Английский язык : учебник / И. Ю. Марковина, З. К. Максимова, М. Б. Вайнштейн; - 4-е изд., испр. и перераб. - 2010. - 368 с.
|
|
|
|
IV. PATHOLOGY
LESSON FIFTEEN
OSTEOMYELITIS. FRACTURES
Повторение: Времена группы: Indefinite (Active and Passive Voice) (?? 10, 14)
Часть I
Слова к части I


Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Найдите и определите время и залог глаголов-сказуемых в следующих предложениях.
1.
The earlier investigators of bacteria thought of them as tiny animals
which were generally grouped together with the microscopic animals
called protozoans. 2. Probably the bacteria are made up of various
kinds of organisms, some are related to algae, others to fungi. Future
research will doubtless throw more light on such relationship. 3.
Before the middle of the nineteenth century, the word «virus» was
commonly applied to all toxic or poisonous substances, including snake
venom. 4. Viruses are distinguished from poisons and venoms because of
their infectious quality.
Упражнение 2. Прочтите первый абзац текста А. Обратите внимание на произношение медицинских терминов.
Упражнение 3. Образуйте производные слова согласно данной модели и переведите их.
Существительное + -ed = прилагательное: mark знак, метка, след; черта; известность - marked отмеченный, заметный; значительный, известный.
fur (мех; налет на языке); bruise (синяк); fracture (перелом); disease; dress
Упражнение 4. Прочтите и переведите данные однокоренные слова.
1.
distant, distance, distantly; 2. evident, evidence, evidently; 3. to
inflame, inflamed, inflammable, inflammation; 4. to suppurate,
suppurative, suppuration; 5. severe, severely, severity; 6. region,
regional
Упражнение 5. Прочтите и переведите следующие словосочетания.
X-ray
evidence, inflammation of lungs, abdominal region, regional operation,
severe pain, attack of coughing, to be severely ill
Упражнение 6. Просмотрите текст А и назовите основные симптомы ос- трого остеомиелита.
Text A Acute Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis
is generally caused by Staphylococcus, which reaches the bones via the
blood stream from a distant focus, often a throat infection. Its rise
was especially sharp during World War II, particulary in 1942-46 when
the lack of due antibiotics made the disease uncured.
2. The
disease generally affects the upper end of tibia or lower end of
femur. The infection is followed by intense reaction, with pus
formation in the marrow spaces. From there the suppuration spreads
along the marrow cavity and also through the cortex, to erupt on the
surface and form a subperiosteal abscess. In some cases the marrow
cavity is widely involved; in others, on the contrary, there is a large
subperiosteal abscess, but little or no pus within the bone.
3. Almost
always part of bone becomes necrotic, due to the toxic effect of pus
under tension and to obliteration by the subperiosteal abscess of the
periosteal vessels supplying the bone cortex. The main nutrient artery
itself may be thrombosed, leading to necrosis of the major part of the
bone.
4. Acute
osteomyelitis generally affects children, especially if in poor
health, after an infectious fever. Sometimes there is a history of
minor injury to the part a few days before the onset of acute symptoms.
6. Acute
osteomyelitis is a dangerous disease, especially when it affects a
deep-seated bone, such as the upper end of the femur, pelvis or
vertebrae. In those who survive the acute phase the disease often
persists as chronic osteomyelitis. Eventually complete restoration of
functions and general health will be expected in most cases, when
appropriate treatment is applied.
Упражнение 7. Прочтите и переведите текст А. Абзац 5 переведите письменно.
Упражнение 8. Найдите в тексте А ответы на данные вопросы.
1.
What kind of diseases is osteomyelitis. 2. When was its rise
especially sharp? Why? 3. What is osteomyelitis caused by? 4. Where
does the infection localize? 5. What is the course of the disease? 6.
How does the disease begin in a typical case? 7. Does the disease
persist as a chronic one or is complete restoration of functions and
general health possible?
Упражнение 9. Переведите данные предложения. Определите, какой частью речи являются выделенные слова.
1. The disease generally affects the upper end of tibia or lower end of femur. 2. The infection is followed by intense reaction, with pus formation in the marrow spaces. 3. Almost always part of the bone becomes necrotic, due to the toxic effect of pus under the tension. 4. The main nutrient artery itself may be thrombosed.
Упражнение 10. Найдите в каждом абзаце предложения, выражающие основную мысль данного абзаца. Выпишите их.
Упражнение 11. Найдите в каждом ряду слово, синонимичное по значению первому слову ряда.
1.
distant - obvious, remote, far-away, distinct, close; 2. to involve -
to invent, to include, to invite, to affect; 3. to spread - to go over,
to divide, to distribute, to cover, to scatter; 4. onset - attack,
beginning, process, turning-point; 5. severe - low, short-turn, acute,
chronic; 6. region - locality, district, area, part, partition
Упражнение 12. Найдите в каждом ряду слово, противоположное по значению первому слову ряда.
1.
acute - dye, due, dull, dry; 2. minor - main, general, major,
important; 3. evident - unclear, obscure; 4. appropriate - unsuitable,
unfitting, common; 5. deeply - above, outside, superficially
Упражнение 13. Поставьте глаголы-сказуемые в форму действительного залога.
1.
Acute osteomyelitis is generally caused by Staphylococcus aureus. 2.
The infection was followed by intense reaction with pus formation in
the marrow spaces. 3. After hospitalization he was prescribed
appropriate treatment at home by his family doctor. 4. The wound will
be dressed by her every second day.
Упражнение 14. Переведите следующие предожения на английский язык письменно.
1. Ее отправили в больницу два дня назад. 2. Доктор сказал, что нужна срочная операция. 3. При остеомиелите поражаются кости. 4. Гипсовую повязку снимут через три дня. 5. Рана зажила и больному разрешили двигаться. 6. При остеомиелите в костном мозге образуется гной.
Часть II Слова к части II

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Прочтите и переведите следующие слова.
communication, position, to restore, correct, to protect, irregularly, especially, to fix
Упражнение 2. Найдите в данном ряду слово, значение которого дано в начале ряда.
1. повреждать (наносить ущерб) - to wound, to hurt, to damage, to harm; 2. заживлять - to cure, to restore, to heal, to treat; 3. выпол- нять (завершать) - to fulfil, to complete, to finish; 4. рвать, ранить - to separate, to lacerate, to tear
Упражнение 3. Назовите корневые слова, от которых образованы данные производные, и переведите их на русский язык.
1.
relation, relationship, relative, relatively; 2. tenderly, tenderness,
tender-hearted; 3. swelling, swelled; 4. dressed, dressing
Упражнение 4. Прочтите текст В (10 мин). 1) Скажите, какие типы переломов описаны в тексте. 2) Найдите в тексте предложения с глаголом- сказуемым в действительном и страдательном залоге. Укажите время сказуемого. 3) Переведите предложения.
Text В Fractures
A fracture is a broken bone. There
may be different types of fractures. A closed or simple fracture
results from an injury which breaks a bone without causing any external
wound at the site of the break. In case of an open or compound
fracture there is a wound of the skin at the site of the fracture, and
this will allow communication between the outside air and the broken
bone, therefore it is «open». When the sharp ends of a broken bone
damage an internal organ such as the brain or lungs, this is known as
«complicated fracture».
In
compound fractures early and prompt healing with good function will be
obtained only by early repositions in correct position. This is
necessary not only to restore the bone structures, but to place the
soft parts in relationship for correct function as well. All compound
fracture patients must be protected against movement, muscle spasm, and
loss of position. This is accomplished by fixation of fracture
fragments in plaster of Paris casts1 or in any other way. Frequent dressing of wounds in compound fractures is unnecessary.
What
are the symptoms and signs of a fracture? Shock is always present in
some degree with any fracture. Sometimes it may be severe. Pain and
tenderness at the site of fracture is quickly followed by bruising and
swelling. Bleeding is frequent in case of an open fracture.
Irregularity on the surface of the bone may also be seen, e.g. on the
collar-bone or the bone of an arm. In an open fracture the ends of the
broken bone may be sticking out of the wound. A person's leg which was
broken may be turned underneath him with the foot turned round the
wrong way. The bones of the leg may be bent in a place where there is
no joint, e.g. between the knee and the ankle if both bones of the leg
are broken.
First-aid treatment of fracture. Lay
the patient down. This will lessen shock. If there is a fracture of
the skull raise the patient's head and shoulders a little and support
them. Stop bleeding if the fracture is open, and apply a dressing. In
all open fractures there is some bleeding, but it can generally be
stopped by putting on a dressing. If bleeding continues, it is
necessary to use indirect pressure, especially if the bleeding is from
an artery.
Fix
the damaged part so that any movement by the patient cannot cause the
broken bone to move, as this will increase the deformity, cause great
pain and make shock worse.
Notes
1. plaster of Paris cast гипсовая повязка
Упражнение 6. Найдите в тексте предложения, более полно выражающие мысль данных суждений, и прочтите их.
1. There may be different types of fractures: closed, open, complete.
Упражнение 7. Передайте основное содержание текста В.
Часть III
Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 15
Упражнение 1. Укажите, в каких предложениях глагол стоит в страдательном залоге.
1. The bones of the leg were bent between the knee and the foot.
(Ответ: 1, 4, 5, 6. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 4 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 2. Определите, в каких предложениях глагол to be является: а) частью страдательного залога; б) глаголом-связкой.
1. If the limb is distorted consult a traumatologist.
(Ответ: a) 1, 2, 5, 6; б) 3, 4, 7. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 15 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 3. Выберите правильные значения выделенных слов.
1. They dreamed of (мечтали, видели во сне) becoming surgeons after they graduated from the Institute. 2. They learned (учить, изучать, узнавать) that their group would begin their practical studies on Friday. 3. Their practical studies in surgery will begin at the surgical department (кафедра, факультет, отдел, отделение).
LESSON SIXTEEN
CORONARY HEART DISEASES
Повторение: Времена группы Perfect (Active and Passive Voice) (?? 12, 14)
Часть I
Слова к части I

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Найдите глаголы-сказуемые в следующих предложениях. Определите их время и залог.
1.
The marked increase in patients entering emergency rooms in hospitals
has resulted in a need for increasing facilities in almost every
hospital. 2. The patient was examined for an injury to his leg which
had been broken in an automobile accident. 3. Four weeks later the deep
abrasions of the thigh were skin grafted. 4. If a bone in the forearm
is broken the splint must reach above the elbow and extend below the
wrist. 5. For thousands of years mankind had accumulated knowledge in
surgery, but real development in this field of medicine started only in
the 19th century. 6. By the end of the week we shall have explored surgically the posterior tibial artery.
Упражнение 2. Образуйте 2 пары предложений от данных ниже: а) с глаголом-сказуемым в Present Perfect (Active, Passive); б) с глаголом- сказуемым в Past Perfect (Active, Passive) согласно образцу.
Образец: The nurse (to dress) the patient's wound.
1. The nurse has dressed the patient's wound. The pa- tient's wound has been dressed by the nurse.
2. The nurse had dressed the patient's wound. The pa- tient's wound had been dressed by the nurse.
1.
The teacher (to demonstrate) open fracture of the thorax. 2. The
physician (to examine) the boy with osteomyelitis. 3. He (to apply)
plaster of Paris cast. 4. The students (to see) patients with a
complicated fracture.
Упражнение 3. Прочтите и переведите следующие слова и словосоче- тания.
heart,
coronary, contraction, approximately, surface, diabetic, per cent,
angina pectoris, obesity, fortunately, degenerative, severity
Упражнение 4. Запомните значение суффикса -ness. Образуйте существительные от следующих прилагательных согласно модели и переведите их.
Прилагательное + -ness = существительное со значением качества или состояния: acute острый - acuteness острота. ill, sick, excessive, distinctive, calm
Упражнение 5. Прочтите и переведите следующие гнезда слов.
1.
to expert - experience, experienced; 2. to die - death, deadly, dying;
3. to cease - cessation, ceaseless; 4. to obstruct - obstructive,
obstruction; 5. to recover - recovery, recoverable
Упражнение 6. Прочтите и переведите следующие словосочетания.
to recover sight (hearing, voice, one's breath, consciousness); deadborn; to experience pain; an obstruction in the throat
1.
The coronary blood vessels surrounding the heart have derived their
name from the fact that they encircle the heart like a crown, or
corona. These vessels transport almost a half pint of blood every
minute over the surface of the heart. Any sudden blockage of one of the
coronary arteries deprives that section of the heart of its blood
supply. Cardiac cells die, heart contractions may cease, and
circulation may come to a standstill. If a coronary artery is completely
plugged, the condition is called a
nary occlusion or heart attack. The vascular pathologic disorder itself has been very variable. If the obstruction is only partial or in one of the smaller coronary tributaries, prompt treatment often leads to the individual's recovery. An occlusion in main coronary arteries is very serious and may cause sudden death. Other causes of the coronary disease in-
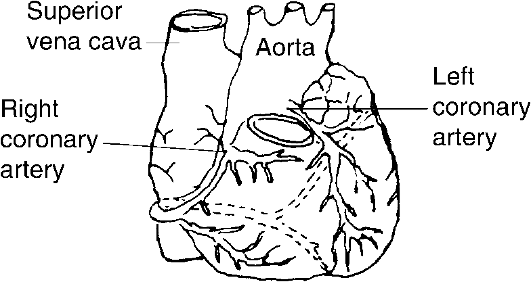
Fig. 14. Coronary arteries supplying the heart
clude heavy physical exercise, aging, dietary habits, obesity, smoking, or hypertension.
2. Pain
which had been developed in the heart may be due to a bloodflow
deficiency in the coronary vessels. This is referred to (actually felt
in) the left arm and shoulder. Such pain from the heart has been called
angina pectoris. Angina pectoris may not actually be noticed until the
work load is too great in relation to the flow in the coronary
vessels. People who had experienced it repeatedly often do not feel
pain unless they experience strong emotion. Others experience it much
of the time.
3. Fortunately,
the great majority of coronary disease patients will have recovered
and have been able to lead active, useful lives, when they receive
proper treatment under good medical supervision. There are many
preparations which have been effective and are under clinical
investigation at the present time.
Heart and Artery Diseases
4. Heart
and artery diseases have been presently the number one health problem
in the world. Cardiovascular ailments are by far the chief
causes
of illness, disability, and death among both middle-aged and elderly
people. Among these, coronary heart disease, illness of the blood
vessels supplying the heart, is responsible for the greatest number of
deaths (over 50 per cent of all cardiovascular diseases). Causes of
other cardiovascular disease deaths, in order of decreasing importance,
are stroke and hypertension. These three diseases are responsible for
more than 80 per cent of all cardiovascular disease deaths.
5. Like
cancer and emphysema, heart diseases appear to be related to the
extension of the average life span. Certain factors are definitely
involved in the high incidence of heart disease - the stress, diets
high in saturated fats, the tendency toward obesity with age, lack of
sufficient physical exercise, and the incidence of smoking. These
factors appear to relate to a higher incidence of heart desease than in
societies lacking these characteristics.
6. The
severity and danger of heart and artery diseases which we had
previously described cannot be minimized; a disease in an arm or leg
may cripple a person, but a disease of the heart may lead to his death.
Упражнение 9. Прочтите и переведите текст А. Абзацы 2 и 3 переведите письменно.
Упражнение 10. Найдите в тексте А ответы на следующие вопросы и прочтите их.
1.
What kinds of cardiovascular diseases have been discribed in text A?
2. What does the sudden blockage of the coronary artery result in? 3.
What are the conditions caused by coronary occlusion? 4. What is angina
pectoris? What do people experience in this condition? 5. Why heart
and artery diseases have been recently the number one health problem in
the world?
Упражнение 11. Составьте письменно план текста А.
Упражнение 12. Передайте основную мысль абзацев 4 и 5 текста А одним- двумя предложениями.
Упражнение 13. Вставьте подходящие по смыслу слова в данные предло- жения: fortunately, approximately, also.
1.
... , the great majority of coronary disease patients recover and are
able to lead active, useful lives if they receive proper treatment
under good medical supervision. 2. ... one fourth of all deaths in the
world result from coronary artery disease. 3. ... it is estimated that
more than
one out of every ten persons suffers some degree of insufficiency of blood supply to the heart.
Упражнение 14. Дайте синонимы к следующим словам.
to cease, obstruction, illness, serious, majority
Упражнение 15. Прочтите и переведите текст. Объяшите употребление глагольных времен и залога.
Twenty
patients with arterial occlusion have been treated by systematic
infusions since May. In many of these patients the obstruction had been
present for so long that irreversible changes had already taken place.
Obstruction in eleven patients was of more than twenty-four-hours' duration and in four was more than forty-eight hours old.
Only
eight patients were treated within twenty-four to thirty hours of the
onset of the obstruction. Of these five (62 per cent) had complete
return of circulation. Return of circulation usually occurred after ten
to twelve hours of continuous intravenous therapy. It became apparent
that even though improvement was obtained by one course of treatment,
this did not assure a permanent response. The reasons for this are
probably multiple and include: 1) a nidus of thrombus may remain on
which complete rethrombosis can develop and 2) intimal damage remains
as a source of rethrombosis. For these reasons we have repeated
treatment for two to three days with the expectation that all thrombus
will be eradicated and the vessel wall will have a chance to repair
itself.
Часть II Слова к части II

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Найдите корневые слова, от которых образованы данные производные, и переведите их на русский язык.
normally, presented, frequently, increasing, imbalance, excessive, weakened
Упражнение 2. Прочтите текст В (10 мин). 1) Назовите симптомы гипер- тонии. 2) Найдите предложения с глаголом-сказуемым в действительном и страдательном залоге в форме Perfect. Укажите время, которым выражены сказуемые. 3) Переведите эти предложения.
Text В Hypertension
Hypertension
simply means high blood pressure. As a normal heart pumps blood
through the body, a certain degree of pressure is excreted against the
blood vessels. With each beat of the left ventricle, a wave ol pressure
starts at the heart and travels along the arteries. This wave is
called the pulse. The pulse can be felt on any arteries that are close
to the surface of the body, such as on the wrist, the sides of the
throat and the temple. The pulse results from the blood pressure. The
blood pressure at the moment of contraction is the systolic pressure; it
should normally be sufficient to displace about
Hypertension
is very common. It is believed that about one out of every five
individuals suffers from it and that about 13 per cent of all deaths
are a direct result of it. Recently hypertension has become more common
with increasing age and now it affects men about twice as often as
women.
In
about 90 per cent of the known cases, it has been described as
essential hypertension, a hereditary condition. In other cases it may
be due to the removal of a kidney, kidney disease, excessive narrowing
of the arteries, hormone imbalance, or excessive salt in the diet.
It
has been known for many years that hypertension is damaging for two
reasons: 1) it puts an excess work load on the heart and the left
ventricle in particular; 2) the arteries may be damaged by excessive
pressure. A hypertensive patient tends to develop cardiovascular
ailments much sooner than a person who has not suffered from
hypertension.
This high
blood pressure in the arteries causes a hardening (sclerosis) of blood
vessels all over the body. The vessels become weakened; clots tend to
form in them much more easily; some vessels rupture and haemorrhage.
For centuries haemorrhage in the vessels of the brain (cerebral
haemorrhage) and vessels of the kidneys has been known to be
particularly destructive.
Упражнение 4. Найдите в тексте В предложения, более полно выражающие мысль данных суждений, и прочтите их вслух.
1.
The pulse results from the blood pressure and can be measured. 2.
There is systolic and diastolic pressure. 3. Hypertension is very
common. 4. The causes of hypertension may be different. 5. Hypertension
is damaging for two reasons. 6. Hypertensive patients have tended to
develop cardiovascular ailments.
Упражнение 5. Передайте основное содержание текста В письменно, использовав в качестве плана предыдущее упражнение.
Часть III
Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 16
Упражнение 1. Укажите, в каких предложениях глагол-сказуемое стоит во временах группы Perfect.
1.
Cardiomyopathy has been defined as «acute, subacute, or chronic
disorder of heart muscle of unknown or obscure etiology». 2. Apart from
discomfort in his chest he had no history suggestive of myocardial
infarction or angina.
(Ответ: 1, 4, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ?? 12, 14 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 2. Укажите, в каких предложениях глагол-сказуемое стоит в форме страдательного залога.
1. The patient was admitted to the hospital with essential hypertension. 2. The woman responded slowly to diuretic therapy.
grossly
dilated with very poor movements of all areas. 6. Gross mitral
incompetence had not been suspected clinically previously.
(Ответ: 1, 4, 5, 6. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 14 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 3. Переведите данные гнезда слов на английский язык.
1. опыт, испытывать, огштный; 2. умирать, смерть, умерщвлять, смертельно; 3. прекращать, прекращение, непрерывный; 4. непроходимость (закупорка), мешающий, закупоривать; 5. выздороветь, выздоровление
LESSON SEVENTEEN
RESPIRATORY INFECTIONS
Повторение: Времена группы Continuous (Active and Passive Voice) (?? 11, 14)
Часть I
Слова к части I

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Найдите сказуемые в следующих предложениях. Определите их время и залог.
1. All control patients were receiving oxygen over a period of two hours.
3. 8
or 9 patients who were being injected with pentazocine for ten minutes
showed a rise of B.P. 4. Other studies have suggested that pentazocine
produces less sedation than the narcotics. 5. The patient had signs of
severe congestive failure due to aortic insufficiency. 6. When the
attendant physician entered the ward, patient P. was being injected
aminophylline intravenously.
Упражнение 2. Напишите исходные слова к нижеприведенным производ- ным и переведите их.
inside, specialized, irritation, respiratory, eventually, mucopurulent,
inflammation, bacterial, staining, to discharge
Упражнение 3. Прочтите и переведите данные гнезда слов.

Упражнение 4. Прочтите и переведите следующие предложения и словосочетания.
1.
bronchial tree; 2. the smoke irritates my eyes; a muscle contracts
when irritated by electricity; 3. to be infected with diphtheria; to
spread by infection; infection may be carried through the air
Упражнение 5. Просмотрите текст А. Передайте основное содержание каждой части.
Упражнение 6. Найдите в тексте А ответы на следующие вопросы и зачитайте их.
1.
Is the upper or lower part of the respiratory tract affected more
often? 2. What happens to the mucous membrane when it is being
inflamed? 3. What does the term «catarrh» indicate and what is the
condition of catarrhal inflammation characterized with? 4. What causes
bronchitis? 5. What are the symptoms of chronic bronchitis?
Text A
Infections of the Respiratory Tract
1.
While the slides were being prepared the lecturer announced the theme
to be discussed. He said: «The respiratory tract is subject to
infection more frequently than any other part of the body. Respiratory
infections stand third as a cause of deaths; they lead all other causes
between ages of fifteen and thirty-five. The upper portion of the
respiratory tract, the nose, throat and trachea, are affected more
often than the lower, the bronchi and lungs. The deeper the
inflammation, the more serious are its consequences; pneumonia is
frequently fatal. Inflammation of the deeper respiratory structures
results from a downward extension of a comparatively harmless
inflammation in the upper structures.»
2. All
the respiratory passages, except the deepest structures of the lungs,
are covered with the mucous membrane; when this tissue becomes inflamed
it is being swollen and there is a profuse flow of mucus. Pus
resulting from bacterial action is mixing with the mucus, making it
opaque and white or staining it yellow; the discharge is then said to
be mucopurulent. Inflammation of the mucous membrane is of the
so-called catarrhal type; the term «catarrh» indicates a chronic state
of inflammation.
Chronic Bronchitis
3. The
inside of the bronchioles is lined with a highly specialized membrane.
This membrane has a layer of mucus to trap the foreign matter that
have entered the lungs. Millions of hairlike cilia are constantly
sweeping the layer of mucus with its trapped foreign particles upward
to the throat where it is being swallowed.
4. Repeated
irritation of this ciliated mucous membrane can paralize the action of
the cilia, eventually destroy them and stimulate an excessive
production of mucus. This is the condition known as chronic bronchitis.
Since the cilia can no longer clear the lungs of mucus, it accumulates
until the flow of air through the bronchioles is obstructed. This
obstruction then evokes coughing that helps to clear the lungs.
Frequent coughing is the most important, prominent symptom of chronic
bronchitis. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath1 and wheezing.
5. The
main treatment of chronic bronchitis consists of eliminating the
irritation that causes it. The source of irritation is often smoking
tobacco. The so-called «smoker's cough» is in reality a symptom of
chronic bronchitis. The first step in treating any lung disorder is to
stop smoking. Coughing itself can contribute to the irritation of the
bronchioles. If the source of irritation is an infection the disease
will be receiving the treatment of a physician.
Notes
1. shortness of breath одышка
Упражнение 7. Заполните пропуски словами until, since, than, that, above all.
1.
The upper portion of the respiratory tract is affected more often ...
the lower one. 2. ... the cilia can no longer clear the lungs of mucus
it accumulates ... the flow of air through the bronchioles is
obstructed.
3. This obstruction then evokes coughing ... helps to clear the lungs.
4. ... chronic bronchitis should receive the treatment of a physician.
Упражнение 8. Определите значения выделенных слов в данных предло- жениях.
1. The cilia can no longer clear (разгружать, освобождать) the lungs. 2. Frequent coughing is the most prominent (заметный, известный, важный) symptom of chronic bronchitis. 3. The first step in treating (лечение, обработка) any lung disorder is to stop smoking.
Упражнение 9. Спишите первый абзац текста А и подчеркните в нем слова, которые могут быть опущены.
Упражнение 10. Прочтите и переведите письменно пятый абзац текста А.
Упражнение 11. Прочтите и переведите следующий текст, найдите глаголысказуемые во временах группы Continuous.
Mrs. Smith had bronchial asthma for four years, before she was admitted to the
Упражнение 12. Составьте план текста А письменно.
Часть II Слова к части II

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Прочтите текст В (10 мин.). 1) Разделите его на смысловые части. 2) Найдите и переведите глаголы-сказуемые во временах группы Continuous в действительном и страдательном залоге.
Text В Tobacco and its Effects
Tobacco
smoking is probably the most widespread and dangerous drug usage. The
cigarette consumption has generally been subject to certain factors.
For example, the greatest increases in smoking have occurred during
wars.
The
main reason for this periodic increase was that the population in
general experienced increased tension. Another reason for this increase
during wartime was that young soldiers were being introduced to
smoking as a tension reliever.
Despite
public information campaigns on the subject, too few smokers realize
the degree and extent of damage to their bodies associated with
cigarette smoking.
Minor ailments directly related to smoking compete with the common cold1 as major causes of the time lost from work and studies.
Recently,
studies of large groups of people have shown that cigarette smokers
are more likely to die of certain cardiovascular diseases than
non-smokers. A cause and effect association has theoretically been
established between cigarette smoking and incidence of coronary attacks
in humans, especially men between 35 and 55 years of age. The risk of
death in male cigarette smokers in relation to non-smokers is greater
in middle age than in old age. Smoking is being increasingly linked to
the development of respiratory diseases, such as bronchitis and
emphysema. Air pollution and respiratory infections as well as smoking
cause and aggravate chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
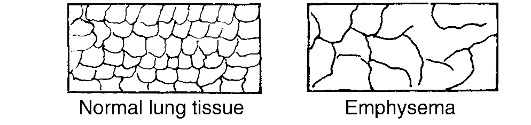
Fig. 15. Alveoli in normal lung tissue and emphysema
Smokers
are not only polluting their own air with their cigarettes but are
subjecting non-smokers, who make up three quarters of the population,
to nearly the same health risk. Subjected to the effects of sidestream
smoke, non-smokers may breathe in many of the toxic chemicals of the
cigarette from the environment they are in and are, in fact, «passively
smoking». «Side-stream smoke» produced from the burning end of the
cigarette contains very high concentrations of toxic chemicals which
are usually perceived as unpleasant by both smokers and non-smokers.
Allergic
reaction to smoke is common. Asthma, chronic bronchitis, emphysema or
ischemic heart disease sufferers experience reactions to passive
smoking that range from mild nasal congestion and eye irritation to
headache, dermatitis and even a few life-threatening asthmatic attacks.
People with advanced respiratory and cardiac breath literally fight
for life.
Tobacco
contains more than hundred known chemical compounds including
nicotine. Some of the substances found in tobacco remain in the ashes
of a burned cigarette; others are greatly changed during the burning
process. Moreover, additional compounds are being produced during
combustion, and it is some of these materials that are of great concern
to scientists and physicians. The composition of the cigarette smoke
that enters the human body has been the primary aim of most analytical
studies.
Nicotine
and at least 15 other compounds found in cigarette smoke are known to
be cancerogens - cancer-causing substances. When a person inhales
cigarette smoke, the smoke is passing down the trachea (windpipe) to
the bronchial tubes and into the lungs. Autopsies of hundreds of human
lungs have shown that it is precisely in these areas of maximum
exposure that precancerous changes are most likely to appear.
Thus there
are some relationships between smoking, lung cancer, and many other
respiratory conditions. Furthermore, cigarette smoke is itself an
irritant. Heavy smokers feel this irritation in their throats and will
be developing «smoker's cough» after a few years of smoking.
Notes
1. common cold простуда
Упражнение 2. Найдите в тексте В предложения, более полно выражающие мысль данных суждений, и прочтите их.
1. The cigarette consumption has been subject to certain factors. 2. Few smokers realize the degree of damage to their bodies associated with cigarette smoking. 3. Allergic reaction to smoke is common. 4. Tabacco contains hundred chemical compounds. 5. Cigarette smoke is an irritant.
Упражнение 3. Опишите вид альвеол в норме и при эмфиземе, используя текст и рис. 15.
Часть III
Контрольно-обобщающее упражнение к уроку 17
Укажите, в каких предложениях глагол-сказуемое стоит в форме страдательного залога во временах группы Continuous.
1.
Neither antibiotic was being used in the course of treatment. 2. Now
everything is done to prevent respiratory diseases. 3. 10 of twenty
experimental patients who thought that they were inhaling irritants or
allergens developed chronic asthma. 4. We were giving penicillin to the
patients with bronchitis from April to May and came to the conclusion
that it is not helpful in this case.
(Ответ: 1, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 14 Грамматического справочника.)
LESSON EIGHTEEN
JAUNDICE. PEPTIC ULCER
Повторение: Модальные глаголы can, may, must и их эквиваленты! (? 17)
Часть I
Слова к части I

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Напишите следующие предложения: а) в прошедшем времени; б) в будущем времени. Переведите предложения.
1.
You must follow all the new important medical researches in your
field. 2. By means of spirometry the dynamic lung volumes may be
assessed without difficulty. 3. He must investigate a series of case
reports before the lecture. 4. You may take your analyses in the
laboratory. 5. Chronic inhalation of cadmium fumes can cause chronic
progressive emphysema.
Упражнение 2. Переведите следующие предложения с модальными глаголами: can, could, may, might, must, shall.
1.
We could not detect any antibiotic activity in the sputum of our
patients. 2. The pre-treatment strains of two patients may be assumed
to be sensitive to streptomicin. 3. Thinking about asthma or hearing a
description of an attack can even provoke asthma. 4. Every physician
must know the pathology of chronic bronchitis and emphysema. 5. Heavy
physical activity shall not be resumed within the first three months
after an attack of myocardial infarction. 6. Professor explained that
dogs inhaling cigarette smoke over long periods might develop lung
damage.
Упражнение 3. Дайте исходные слова к нижеприведенным производным. stimulation, population, lining, investigation, accompanying
Упражнение 4. Прочтите и переведите данные гнезда слов.
1.
to investigate - investigator, investigation, investigatory; 2. bile -
biliary, bile-stained, bile-stone; 3. to complicate - complicated,
uncomplicated, complication; 4. serum - sera, serous
Упражнение 5. Прочтите и переведите данные словосочетания.
bile duct, bile colic (calculus), complicated system (problem, mechanism, apparatus), complicated disease
Упражнение 6. Просмотрите текст А и скажите, сколько типов желтухи описано в тексте.
Text A Jaundice
1. Perhaps
the most obvious symptom that may result from disease of the liver or
biliary passages is jaundice, and the estimation of the level of
bilirubin in the serum is to be therefore frequently carried out in the
investigation of a case of liver disease.
2. The
fact that sera from different cases of jaundice can give different
types of reaction has been used as a basis for differentiating between
different types of jaundice. Jaundice should be divided into three main
types, viz.: obstructive jaundice, hepatocellular or «toxic» jaundice
(with or without some degree of accompanying obstruction) and hemolytic
jaundice. In uncomplicated obstructive jaundice, liver function is
largely or wholly normal, so that the bile pigments are excreted
normally into the bile passages; but owing to the presence of some
obstruction (either a stone impacted in the common bile duct, or
obliteration of the duct by a carcinoma of the head of the pancreas) the
bile is unable to enter the duodenum and has instead to be re-absorbed
into the circulation. In hepatocellular jaundice the function of the
liver cells is changed so that they can not excrete the normal amount
of bile pigment reach- ing them in the blood stream. In this case
bilirubin level gradually rises. In hemolytic jaundice the excessive
amounts of bile pigment (which are formed as a result of the excessive
red cell destruction) are incompletely excreted by the liver cells and
have been re-absorbed from the obstructive bile passages. In
hepatocellular or obstructive jaundice the excess of circulating pigment
has not passed through the liver cells.
Упражнение 7. Просмотрите текст А и найдите предложения, в которых описываются симптомы каждого типа желтухи.
Упражнение 8. Найдите в тексте ответы на следующие вопросы и зачи- тайте их.
1.
What procedure has to be performed to diagnose a liver disease? 2. How
can a doctor differentiate between the types of jaundice? 3. How
many types of jaundice are there? 4. How does the function of the liver change in the cases of hepatocellular jaundice?
Упражнение 9. Прочтите и переведите данные слова.
perhaps, the fact that..., viz. (videlicet), so ... that, whereas
Упражнение 10. Составьте план текста А письменно.
Упражнение 11. Перепишите схему в тетрадь. Дополните ее.
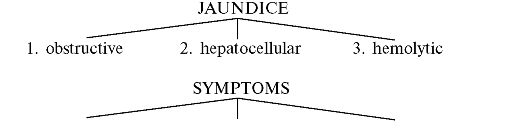
1. 2. 3.
Упражнение 12. Заполните пропуски модальными глаголами can, could; may, might; must; should.
1.
If you are ill you ... consult a physician and ... do what he says. 2.
Since one pack of 20 cigarettes contains 30 mg of cadmium, it is
possible that chronic inhalation of cigarette smoke ... lead to an
enhanced cadmium intake. 3. The patient who receives the blood of the
diseased donor ... develop a positive test for the hepatitis antigen
shortly after transfusion. 4. This patient had received 1 unit of blood
at operation and ... have viral hepatitis. 5. The patients with
jaundice ... be immediately transferred to an infectious hospital. 6.
Sera from apparently healthy blood donors ... be always tested for the
presence of hepatitits antigen.
Упражнение 13. Переведите следующие предложения с модальными глаголами и их эквивалентами.
1.
Infectious hepatitis with a short incubation period can also be
transmitted during blood transfusion. 2. There is experimental evidence
that the passive administration of IgG antibody interferes with the
synthesis of IgM antibody and in this way is able to alter the immune
response. 3. Some researchers suggest that the differences between
serum hepatitis and infective hepatitis might depend on whether a
common causative agent is or not bound by antibody. 4. The strong
association of the hepatitis antigen with acute viral hepatitis
increases the
suspicion
that donor blood containing the antigen may be infectious. 5. You should
take the drug three times a day before meals. 6. We had to examine
samples from normal subjects who had been exposed to hepatitis. 7.
Convalescent sera from patients with hepatitis may contain trace
amounts of antibody and require further study. 8. 10 patients were to
be studied with a clinical picture quite compatible with acute
hepatitis. 9. We were allowed to follow up sera in 27 of 49
experimental patients with positive reactions for hepatitis.
Часть II
Слова к части II

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Определите значения указанных слов в данных словосоче- таниях и предложениях.
1. condition - состояние, условие, заболевание;
in good, bad con- dition; under favourable conditions; Ulcer is a
common condition in any country. The patient is in a critical
condition.
2. to recognize - распознавать, признавать; An emotional stress is a commonly recognized factor. The disease is easily recognized.
Упражнение 2. Прочтите текст В (10 мин). 1) Разделите его на смысловые части. 2) Найдите и переведите предложения с модальными глаголами и их заменителями.
Text В Peptic Ulcer
Ulcer is a common condition.
What
causes ulcers? A peptic ulcer, as the name says, is an erosion in the
lining of the digestive tract as a result of the action of the enzyme
pepsin. An increase in the acid content of the gastric juice starts
pepsin
digesting
the mucosa. Most of the symptoms are ascribed to the high degree of
acidity of the juice. Not all persons with hyper-acidity must develop
ulcers. The second, commonly recognized factor is emotional stress.
Emotional stress produces conditions especially favourable to ulcer
formation. Peptic ulcer disease can be called a psychosomatic disease;
an actual bodily ailment, produced, or at least aggravated, by the
mental and emotional state.
There are two
very distinctive varieties of peptic ulcer - gastric and duodenal.
Although they are found in two different places-the stomach and the
duodenum respectively - they look alike and cause similar distress.
Gastric ulcer is caused by the hormone gastrin, secreted during the
gastric phase of digestion. Distention of the stomach lining causes
gastrin to be secreted from the antrum; gastrin in turn stimulates the
gastric glands to work overtime. Gastric ulcers bleed into the stomach
and may actually perforate the stomach wall.
Duodenal
ulcer, found in the first ten inches of the small intestine, is four
times as common as gastric ulcer. This is the «ulcer of stress»
mentioned earlier, though the psychic factor is also present in other
forms. The patient usually complains of a pain and «heartburn» after
meals (within the first hour in case of gastric ulcer, from three to
four hours after meal in duodenal ulcer). Besides the pain which the
patient is often unable to bear, he may also suffer from frequent
vomiting. If the gastric juice shows an abnormal concentration of HCl1, the diagnosis is practically certain.
Since the secretion of gastric juice is excessive in all forms of peptic ulcer, proper diet should be neccessary for the suppression of secretion. This means that the diet, instead of being appetizing, has to be monotonous, in order to suppress the appetite juice. Meat and alcohol are to be forbidden.
Notes
Упражнение 4. Найдите в тексте В предложения, более полно выражающие мысль данных суждений, и прочтите их вслух.
1.
Ulcer is a common condition. 2. The first cause of peptic ulcer is an
increase in the acid content of the gastric juice. 3. Not all persons
with hyperacidity develop ulcers. 4. Gastric ulcer may perforate the
stomach wall. 5. Duodenal ulcer is the ulcer of stress. 6. The proper
diet should be nesessary for normal secretion.
1HCl hydrochloric-acid - соляная кислота
Упражнение 5. Просмотрите еще раз текст В и выпишите предложения, несущие, на ваш взгляд, наиболее важную информацию.
Упражнение 6. Передайте краткое содержание текста, используя предыдущие упражнения и слова к тексту В.
Часть III
Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 18
Упражнение 1. Укажите, в каких предложениях модальные глаголы или их эквиваленты выражают долженствование.
1.
As the proportion of low titre sera was so high among hepatitis
patients, the percentages of anticomplementary sera had to be
calculated. 2. You should use ampicillin intramuscularly for treatment
of this infection. 3. Donors with a history of hepatitis are not
allowed to give blood. 4. Two of 18 patients were to receive spaced
transfusions during their hospitalization. 5. Since the antibodies in
commercial γ- globulin have a half-life of
about 32 days, high levels of hepatitis «antibody» from the two
injections must be present in the majority of patients.
(Ответ: 1, 2, 4, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 17 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 2. Найдите в левой колонке перевод слов из правой колонки.
1. to bring about 1. обращаться к кому-л.; применять
2. lesion 2. конкурирующий, конкурсный
3. to apply 3. еда, принятие пищи
4. application 4. быть причиной, вызывать
5. competitive 5. гниение, разложение, гнилость
6. putrefaction 6. рана, поражение
(Ответ: 1-4, 2-6, 3-1, 4-7, 5-2, 6-5, 7-3.)
Упражнение 3. Прочтите данные предложения и скажите, соответствуют ли действительности упоминаемые в них факты.
1.
Both duodenal and gastric ulcers are caused by hypersecretion of
gastric juice. 2. Gastric digestion is brought about by putrefaction.
3. Pure pancreatic juice or bile alone can produce a destruction of
mucosa.
juice occurs
in healthy individuals. 5. Physiologic mechanism of regulating gastric
secretion has been worked out by experimental studies on higher animals.
LESSON NINETEEN
KIDNEY DISEASES
Повторение: Функции причастий (?? 20, 21)
Часть I Слова к части I

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Прочтите и переведите следующий текст. Найдите пред- ложения, где употребляются I и II формы причастий.
Patients
with diseases requiring very large numbers of blood transfusions are
presumably exposed to hepatitis repeatedly and might be expected to
possess antibody against the hepatitis virus(es) or its products. When
employing sera from such repeatedly transfused individuals as antisera,
Blumberg et al. found an antigen in the serum of an Australian
aborigine which has become known as the
As previously mentioned, it seems likely that the
We
have detected a specific antigen in a high percentage (80%) of
patients with both forms of viral hepatitis. Patients studied were from
the wards and clinics of the Presbyterian, Francis Delafield, and
Упражнение 2. Прочтите и переведите данные слова. Запомните их значение.
severe, anorexia, variable, albumin, calculus (pl. calculi) radiopaque, thigh, spontaneously, descent, morphine
Упражнение 3. Прочтите и переведите данные однокоренные слова.
1.
ultimate, ultimately; 2. thigh, thigh-bone; 3. sign, to sign, signal,
signature, sign-board; 4. to incise, incised, incision, incisive
Упражнение 4. Просмотрите текст А. Передайте основное содержание текста.
Text A Stones in the Kidneys
1. Clinical manifestation. In
many instances stones are carried in the kidneys for years producing
no symptoms. More commonly, a mild infection develops in the pelvis
about the stone and gradually involves the cortex of the kidney until a
severe pyelonephritis develops. If the stone is large, or several are
present, the infection may progress to a pyelonephrosis, resulting in
the destruction and ultimate loss of the kidney. Mild fever, pain,
malaise and anorexia are usually present. Pus and a variable amount of
albumin are present in the urine. Such symptoms as frequency of
urination and mild burning pain usually accompany infection of this
type. The diagnosis of renal calculi can be made by an X-ray film since
most of these stones contain sufficient calcium to be radiopaque.
2. The
most dramatic manifestation of renal calculi is renal colic brought
about by the entrance of a stone into the ureter and its passage
downward to the bladder. The pain described usually radiates downward
toward the thigh. Hematuria is a constant symptom and is an important
diagnostic sign.
3. While
passing slowly, the stone may develop infection and pus as well as
bacteria will be found in the urine. Fever is absent except the
instances
when the obstruction is present long enough to allow the development
of infections. On rare occasions the stone produces sufficient
ulceration in the ureter during its passage. Differentiation of renal
colic from other acute abdominal conditions can usually be made by
urine examination, and X-ray.
4. Treatment. Unless
the renal stone is «silent», treatment should be directed toward its
removal. Most stones having entered the ureter will pass spontaneously
into the bladder by the prescuption of conservative treatment such as
forcing fluid, sedation, etc. During the attack of colic analgetics may
be required to control the pain; if after many days, there is no
evidence of progression in the descent of the stone, ureteral
catheterisation may be used in dislodging it. On rare occasions an
operation (usually extra-peritoneal with incision into the ureter)
should be performed to remove the stone. Large stones in the kidney
cannot be passed by way of the ureter and if symptoms are produced
operation is necessary. If the stones are present in both kidneys, it
is usually preferable to operate first on the kidney with the poorer
function, since the operation may produce a temporary anuria; if the
better kidney is the one operated on first, and temporary anuria
results, a fatal outcome may follow.
Упражнение 5. Просмотрите текст А еще раз и перечислите основные симптомы и способы лечения мочекаменной болезни.
Упражнение 6. Найдите в тексте А ответы на следующие вопросы и зачитайте их.
1.
Do stones in kidneys usually produce pyelonephritis? 2. What symptoms
help to diagnose renal calculi? 3. What is renal colic and how does it
manifest? 4. When is conservative treatment used in cases of renal
calculi? 5. What kidney is operated on first if the stones are present
in both of them and why?
Упражнение 7. Напишите возможные сочетания: а) глаголов и существи- тельных; б) прилагательных и существительных.

Упражнение 8. Прочтите и переведите аннотации. Скажите, какая из них передает содержание текста наиболее адекватно и более полно отвечает требованиям, предъявляемым к аннотации.
Stones in the Kidneys Clinical manifestation
Very often an infection about the stone causes pyelonephritis or pyelonephrosis, resulting in the loss of the kidney.
The
symptoms are mild fever, pain, malaise, anorexia, pus and albumin in
the urine, frequency of urination and mild burning. The diagnosis can
be made by X-raying. The pain toward the thigh, hematuria, on rare
occasions ulceration in the ureter, fever are signs and symptoms of
renal colic. Treatment should be directed toward its removal unless the
stone is «silent».
Stones in the Kidneys Clinical manifestation
In
many instances for years without symptoms. More commonly a mild
infection about the stone develops into pyelonephritis or if the stone
is large, into pyelonephrosis. Mild fever, pain, malaise and anorexia,
pus and albumin in the urine, frequency of urination and mild burning
pain accompany this infection. The diagnosis can be made by an X-ray
film. Renal colic is brought about by the entrance of a stone into the
ureter while passing downward to the bladder. The pain described
radiates toward the thigh. Hematuria is a diagnostic sign.
If
the stone is not passed rapidly, infection may develop: pus in the
urine, fever, when obstruction is present. Ulceration in the ureter is
rare. Urine examination and X-ray help to diagnose renal colic. Treatment. If
the stone is «silent», conservative treatment such as forcing fluid,
sedation, etc., is prescribed. Analgetics may be required during the
attack of colic. Ureteral catheterization, on rare occasions
extra-peritoneal operation with incision into the ureter is necessary.
If the stones are present in both kid- neys, it is preferable to
operate first on the kidney with the poorer function.
Упражнение 9. Раскройте скобки, выбрав нужную форму причастия. Переведите предложения.
1.
One week prior to the admission, the patient developed diarrhea
(associated, associating) with weakness, fever and general malaise. 2.
That report describes an (immuno suppressing, immuno suppressed)
patient with mucosal and serosal ulcerations of the stomach, jejunum,
ileum and ascending colon.
ly
(associated, associating) with the gastrointestinal system is the
peptic ulcer (occurring, occurred) as a gastric or duodenal ulcer. 5.
The result of nephrolithiasis may be obstruction of the kidney, ureter,
or bladder leading to (increased, increasing) pressure behind the
stone.
Упражнение 10. Замените причастные обороты придаточными предложе- ниями, сделав соответствующие изменения, согласно образцу; используйте союзы или союзные слова as, and, when, which.
Образец: The usual manifestation of renal calculi is renal colic brought about by a stone in the kidney or ureter. The usual manifestation of renal calculi is renal colic which is brought about by a stone in the kidney or ureter.
1.
The conditions for stone formation are: a cavity containing a fluid;
the fluid having salts in solution. 2. The salts held in solution in
the fluid are deposited on the foreign substances. 3. The foreign
objects forming stones in the kidneys and bladder are bacteria and the
small shreds of mucus. 4. All experimental patients described here had
stones in the bladder. 5. When collected in polypropylene bottles the
urine was kept in refrigerated lockers.
Упражнение 11. Опишите виды камней при мочекаменной болезни, используя текст и рис. 16.
Часть II Слова к части II

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Прочтите
текст В (10 мин). 1) Скажите, о каких заболева- ниях идет речь в
тексте и существует ли какая-либо взаимосвязь между ними. 2) Найдите
предложения: а) где употребляются I и II формы причастий; б) определите
их функции. 3) Переведите эти предложения.
Text В Kidney Diseases
There
are three structures of the kidney which are susceptible to disease:
the glomeruli, the tubules and the blood vessels. However, it is
rare that only one of these structures is affected; what happens to one frequently affects the others as well.
The
disease in which the glomeruli are particularly involved is called
glomerulonephritis. It may be acute or chronic, the first frequently
leading to the second. It is often a sequel1 to such a
childhood infectious disease as scarlet fever. In glomerulo-nephritis,
the glomeruli become clogged with exudate and cell debris so that the
blood no longer flows through them. Here a clearance test is useful; it
will show that much smaller quantities of filtrate are being formed
than normally. The glomeruli being still open become permeable to
protein and albuminuria becomes very marked. This leads to edema.
Diseases
involving the tubules are called nephroses. They are usually caused by
poisons of various kinds, such as mercury, bismuth, uranium, or
carbolic acid. Some degree of tubular degeneration occurs, however, in
such diseases as diabetes, malaria and pernicious anaemia2,
and also in traumatic shock. Finally, athero-sclerosis of the kidney
may occur, reducing the total blood flow through the kidney's blood
vessels.
What happens to the kidneys when incompatible blood has been used in a transfusion? Hemolysis of red cells occurs, of course, and the liberated hemoglobin circulates in the blood. Passing through the kidney, hemoglobin (although its molecular weight is 68,000) passes through the membrane into the tubules. If the amount is small, reabsorption occurs, but in the amounts increased after an incompatible transfusion the hemoglobin, passing through the tubules, is precipitated. This blocks the tu-
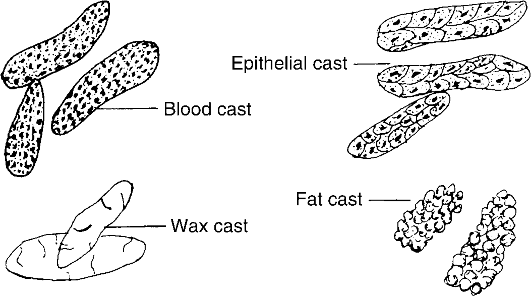
Fig. 16. Urinary casts.
sequel - следствие.
pernicious anaemia [s'nimp] - злокачественная анемия.
bules;
they cease to function and finally die. Patients having received the
wrong type of blood can often be saved if the blood is thoroughly
alkalinized; an alkaline filtrate is formed and thus prevents
precipitation.
A
common disease of the kidney, known as Bright's disease, includes a
number of different conditions. Bright was a physician establishing a
connection between degenerative changes in the kidney and the presence
of albumin in the urine. The discovery of albumin in the urine usually
indicates a faulty working of the kidneys. It means that albumin from
the blood plasma is being allowed to pass through the renal tubules,
and thus be excreted in the urine. At the same time the damaged tubules
fail to eliminate fluid. This fluid collects in the tissues and causes
swelling, or edema, of various parts of the body. The fluid is more
likely to collect in the legs and in the eyelids. Hence the puffy face
and swollen legs of the sufferers from advanced Bright's disease.
It
must not be assumed, however, that the presence of a small amount of
albumin in the urine is necessarily a sign of Bright's disease. It is
often transient and of no great significance.
Notes
Упражнение 2. Найдите в тексте В предложения, более полно выражающие мысль данных суждений, и прочтите их вслух.
1. There are three structures of the kidney which are susceptible to disease.
Упражнение 3. Назовите заболевания почек, описанные в тексте В.
Часть III
Контрольно-обобщающее упражнение к уроку 19
Найдите в следующих предложениях причастия, выполняющие функцию определения.
1.
Case 5 had his blood pressure raised over all period of investigation.
2. Transient or reversible albuminuria accompanied by oliguria and
highly concentrated urine can be due to functional changes in the
glomerular
membrane. 3. When damaged the glomerular epithelium becomes permeable
to the blood coloids. 4. Oliguria or decreased secretion of urine, may
be due to a number of renal factors. 5. Albuminuria is common in
passive congestion accompanying cardiac decompensation. 6. Intravenous
pyelography having been performed, the patient was operated on.
(Ответ: 1, 2, 4, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ?? 20, 21 Грамматического справочника.)