coughing causes pain in the chest.
Упражнение 10. Прочитайте диалог еще раз и объясните разницу в употреблении английских слов: «pain», «ache», «hurt».
Упражнение 11. а) Прослушайте (прочитайте) диалог и скажите, какую проблему обсуждают американская студентка и ее подруга из России, которая учится в США; б) прочитайте диалог еще раз и найдите английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
быть больным, плохо себя чувствовать; слабость в ногах; измерять температуру; повышенная температура (жар); посчитать/из- мерить пульс; частый пульс; белый/обложенный язык; воспаленное горло; заболеть гриппом (подхватить грипп)
Dialogue
Linda: You look rather pale,
Linda: Did you take your temperature?
Linda: Let
me have a look at your tongue and feel your pulse. First show me your
tongue. It is coated (white, furred), and your pulse is rapid and
irregular. Besides, you have a sore throat.
Linda: I fear you have caught a bad flu (influenza). You'd better see a doctor.
Упражнение 12. Используя информацию и лексический материал диалога (упр. 11), разыграйте ситуацию, в которой Марина приходит на прием к врачу.
Doctor: Well, what seems to be the problem?
Doctor: How long have you had this headache? Which part of your head hurts?
Doctor: Apart from your headache are there any other problems?
Doctor: I'd just like to examine your mouth. Your tongue is coated. Any other problems?
Doctor: I am going to check your temperature and I would also like to feel your pulse. Some laboratory tests will be needed as well.
Упражнение 13. Приведенные в случайном порядке высказывания взяты из беседы врача и его пациента:
а) запишите эту беседу, поставив высказывания в логической последовательности.
б) прочитайте диалог несколько раз и постарайтесь воспроизвести его как можно ближе к тексту.
Dialogue
Patient: About
Doctor: Does
it come on at any particular time?/ Show me where it hurts /Well, what
seems to be the problem?/ Is your pain continuous or does it come and
go?/ Do you eat big meals?/ I would like to take some measurements - we
need your BMI (body mass index)/ What is your weight?/ How long have
you had this pain?/ After meals?/ You'd better not eat so much/ I'll
check your blood pressure first/Try to get your weight down by 5% in
three months/ That is probably the cause of your pain/ Some laboratory
tests will be needed : let's begin with fasting blood sugar/Let's first
of all discuss your diet: no heavy meals, not so much bread, no sugar
in your tea, no cake/ But before we decide on the treatment I would
like to examine you/
Упражнение 14. Иностранные
друзья попросили вас рассказать о вашей сестре, которая работает
участковым врачом в районной поликлинике. Составьте рассказ, используя следующие слова и словосочетания:
local
polyclinic, to be on call, to visit patients in their homes, to work
in shifts, to examine patients, to have the patient X-rayed, to
auscultate the heart and lungs, to check the blood-pressure, to give a
sick-leave (certificate), to diagnose, to prescribe medicine
Упражнение 15. Прослушайте
(прочитайте) диалог между врачом терапевтического отделения клиники
Московской медицинской академии и ординатором из Малайзии. Определите тему беседы.
Dialogue
Resident: This patient is doing well with treatment for heart failure but I have problems in treating his hypertension.
Dr. Pavlova (head of the department): What is his case history?
Resident: He
is 53. Six years ago he consulted a physician because of morning
headaches. He was diagnosed to have hypertension, and weight reduction,
shorter hours of work, and small doses of captopril and betablockers
were prescribed.
Dr. Pavlova: Is there hypertension in the family?
Resident: No,
there's no cardiovascular disease in the family. As I said earlier,
his heart failure has been corrected but the blood pressure remains
220-180 over 120-110 mm Hg.
Dr. Pavlova: Give
the patient antihypertensive drugs and then we will try to find out
the cause of his high blood pressure. The cause of hypertension may be
renal, vascular or endocrine. Tomorrow we'll have the results of the
laboratory tests and then we'll try to clear up the case.
Упражнение 16. Прослушайте (прочитайте) диалог еще раз. Скажите, какие утверждения соответствуют содержанию диалога.
1. а) Больной поступил в больницу по поводу почечной недостаточности; б) Больной поступил в больницу по поводу сердечной недостаточности. 2. а) У родителей больного отмечалась гипертония; б) Никто в семье больного не жаловался на гипертонию. 3. а) Причиной гипертонии может быть заболевание почек; б) Пиелонефрит не может быть причиной высокого давления.
Упражнение 17. Прослушайте (прочитайте) диалог и скажите, о чем беседуют Дима и Джон.
Dialogue
Dima: What are you reading, John? John: It's a book «You are what you eat».
Dima: I can't understand what the book is about.
John: «If
you know what you eat, you know yourself», said the philosopher. It's
important to know what we eat, it explains a lot about how our body
functions. So let's find out what we know about our diet. Here are some
statements which are, in fact, questions, and the answers to them.
Let's test ourselves.
Dima: It sounds very interesting. What's the first statement?
John: Meat contains certain vital amino acids not found in vegetable matter - true or false?
Dima: I
think, true. All the amino acids needed by the body for protein
synthesis can't be obtained even from a well-chosen combination of
vegetables.
John: Yes, right you are. The next statement is like this: eating carrots will improve your ability to see at night - true or false?
Dima: Oh,
it's very simple. Of course, it's true. Night vision depends on the
presence in the retina of the eye of a pigment called «visual purple».
The body manufactures this pigment and requires vitamin A to do so.
Carrots contain no vitamin A but they do contain large amounts of a
pigment called beta carotene, which the body can convert to vitamin A.
So, if you are suffering from impaired night vision due to vitamin A
deficiency carrots can help.
John: Simple sugars should be included in the diet in minimal quantities. True or false?
Dima: Well,
I think it is correct. It is known that excessive uptake of simple
sugars (cakes, sweets, rolls, etc) may lead to frank obesity.
John: Yes, you are absolutely right.
Dima: What's the next statement?
John: And the next statement sounds like this. It is impossible to take too much protein - true or false? Dima: I think it's false.
John: No.
«True» is correct. Excess protein cannot be stored and thus is
excreted. Nutritionists recommend that protein should make up only 10
or 15 per cent of the daily caloric allowance.
Dima: The book is really very interesting. I'd like to read it.
John: I'll give you the book in two days after I finish reading it.
Упражнение 18. Прослушайте (прочитайте) диалог еще раз.
1) Найдите и запишите английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
жизненно важные аминокислоты; продукты (вещества) растительного происхождения; правильно (хорошо) подобранное соче-
тание; организм вырабатывает; организму требуется; превращать (преобразовывать) в витамин; недостаток (дефицит) витамина; (ежедневный) рацион питания; чрезмерное потребление; ожирение; минимальное количество; избыток (чрезмерное количество); накапливаться (сохраняться в организме); диетолог; ежедневная норма потребления калорий
2) Используя текст диалога, сформулируйте требования к рациону питания здорового взрослого человека. Начните со следующей фразы: The daily diet of a normal adult should contain...; I would recommend you to...
Упражнение 19. Вы участвуете в конференции «Медицинское обслуживание в России».
а) шесть студентов вашей группы подготовили доклады по следующим темам: 1. Medical care in
б) прослушайте выступления и задайте вопрос каждому докладчику.
MEDICAL EDUCATION IN THE
Упражнение 1. Прослушайте (прочитайте) и запомните следующие слова и словосочетания. Переведите предложения.
1. humanities гуманитарные науки.
The girl was very capable in the humanities. The humanities are included in the school cirriculum in our country.
2. academic achievement успеваемость.
In his report the Dean of the Faculty spoke about the academic achievements of the second-year students.
Academic achievement is a decisive factor in the selection of students for medical schools.
3. to assess (the general qualities of an applicant) зд. определять, оценивать (общий уровень абитуриента).
A
special committee assesses the professional qualities of young
doctors. The admission committee worked out new criteria to assess the
general qualities of the applicants.
4. teaching hospital клиническая база.
Students
of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine do their medical
practicum at the Johns Hopkins teaching hospital. The Johns Hopkins
teaching hospital has 1050 beds.
There are four patients in this ward.
The patient asked his ward doctor to give him some medicine for a headache.
Упражнение 2. Прослушайте и повторите за диктором (преподавателем) следующие слова. Обратите внимание на ударения.

Упражнение 3. Назовите пары слов, относящихся к одному лексическому гнезду.
to admit, to achieve, emphasis, academy, achievement, to concentrate, admission, to emphasize, academic, concentration
Упражнение 4. Прочтите и переведите текст.
Medical Education in the
Dr. Frank Nelson and his colleagues from the
Dr. Nelson: To
begin with, after finishing his primary school and secondary studies
at the age of 18, the candidate for a medical school must complete at
least three years of higher education in a college or university.
This
period of college or university studies is called «the pre-medical
phase». The students who are taking this course of studies preparing
them for a medical school are called «pre-meds». A student applies to a
medical school when he has completed pre-medical studies. The
application costs approximately $ 50.
Sasha Nikiforov: Dr. Nelson, would you kindly tell us about the selection of students for medical schools?
Dr. Nelson: Sure.
Academic achievement is the most important factor in the selection of
students. In most medical schools candidates are required to pass the
admission test. This is a national multiple-choice test. The test lasts
about eight hours over a one-day period and includes questions in
biology, chemistry, physics, mathematics, and English. Then, special
admission committees have personal interviews with the applicant in
order to assess the candidate's general qualities, his character and
his ability to study medicine.
Nina Mironova: Dr. Nelson, is there any competition among the applicants to medical school?
Dr. Nelson: There
certainly is. I must tell you that the competition is very high and
only about half of those who apply to medical school are accepted and
begin their medical education. By the way, what we call «medical
school» is «medical institute» in your country.
Dean of the Medical Faculty: Dr. Nelson, we know that the curriculum of medical schools in the
Dr. Nelson: Well,
the basic sciences are taught largely during the first two years of
medical studies. For instance, in the first year at Johns Hopkins
students study anatomy, biophysics, biochemistry, physiology,
bacteriology, histology and other subjects. In the second year they
study microbiology, pathology, physical diagnosis, pharmacology and
laboratory diagnosis.
The
curriculum of the final two years includes clinical subjects. Medical
students do their practicum at teaching hospitals affiliated to the
medical school. Students in small groups meet their teachers in the
wards and in the out-patient departments where they participate in the
treatment of patients.
At
the end of four years all students receive the Degree of Doctor of
Medicine, that is the M.D. Then they must work for one year as interns.
This course of training at the hospital or clinic is called an
internship.
Dr. Smirnov: Dr.
Nelson, yesterday we spoke about the work of young doctors. You told
us that after their internship young doctors must have a period of
residency at the clinic. For how many years must a doctor work as a
resident?
Dr. Nelson: First
of all, the period of residency is obligatory for all medical
graduates. This period varies, depending on the specialty of the
doctor. Generally, the period of residency is three or four years. For
instance, residency in surgery and neurosurgery in the Johns Hopkins
School of Medicine lasts four years. Residency in internal medicine,
preventive
medicine and radiology lasts for three years. After the residency, the
graduate is granted a licence to practice and he may work either in
government service or in private practice.
Sasha Nikiforov: Dr. Nelson, what is the cost of medical education in
Dr. Nelson: Well, medical schools are gradually increasing their tuition fee in all the universities of the
Tuition - 9,100 dollars; books, instruments, etc. - 600 dollars; food
- 1,800 dollars; lodging and utilities - 1,400 dollars; health service fee
- 200
dollars; hospital insurance - 143 dollars, personal - 1,200. All in
all it amounted to 14,443 dollars. These figures represent what used to
be a typical budget for an academic year.
The
Dean of the Medical Faculty thanked Dr. Nelson and his colleagues for
the talk and invited them to visit the clinics of the Academy.
Active Words and Word Combinations


Упражнение 5. Найдите в тексте ответы на следующие вопросы и прочтите их вслух.
1.
When does a student apply to medical school? 2. What is the most
important factor in the selection of students? 3. What is the aim of
the personal interview with applicants to medical school? 4. What
degree do students receive at the end of four years of study? 5. Where
can the graduates work after their residency?
Упражнение 6. Согласитесь с собеседником, употребив фразы: I agree with you that.. . That's right. It's true, that.. .
1.
At the age of 18, Americans finish their secondary school. 2. Students
study at least 3 years in a college before they apply to a medical
school. 3. The competition to medical school is very high. 4. The
thirdand fourth-year students work in clinics and outpatient
departments, gaining practical medical experience. 5. During their
period of residency the young doctor works under the supervision of a
specialist. 6. The cost of medical education in the
Упражнение 7. Ваш
товарищ был болен и не мог принять участие в беседе с д-ром Нельсоном.
Расскажите ему, что нового вы узнали о подготовке врачей в США.
Используйте в своем рассказе следующие слова и словосочетания.
to
enter a college, an admissions test, an admissions committee, to
assess the character of an applicant, the ability to study medicine,
premedical school curriculum, pre-meds, final years, tuition fee, the
degree of Doctor of Medicine, interns, residency at the clinic, to be
granted a licence
Упражнение 8. Ознакомьтесь с расписанием занятий студентов медицинс- кого факультета Университета Джонса Хопкинса (2 курс). Расскажите о структуре учебного года. Какие предметы изучают студенты 2 курса?
Year 2. First Trimester (15 weeks). September 8-December 22.
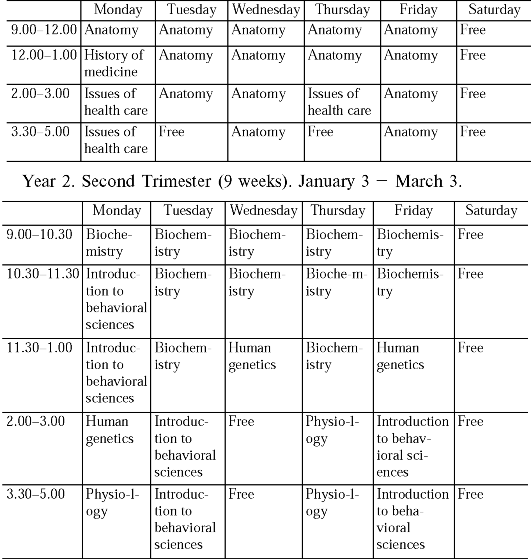
Year 2. Third Trimester (12 weeks). March 8-June 2.
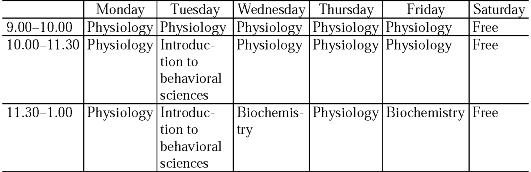
2.00-5.00 Physiology Physiology Free Physiology Physiology Free
Упражнение 9. Прочтите
методические указания к курсу физиологии для студентов 2 курса
медицинского факультета Университета Джонса Хопкинса. Расскажите, как организован этот курс в вашем институте.
The
department provides instruction in cell physiology and systems
physiology for second year medical students. The general subject of
physiology and certain aspects of biophysics are presented to the
second year medical students in lectures given two times a week during
the second trimester, and five times weekly throughout the third
trimester. During the second trimester lectures on the general
properties of cells are delivered. Lectures of the third trimester are
devoted to systems of mammalian physiology. During the third trimester
laboratory experiments are carried out on two days of each week by
students in small groups, under the supervision of the teaching staff.
The laboratory work of each week is summarized in small group
conferences at which the significance of the findings is reviewed and
discussed. Seminars in renal and electrolyte physiology are held
throughout the third trimester, with an emphasis on clinical problems
and pathological physiology.
Упражнение 10. Группа американских студентов беседует со студентами 2 курса Московской медицинской академии. Выступите в роли переводчика. Используйте в вашем переводе данные в скобках слова и словосочетания.
Игорь: Мы знаем, что вы - студенты-медики из Балтимора. Как называется ваше учебное заведение (medical school)?
Alan: We study at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine (медицинский институт).
Игорь: Скажите, пожалуйста, Алан, Джонс Хопкинс был известным американским ученым?
Alan: Oh, no. Johns Hopkins was a merchant (коммерсант) of Baltimore who gave 7,000,000 dollars for the establishment (основание) of a university and a hospital. And in 1876, three years after Johns Hop- kins' death, the
Наташа: А наша Академия названа в честь (was named after) основоположника (founder) русской школы физиологии И.М. Сеченова.
Paul: Yes, we know that Sechenov was a great physiologist. He developed the theory of brain (головной мозг) reflexes. I've read his book «Reflexes of the Brain».
Лена: Сеченов закончил медицинский факультет Московского университета, а затем возглавлял (to be the head of) кафедру фи- зиологии. У нас в Академии есть музей-лаборатория И.М. Сеченова.
James: Oh, it would be very interesting to visit it. Do you think it's possible?
Саша: Конечно. Давайте пойдем в этот музей в среду в три часа после лекции по физиологии.
Alan: That will be wonderful. So, good-bye till Wednesday.
Упражнение 11. Прослушайте (прочитайте) диалог и скажите, какие вопросы интересуют английского профессора.
Dialogue
An English professor is interviewing his American colleague.
Dr. Kelly: I'm glad to have this opportunity to talk to you, Dr. Barton. Do you mind my asking some questions about medical school in
Dr. Barton: Certainly not. What do you want to know?
Dr. Kelly: First, can students go to a medical school free of charge?
Dr. Barton: No,
everyone must pay a tuition fee. The amount varies from state to state
and from one school to another. A student's total expenses throughout
the year are about several thousand dollars. This creates financial
hardship for some people. Though each school offers a number of grants,
many of the students have to work to pay part of their expenses.
Dr. Kelly: What degree does a medical school offer?
Dr. Barton: After completing 4 years all students receive the Degree of Doctor of Medicine.
Dr. Kelly: That
clears up most of my questions, Dr. Barton. It's good to have this
information from someone directly connected with the world of medicine.
I hope to visit two medical schools - the
Dr. Barton: It was a pleasure to talk with you.
Упражнение 12. а) прочитайте диалог (упр. 11) и найдите английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
бесплатно учиться в медицинском вузе; плата за обучение; общие (суммарные) расходы; создавать финансовые/материальные затруднения; предоставлять гранты; получать звание (степень).
б) используя диалог в качестве модели, составьте новый диалог между российским и американским студентами-медиками. Расспросите друг друга
об изучаемых предметах, о вступительных экзаменах и конкурсном отборе и т.д.
Упражнение 13. Вы участвуете в конференции «Медицинское образование
в США».
а) Четыре студента вашей группы подготовили доклады по следующим темам:
1.
The selection of students to a medical school. 2. Pre-medical and
medical subjects studied at medical schools. 3. The work of a resident.
4. The work of young doctors after residency.
б) Прослушайте доклады и задайте вопрос каждому выступающему.
HEALTH CARE IN THE
Упражнение 1. Прослушайте и повторите за диктором (преподавателем) следующие слова. Обратите внимание на ударения.
society [sa'saiati], physician [fi'zijn], relationship [n'leijnjip], staff [sta:f], trauma [Чго:тэ], insurance [in'juarans], atherosclerosis [,a369r9skli9 rousis]
Упражнение 2. Прочтите и переведите следующие словосочетания.
in
case, government-financed hospitals, intensive care unit, health
insurance, place of employment, maternal and child health care,
retirement benefits
Упражнение 3. Прочтите следующий ряд слов. Выпишите слова, относящиеся к теме «Медицинское обслуживание».
medical,
health, need, patient, gradually, hospital, program, illness, disease,
week, nausea, importance, death, chief, forget, disability, pregnancy,
arthritis, cancer, opinion, emphysema, chronic bronchitis
Упражнение 4. Прочтите и переведите текст.
Health Care System in the
The second meeting of Dr. Nelson and his colleagues with the Professors and students of the Medical Faculty of the
Dr. Nelson: Dear
colleagues, it is a great pleasure for all of us to meet you again.
Today we'll speak about medical service in our country.
As
for the health care system in my country, it exists on three levels:
the level of the family doctor, the medical institution or hospital and
the United States Public Health Service.
Dr. Kruglov: Do many Americans seek medical help from private doctors?
Dr. Haddow: Not
many, I should say. A private doctor, we call him a family doctor,
gives his patients regular examinations and inoculations. In case
professional care is needed, the family doctor arranges for the patient
to see a specialist or to go to a hospital. The family doctor receives
pay directly from the patient. Most physicians have private practices.
They make use of the hospital's facilities whenever necessary. A
family doctor either has his own private office or works with several
other doctors in a so-called group practice.
Sasha Nikiforov: Dr. Haddow, what is characteristic of American hospitals? Do all patients pay for their treatment at hospitals?
Dr. Haddow: I
should like to point out first that many Americans have no family
doctor and they come directly to the hospital for all their medical
needs. The hospital provides health care to the sick and injured. We
have government-financed and private hospitals. The patients are
admitted to hospitals or clinics staffed by consulting physicians,
residents, interns and highly skilled nurses. The nursing staff is very
important. Nurses and patients are in close contact throughout the
patients' stay in the hospital. Social services are available to the
patients and families regarding personal, emotional, and financial
problems that may arise from continued illness or disabilities.
Most
hospitals have at least the following major departments or units:
surgery, obstetrics and gynaecology, pediatrics and general medicine.
They may also have trauma and intensive care units, neurosurgical and
renal care units, and a psychiatric unit. The Emergency Room (unit) is a
very special area in the hospital. The emergency patients receive
immediate attention.
Dr. Nelson: Let's
not forget about the high cost of medical care in our country. Two
thirds of the population have private health insurance. Some people have
health insurance, life insurance (financial assistance for the
relatives in case of death), disability insurance and retirement
benefits at their place of employment. Most employees and their
families now pay more than 50 per cent of the costs of health
insurance. The great cost of medical care in the country and the great
number of people who could not pay for it forced the federal government
to devel-
op two health
insurance programs - Medicaid and Medicare. Medicaid, started in 1966,
is a federal program providing free medical care for low-income people,
the aged, the blind and for dependent children.
Dean of the Faculty: Dr.
Kendall, I've read that Medicare is a health insurance program for the
elderly and disabled. What age group does the Medicare program provide
for?
Dr. Kendall: Medicare,
started in 1967, is a federal program providing free medical care
for_aged Americans over 65, for those who in the past had the greatest
medical expenses.
Dr. Kruglov: Dr. Nelson, what are the scientific problems facing American medicine?
Dr. Nelson: Well,
in my opinion, the chief scientific problems facing American medicine
are the same as those facing Russian medicine, they are heart disease
and cancer. The chief causes of suffering and death today are cancer and
cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension, stroke and
atherosclerosis. Also much medical research is done on illnesses of
aging, disabilities caused by arthritis, mental illness, drug
addiction, and genetic problems.
Dean of the Faculty: Dear
colleagues, you've given us a clear picture of the American health
care system. We all want to thank you and wish you the best of luck in
your work.

Упражнение 5. Задайте вопросы, ответами на которые будут следующие предложения.
Model: A family physician provides health care for the entire family. Who provides health care for the entire family?
1. Cigarette smoking is the leading preventable cause of death and disability in the
Упражнение 6. Ответьте на вопросы вашего товарища. Используйте в ответах слова и словосочетания, данные в скобках.
1. What kinds of hospitals are there in
Упражнение 7. Расскажите вашим товарищам о работе частного врача в США. Используйте в своем рассказе следующие словосочетания.
private
doctor, family doctor, to give regular examinations, to arrange for
the patient to see a specialist, to make use of hospital facilities,
private office, group practice
Упражнение 8. Прочтите следующие утверждения и выразите свое согласие или несогласие. Начните свои ответы со следующих фраз: Quite so./ Exactly. /Yes, I think that.. . Или: I don't think that is correct... . I can't agree with the fact that.. . No, I don't think you are right...
1.
Medicaid is a federal program, which provides free medical care for
low income people, the aged, the blind and for dependent children.
2.
Medicare is a federal program, which provides free medical care for
aged Americans over 65. 3. Most employees and their families do not
have their health insurance. 4. Many people in America have health
insurance, life insurance, disability insurance and retirement benefits
at their place of employment. 5. The chief scientific problems facing
American medicine are heart disease and cancer.
Упражнение 9. Ведущий радиопередачи «В мире медицины» («In the World of Medicine») беседует с американским врачом-гомеопатом д-ром Карлом Робинсоном. Используя приведенные ниже текст и диалог, составьте и разыграйте радиоинтервью.
Ведущий: представляет доктора Робинсона, сообщая краткие сведения о нем (см. Текст), и предлагает д-ру Робинсону ответить на вопросы радиослушателей (см. Диалог)
Доктор Робинсон: отвечает на вопросы ведущего и радиослушателей (см. Текст)
Text
1. Dr.
K. Robinson received his B.A. from Yale University, his M.D. from
Hahnemann Medical College in Philadelphia and he did his residency in
internal medicine in New York City. Then he studied homeopathy at the
Royal Homeopathic Hospital in London. Now Dr. Robinson practices in
Albuquerque, New Mexico.
2. The
word «homeopathy» is derived from the Greek language. «Homeo» means
«like», «pathy» means «suffering». Homeopathy means «like suffering» or
«like disease». Homeopathy is a scientific medical practice, which
treats the whole person, that is the body, the mind and the emotions,
which are affected when a person is sick
Homeopathy
is a natural medicine. A homeopathic medicine is used to stimulate the
person to heal himself. It is a system of therapy based on the law
«Similia similibus curentur». In other words, homeopathy is a
scientific system of medicine based on the discovery that a substance
can cure the same problems that it causes - usually by varying the
dosage of the substance.
Homeopathic remedies are made from natural animal, vegetable or mineral sources.
Homeopathic
medicines are not used to treat any particular organ of the body. Side
effects such as tissue destruction do not occur in homeopathy
treatments.
Dialogue
Interviewer: We
have some questions dealing with homeopathy. The questions were sent
to the National Center for Homeopathy in Washington. We invited Dr.
Karl Robinson to answer our listeners' questions. Now I'll introduce
Dr. K. Robinson to you...
And now, Dr. Robinson, would you answer the first question of our listeners: What is homeopathy?
Dr. R.:
Interviewer: Is homeopathy a scientific system of medicine or is it based more on the intuition of the practitioner?
Dr. R.:
Interviewer: What are homeopathic remedies made from?
Dr. R.:
Interviewer: Do homeopathic medicines cause side effects?
Dr. R.:
Interviewer: Dr Robinson, thanks very much for your answers. With this we will end our program. Good-bye.
Упражнение 10. а) Прослушайте (прочитайте) фрагмент беседы профессора Андерсона со студентами Медицинского колледжа университета штата Огайо. Скажите, какие вопросы были затронуты во время этой беседы. б) Прочитайте текст выступления профессора Андерсона и найдите английские эквиваленты следующих слов и словосочетаний:
здоровье нации; общественное здоровье; личные/индивидуальные привычки; оказывать огромное воздействие; профилактическая медицина; здоровый образ жизни; главная цель; умеренная физическая нагрузка; поддерживать вес; иметь избыточный вес; курильщики; выбор образа/стиля жизни.
This
is what professor Anderson said about the effect of life style and
personal habits on the standards of health of a nation: «There is
perhaps no more important principle in the field of public health than
the realization that life style and personal habits have a great effect
on the standards of health of a nation. The promotion of preventive
medicine through a healthy life style is a major goal of the Federal
Bureau of Health Education. Billions of dollars could be saved if the
following lifelong habits were established in the US population.
1. Eat three meals a day at regular time; avoid snacks.
2. Eat breakfast every day.
3. Engage in moderate exercise at least three times a week.
4. Sleep seven or eight hours a night.
5. Don't smoke.
6. Maintain
weight at or slightly below the «ideal» level. Statistics show that
40% of all Americans are 20 or more pounds
overweight
and that smokers have a 70% greater chance of developing coronary
heart disease than non-smokers. American physicians claim that the best
way to improve the health statistics in the USA is to make people
aware of the necessity of choosing a healthy life-style.
Упражнение 11. Составьте 8-10 вопросов к тексту Упражнения 10 и разыграйте беседу американского профессора с российскими студентами-медиками.
Упражнение 12 Вы участвуете в викторине «Что я знаю о медицинском обслуживании в США». Несколько студентов вашей группы подготовились к викторине в качестве экспертов по следующим темам.
1. The three levels of health care in the USA. 2. The work of the family doctor. 3. The system of Medicaid. 4. The system of Medicare. 5. The medical units at American hospitals. 6. The chief scientific problems of American medicine.
Составьте по три вопроса к каждой теме и задайте их экспертам. Определите, кто лучше знает свою тему и, следовательно, является победителем викторины.
MEDICAL EDUCATION IN GREAT BRITAIN
Упражнение 1. Прослушайте (прочитайте) и запомните следующие слова и словосочетания. Переведите предложения.
1. to charge a tuition fee взимать плату за обучение charge плата; free of charge бесгшатный
In
Great Britain higher medical education is not free of charge. Tuition
fees are charged in all medical schools in Great Britain.
2. the degree of Bachelor of Medicine степень бакалавра в области терапии
In Great Britain the degree of Bachelor of Medicine is given to a medical student after passing his final examination.
In
order to obtain the degree of Doctor of Medicine in Great Britain a
post-graduate must write a thesis based on original work.
Упражнение 2. Прослушайте (прочитайте), следующие гнезда слов и определите, какой частью речи является каждое слово. Переведите.
to
qualify, qualification; to supervise, supervision, supervisor; to
instruct, instructor, instruction, instructive; to require, requirement
Упражнение 3. Прочтите и переведите текст.
Medical Education in Great Britain
A
delegation of English doctors visited the Pavlov St. Petersburg
Medical University. They were shown the clinics and laboratories of the
University. At the end of their visit the Rector of the University
invited the guests to the Conference Hall where they had a meeting with
the teaching staff and students. Dr. Glenn Stanton was asked to speak
about medical education in Great Britain. This is what Dr. G. Stanton
said:
«Dear
colleagues. In Great Britain physicians are trained in either medical
schools or faculties of Universities. We have medical schools in the
Universities of London, Oxford, Birmingham, Bristol and Edinburgh.
There are faculties of medicine in the Universities of Liverpool,
Manchester, Glasgow and Aberdeen. And there is the School of Clinical
Medicine in the University of Cambridge. Entry to a medical school is
highly competitive and usually the number of candidates is much higher
than the number of the places.
To
enter a medical school in Great Britain candidates must pass entrance
examinations. Entrance examinations are both oral and written. Students
take these examinations at the end of their 6-year secondary-school
course, generally at the age of 18-19 years. For entrance to a faculty
of medicine or a medical school, it is required that the subjects of
chemistry, physics and biology or mathematics should be taken at the
advanced level. Tuition fees are charged. Most students receive
financial assistance in the form of grants, which cover their expenses
wholly or in part.
Now about the
academic year. It is divided into 3 terms, each of 10-11 weeks'
duration. The terms run from October to December, from January to March
and from April to June. Clinical students, however, attend for 48
weeks of the year. I must tell you that undergraduate education
occupies five years, consisting essentially of two years of basic
sciences and three years of clinical work.
Two
pre-clinical years are occupied by human anatomy and biology,
physiology and biochemistry. They also study physiology, statistics and
genetics. Students attend lectures, do dissections and practical work
in labs. Unlike in your country Latin is not taught in all medical
schools.
English and Latin spellings are similar and it is possible to write out prescriptions in English too.
Beginning
with the third year the students study the methods of clinical
examinations and history taking, general pathology, microbiology,
pharmacology and community medicine. Senior students and especially
undergraduates spend most of their time in teaching hospitals, which
have both in-patient and out-patient departments, or units. Daily
bedside instruction in hospital wards and out-patient departments is
given by teachers and doctors. Students follow up their patients and
attend ward rounds. Besides the work in the wards the students attend
demonstrations and clinical conferences as well as lectures in clinical
subjects which are being studied.
And
now about the examinations. As in your country examinations in our
medical schools are held at the end of each term. In our case it is
three times a year. At the end of each term and after each special
course students take final exams. They are called sessionals. Most of
the exams are written. They include academic and practical problems.
The final examinations or finals are in Medicine, Surgery, Obstetrics
and Gynaecology and Pathology. Finals also include history taking and
diagnosing. Before finals in Surgery students assist in operations.
Before finals in Obstetrics and Gynaecology they must assist during the
delivery of at least 20 babies. These examinations are both written
and oral. Written test includes short and long questions and questions
of multiple choice. Oral tests include diagnosing a case. So three
years are spent in clinical studies to obtain. degrees of Bachelor of
Medicine (MB) and Bachelor of Surgery (BS). The degrees of Bachelor of
Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery give the right to register as a
medical practitioner
After the
finals graduates work in hospitals for a year. This period is called
internship. The newly qualified doctor must serve for six months as a
house physician and six months as a house surgeon under the supervision
of his medical school. House physicians and surgeons are on call every
second or third night. The work of interns is very difficult and their
salary is very small. After internship a young doctor obtains a
«Certificate of Experience» from the medical school and he or she may
work as a medical practitioner.
Further
specialization requires training in residency. It takes one or two
years of work in a hospital in some field. Residency trains highly
qualified specialists in a definite field: gynaecologists, urologists,
neurologists and others. The salary of residents is higher than the
salary of interns. After residency a specialist gets rather a high
salary.
Besides
the degrees of MB and BS, we have the degree of Doctor of Medicine
(MD). This degree is a postgraduate qualification ob-
tained
by writing a thesis based on original work. It is not required for
practice. Such a degree in surgery is termed a mastership (MS)»
Dr.
Glenn Stanton answered the questions of the teachers and students.
Then the Rector thanked Dr. Stanton for his interesting talk and
invited the British delegation to the performance of the students'
amateur theatre.

Упражнение 4. Прочтите вопросы, которые были заданы во время беседы доктору Стентону преподавателями и студентами Университета. Ответьте на эти вопросы, используя текст.
1.
When are entrance examinations to a medical school taken? 2.What kind
of financial assistance do medical students receive in Great Britain?
3. What examinations do medical students take? 4. What degrees are
given to medical students after their final examinations? 5. Is it
obligatory to obtain the degree of Doctor of Medicine for all graduates
of a medical school? 6. When can a young doctor start working as a
medical practitioner?
Упражнение 5. Прочтите следующие утверждения и выразите свое согласие или несогласие. Начните свои ответы со следующих фраз: Yes, you are right. I agree with you that...; No, . I don't think you are right ...
1.Entry
to a medical school in Great Britain is a simple matter. 2. The
Certificate of Experience is obtained at the end of a one-year
internship. 3. The examinations in medical schools in Great Britain are
only oral. 4. Different grants are available to aid those students who
do not have sufficient funds to finance their medical education.
Упражнение 6. В дискуссионном клубе международного молодежного лагеря вы познакомились с Дональдом Эдвардсом, студентом 4 курса медицинского факультета университета Глазго. Попросите Дональда рассказать, сколько лет учатся студенты-медики в Англии, какие экзамены сдают студенты, сколько учебных недель в каждом семестре? Можно ли получить высшее медицинское образование в Англии бесплатно?
Задавая вопросы, начните со следующих фраз: What can you say about...; Could you tell us...; And what about...?
В ответах на вопросы используйте следующие фразы: Well, I have to say that... ; As for (exams)... ; I can add that... ; I want to stress that...
Используйте в своей беседе следующие словосочетания:
the curriculum; to occupy five years; pre-clinical studies; clinical
work; tuition fees; financial assistance; grants; to be available;
methods of clinical examination; history taking; clinical subjects;
teaching hospitals; to attend a ward round; final exams; sessionals;
questions of multiple choice; oral and written tests; written exams.
Упражнение 7. Расспросите Дональда Эдвардса о том, как проходит специализация выпускников медицинских школ в Великобритании. Используйте в вашей беседе следующие словосочетания:
internship,
house physician; house surgeon; under the supervision; Certificate of
Experience; medical practitioner; to train qualified spe-
cialists; training in residency; to be given the B.M. or B.S. degrees; post-graduate qualification; to write a thesis.
Упражнение 8. Прослушайте (прочитайте) диалог и скажите, о чем беседуют Марина и студент из Иордании, которые учатся в медицинской академии в России.
Dialogue
Marina: Hello, Mohammed, Where are you going?
Mohammed: I'm going to the library. I'd like to take some books for my report in histology next Wednesday. Come with me.
Marina: I wish I could join you now, but I'll go to the library after the lecture on microbiology.
Mohammed: Do you know that attendance at lectures in the Oxford University Medical School is free?
Marina: But we are not in Oxford. Who told you that?
Mohammed: I
was in Great Britain this summer. I visited Oxford and met two guys
who turned out to be students of the Medical school there. Now I know
that they have no academic groups and students work according to their
own plans. But they have tutorials with their tutors.
Marina: And what do the tutors do?
Mohammed: As
far as I remember, tutors plan the work of students and suggest the
books to be read. At the end of each term students have written
examinations. The students' papers are corrected and marked by the
tutors. And on the last day of the term the tutors give a report on the
students' work for the term.
Marina: Do students meet their tutors every day?
Mohammed: Certainly
not. You see, each week 2 or 3 students go to their tutor, bring
essays for criticism and he discusses with them the work they have
done. Such classes with the tutor are called tutorials.
Marina: Does the tutor deliver lectures?
Mohammed: Yes. Some lectures are delivered by tutors, others are delivered by professors. But usually professors don't do teaching. Marina: You want to say that Professors carry on academic research,
don't they?
Mohammed: Quite so. Professors in Oxford mainly carry on academic research in their practical subject.
Marina: You
really know a lot about the British system of medical training. Could
you explain to me what the words «undergraduate», «graduate» and
«post-graduate» mean? I can never use them correctly.
Mohammed: Well, I'll try. First of all, an undergraduate is the student who hasn't yet taken a University degree. Marina: Did you say «degree»?
Mohammed: Yes.
A University degree is given to a student who has finished a course of
studies and passed his final examinations. By the way, a person who
has taken a Degree of Bachelor, that is the lowest degree, is called a
graduate, while any graduate who continues his studies or does research
to receive a Degree of Master or Doctor is called a post-graduate.
Marina: How
very interesting! And, how very different from the Russian system of
medical training. Thanks a lot. Well, bye-bye. The lecture will begin
in two minutes.
Mohammed: See you at the library. Bye.
Упражнение 9. а) прочитайте диалог (упр. 8), найдите и выпишите английские эквиваленты следующих слов, словосочетаний и фраз:
жаль, что не могу пойти с тобой; свободное посещение лекций; учебная (академическая) группа; заниматься по собственному плану; занятия с руководителем/тьютором; предлагать (рекомендовать) литературу, которую следует прочитать; письменная работа студента; исправлять и оценивать (работу); критический анализ; читать лекции; проводить научные исследования
б) расскажите о работе тьюторов со студентами-медиками в Великобритании, используя выписанные при выполнении задания. «а)» слова и словосочетания
Упражнение 10. Джоан Петерсон - студентка медицинского факультета Лондонского университета. На встрече английских и русских студентов Джоан рассказывает о системе высшего медицинского образования в Англии. Попросите ее ответить на интересующие вас вопросы.
Упражнение 11. Студенты
вашей группы дают интервью корреспонденту английского молодежного
журнала. Основная тема интервью - сравнение систем подготовки
медицинских специалистов в нашей стране и в Великобритании. Что вы расскажете корреспонденту?
Чтобы отметить сходство, начните со следующих слов: What we have in common is...; The similar aspects are...; Both in Russia and in Great Britain... .
Чтобы отметить различия, начните со следующих слов: The major difference is...; Unlike (the British system of medical training...); In contrast to ( the Russian students...).
HEALTH SERVICE IN GREAT BRITAIN
Упражнение 1. Прослушайте (прочитайте) и запомните следующие словосочетания. Переведите предложения.
1. to pass an act through Parliament утвердить законопроект в парламенте
The National Health Service Act was passed through Parliament in 1946.
2. to receive the Royal Assent получить одобрение Королевы. The National Health Service Act received the Royal Assent in 1948.
3. the United Kingdom = the U.K. Соединенное Королевство Великобритании.
The United Kingdom unites England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland.
Упражнение 2. Прослушайте и повторите за диктором (преподавателем) следующие слова.

Упражнение 3. Прослушайте (прочитайте) и переведите следующие гнезда слов, указав, какой частью речи являются эти слова (обратите внимание на словообразовательные суффиксы).
to
administer, administration, administrative; to provide, provision,
provisional; to satisfy, satisfaction, satisfactory; to specialize,
specialization, specialist, specialty; to consult, consultation,
consultant
Упражнение 4. Определите, от каких глаголов образованы данные существительные, и переведите их.
service, introduction, contribution, treatment, payment, prescription, appointment, reception, consultation, discussion
Упражнение 5. Прочтите и переведите текст.
Health Service in Great Britain
A
delegation of Russian doctors went to Great Britain on a return visit.
They were met by the British doctors who had been the guests of
the
Russian Medical Workers' Union last year. The Russian doctors visited
the Health Centre in Hampshire and some hospitals in London, Liverpool
and Aberdeen. Now they are having a talk with their British colleagues
on the health care system in Great Britain.
Dr. Sharova, head of the Russian delegation: Dear
colleagues. During our stay in Great Britain we visited many medical
institutions. The doctors kindly acquainted us with their work. We were
told that the National Health Service Act was passed through
Parliament in 1946 and in 1948 this Act received the Royal Assent and
was brought into operation. And what about Scotland and Ireland?
Dr. McDonald: Similar
services operate in England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland.
Further administrative changes were introduced by a number of other
Health Service Acts.
Dr. Kelly: I'd
like to say that most medical treatment in our country is free, but
charges are made for drugs, spectacles and dental care. Free emergency
medical treatment is given to any visitor from abroad who becomes ill
while staying in our country. But those who come to England
specifically for treatment must pay for it.
Dr. Nikitina: The
National Health Service provides free medical care both in hospital
and in the out-patient clinic. So you have no private patients in Great
Britain, have you?
Dr. Sharland: Not
quite so. People may use the NHS or they may go to doctors as private
patients. In big cities there are some private hospitals which people
may use. Many people who have enough money still prefer to be private
patients because they think that they can in that way establish a
closer relationship with the doctor or because they do not want to be
put in a large room with other patients.
Dr. McDonald: I'd
like to add that a patient in our country can choose between NHS or
private treatment at any time. Moreover he can take some of his medical
care through the NHS, and some privately. If a patient is dissatisfied
with his NHS family doctor or dentist, he may change to another one. In
fact, 97 per cent of the population use the NHS.
Dr. Kruglov: What is the role of the family doctor in the Health Service system?
Dr. Kelly: The
role of the family doctor (General Practitioner) is very important.
Not all patients need highly specialized attention and the GP does
invaluable work by filtering off 90 per cent or so of the total medical
work.
Dr. Sharova: You
told us that if a patient is dissatisfied with his family doctor he
may change to another one. And what about the doctors? Does this freedom
of choice apply to them?
Dr. McDonald: Yes.
This freedom of choice applies to doctors and dentists too. They can
choose whether they want to join the NHS or not, and whether they will
have NHS patients or private ones. In fact, the majority work in the
NHS.
Dr. Kruglov: We
visited the St. Thomas' and St. Bartholomew's Hospitals in London and
noticed that they are small hospitals with about 200 beds. They are
housed in inconvenient buildings. Can such small hospitals provide a
full range of medical service?
Dr. McDonald: You
see, we do have modern hospitals but half of the buildings are over
100 years old. 70 per cent of our hospitals are small, with only about
200 beds. Such hospitals are not economical and cannot provide a full
range of service, which requires a district hospital of 800 beds or
more. Now we have more than 150 health centres in the U.K. The first
Scottish health centre was opened in Edinburgh in 1953. These health
centres are an integral part of a unified comprehensive health service.
Health centres provide all the special diagnostic and therapeutic
services which family doctors may need, such as electrocardiography,
X-ray, physiotherapy and good administrative and medical records
systems. Family doctors work in close cooperation with the hospital
doctors. Health centres are the basis of primary care.
Dr. Nikitina: Are there consultant services in such health centres?
Dr. Sharland: There
are centres which provide consultant services in general medicine and
surgery, ear-nose-throat diseases, obstetrics and gynaecology,
ophthalmology, psychiatry and orthopaedics. All consultations in the
centre are by appointment only. The patient is given a definite time at
which to attend. This is recorded on a card for him. Each doctor
decides for himself how many patients he can examine in one hour. We
believe that the patient is the most important person in the health
centre and that we should direct all our energy towards helping him as
much as possible.
Dr. Sharova: Dear
colleagues, thank you ever so much for the warm reception, for this
interesting discussion and for the opportunity to get acquainted with
the health service system in your country.


Упражнение 6. Прочтите вопросы, которые были затронуты в беседе английских и русских врачей. Ответьте на эти вопросы, используя текст.
1. When was
the National Health Service Act brought into operation? 2. Are there
private patients in Great Britain? 3. Why do many people who have
enough money prefer to be private patients? 4. What is the role of the
family doctor in the National Health Service system? 5. What is the
role of health centres in the health service system in Great Britain?
6. Are there consultant services in health centres?
Упражнение 7. Подтвердите следующие суждения. Используйте в ваших высказываниях следующие словосочетания:
Yes, I agree that...; Yes, as far as know It is true that... .
1.
The general practitioner services include the family doctor service,
the dental service, the pharmaceutical service, and the ophthalmic
service. 2.The GPs do very important work, which consists in filtering
off 90 per cent of the total medical workload. 3. Health centres are
institutions where various medical services, both preventive and
curative, are brought together. 4. The patients are the most important
people in the health centre and the doctors should direct all their
energy towards helping them as much as possible.
Упражнение 8. Приведенные в случайном порядке высказывания взяты из беседы врача и его пациента:
а) запишите эту беседу, поставив высказывания в логической последовательности
б) прочитайте свой диалог и скажите, в помощи хирурга или терапевта нуждается больной.
Dr. Young: Good morning, Mr. Hollister./ Are you still taking your digitalis?/ I believe you have hardening of arteries (облитерация артерий) with heart involvement (поражение сердца)./
How are you getting along? / Now your heart is not able to perform the
work it is supposed to./ Regarding your treatment, I think you should
continue to take one tablet of digitalis daily and stay on a salt free
diet./ You need to do this indefinitely, otherwise (иначе)
you'll get into trouble./ What seems to be the problem?/Three weeks
from today. Good-bye now and be careful ./ Do you put any salt in your
food?
Mr. Hollister: I've
not been feeling well for the last week./Well, Doctor, I've been not
taking digitalis for the last week./ Doctor, could you tell me what my
problem is?/When shall I come back?/ I've had some shortness of breath,
and as you can see, my legs are swollen now./ Bye. See you in three
weeks then./ I find it hard to eat completely without salt./
Упражнение 9. Прочитайте текст беседы врача и пациента еще раз. Ска- жите, какие утверждения соответствуют содержанию беседы.
1. а) Больной жаловался на одышку и отечность ног. б) У больного не было жалоб на одышку. 2. а) Больной принимал по одной таблетке дигиталиса в течение недели, б) Больной не принимал дигиталис в течение недели. 3. а) Больной чувствовал себя хорошо. б) У больного была сердечная недостаточность. 4. а) Врач посоветовал больному придерживаться бессолевой диеты. б) Больной соблюдал бессолевую диету.
Упражнение 10. Вы ведете прием. Составьте беседу врача и больного с подозрением на стенокардию. Используйте данные слова, словосочета- ния и фразы.
Where
does it hurt?, Can you describe the pain?, What makes it worse?,
complaints, to complain of, to have troubles with the heart, to have
pain in the heart, the character of the pain, dull pain, sharp pain, to
have pain on physical exertion, arterial pressure, angina pectoris,
cardiac failure
Упражнение 11. Прослушайте (прочитайте) диалог. Какой анамнез со- бирает врач? Перечислите основные вопросы, которые были заданы больному.
Dialogue
Dr. Harper: Have you ever been sick before?
Patient James Ross: Yes, sir. I have had scarlet fever and pneumonia.
Dr. H.: Have you ever had measles? Chicken-pox? Whooping cough?
Patient: Yes, sir. I had all the childhood diseases.
Dr. H.: How about adult illnesses, have you ever had ТВ, jaundice, heart or kidney trouble?
Patient: No, I have only had the ones I just told you.
Dr. H.: Have you ever been operated on? Have you ever had any operations?
Patient' Yes, several. I've had my appendix out. And I've also had my tonsils operated on.
Dr. H.: Did you ever break any bones?
Patient: I broke my arm when I was a child and that's all.
Dr. H.: Are your parents living?
Patient: No, both are no longer living. My father died of natural causes and my mother died of cardiac insufficiency.
Dr. H.: Do you have brothers and sisters? Are they in good health?
Patient: I have two brothers, one is living and the other is not. He had a stroke. My sister has diabetes.
Dr. H.: Are you married? Do you have any children?
Patient: Oh, yes. I'm married. I have two boys and they seem to be all right.
Dr. H.: Do you smoke?
Patient: I smoke 10 cigarettes a day. I tried to quit twice, but with no success.
Упражнение 12. Прочитайте диалог еще раз и составьте рекомендации для студентов по сбору анамнеза жизни и семейного анамнеза. Используйте следующие фразы: To
take a past history and a family history, you should ... , You will
also need the information about... , Remember to ask your patient ... ,
It is important to know ... .
Упражнение 13. а) прочитайте текст и скажите, какие органы и функции обследует врач при осмотре больного
б) назовите основные этапы физикального обследования, используйте следующие фразы: First
it is necessary to...; The next step is to...; The physical
examination also includes...; It is important to...; Finally, ... .
Doing the Physical Examination
Dr.
Hudson came closer to the patient. He noted the patient's general
appearance and checked the skin and mucous membranes carefully. With an
ophthalmoscope he examined the eyegrounds; and with the otoscope - the
tympanic membranes. He checked the patient's neck and chest.
Dr. Hudson
asked the patient to take a deep breath and hold it. Then to blow the
air out and hold it. Then not to breathe at all. Then he wanted the
patient to breathe in and out through his mouth and to say -
«ninety-nine, ninety-nine»...
Dr.
Hudson asked the patient to lie down on the examining table and
palpated the abdomen. The patient had no pain in the abdomen.
After
checking the patient's back and extremities, he took the reflex hammer
and checked the reflexes. He then checked the patient's blood
pressure. It was 120 over 70. That was normal. The doctor's plan was to
have some laboratory tests done the next day including blood and urine
tests, and an X-ray of the stomach. He invited the patient to come to
discuss the diagnosis and treatment after he would have received the
tests results.
Упражнение 14. Вы участвуете в конференции на тему «Медицинское обслуживание в Англии». Студенты вашей группы подготовили доклады по следующим темам.
1. The character of health service in Great Britain. 2. The types of patients receiving medical treatment and care in
Прослушайте доклады и задайте вопрос каждому выступающему.