Английский язык : учебник / И. Ю. Марковина, З. К. Максимова, М. Б. Вайнштейн; - 4-е изд., испр. и перераб. - 2010. - 368 с.
|
|
|
|
LEARNING TO UNDERSTAND A MEDICAL TEXT I. ANATOMY
LESSON ONE
THE SKELETON
1. Оборот there is, there are (? 16)
2. Основные формы глагола to be (? 15)
3. Времена группы Indefinite (Active Voice) (? 10)
Часть I
Слова к части I

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Укажите время глагола-сказуемого в следующих предло- жениях.
1. There will be a new student in our group. 2. There are 14 faculties in the
Упражнение 2. Составьте 5 предложений с оборотом there is, there are, используя данные ниже слова. Согласуйте форму глагола с последующими существительными.

Упражнение 3. Выберите правильный вариант для русского предложения. Обратите внимание на порядок слов русского и английского предложений.

Упражнение 4. Напишите II, III, IV формы следующих глаголов. Проверьте себя по таблице (см. Грамматический справочник, ? 9).
to ask, to use, to work, to enter, to speak, to found, to try, to study, to know, to like, to be, to consist
Упражнение 5. Определите время глагола-сказуемого в следующих пред- ложениях.
1.
Doctors help people when they are ill. 2. The lecture on anatomy will
begin at 12 p.m. 3. I go to the Academy by bus. 4. She went home an
hour ago. 5. Hippocrates established medical schools in
Упражнение 6. Поставьте подлежащие в следующих предложениях в един- ственном числе и согласуйте с ними форму сказуемого. Переведите пред- ложения.
1. Medical students study the structure of the human body. 2. These texts are easy to translate. 3. We shall work in the hospital this month. 4. My friends want to enter a medical college. 5. They speak English well.
Упражнение 7. Укажите, какие сказуемые в данных предложениях выра- жены правильными глаголами.
1. The teacher asked many questions at the lesson. 2. She got all her text-books from the library. 3. The students worked at the laboratory under the guidance of their teacher. 4. Naturalists divided all animals into two classes.
Упражнение 8. Прочтите следующие слова и сочетания слов. Переведи- те их.

Упражнение 9. Отработайте чтение следующих предложений:
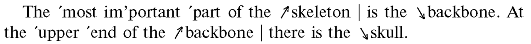
Упражнение 10. Прочтите и переведите следующие слова. Запомните зна чение:
1. приставок: а) глаголов:
ге- опять, назад: replace, reread, rewrite in- в, на: include, inhale, inflame
ex- из: exclude, exchange, expel б) прилагательных:
un-, in-, im-, ir-, il- - отсутствие качества: unimportant, uneasy, invertebrate, impure, irregular, irresponsive, illegal, illogical 2. суффиксов:
а) прилагательных:
-у: bony, windy, healthy
-al: social, local, special, spinal, medical, biological -less - отсутствие качества: frameless, helpless, lifeless
б) наречий:
-ly: quickly, really, usually, easily, especially, carefully
Упражнение 11. Переведите следующие производные слова.
1.
bone, bony, backbone, breastbone; 2. to divide into, division, to
subdivide, subdivision, divisible; 3. to include, to exclude, to
conclude, included, exclusively, conclusion;
Упражнение 12. Просмотрите текст А и скажите, какие части скелета описаны в данном тексте.
Text А The Skeleton
1. The
bones form the skeleton of the body. The most important part of the
skeleton is the backbone. It is so important that naturalists divided
all animals into two classes - those which have a backbone and those
which have none. All the higher animals have a backbone, or vertebral
column and they are therefore called (называются) vertebrate animals. The others are called invertebrate animals.
2. The
bones which form the skeleton or bony framework of the body include the
bones of the head, the bones of the trunk, the bones of the lower and
upper limbs.
3. At
the upper end of the backbone there is the skull. Inside the skull is
the brain. The bones of the head include the bones which make up the
box-like structure, the skull, and freely movable bone which forms our
lower jaw.
4. There
is another box of bones in front of the backbone. The ribs, which join
the backbone behind and bend round towards the breastbone in front,
form a strong cage - the chest, inside of which there is the
heart and the lungs. The bones of the trunk include the spinal column, the ribs and the breastbone.
5.
The arms join the body at the shoulder, and the shoulder itself
consists of two bones - the collar-bone in front, and the
shoulder-blade behind. Between the shoulder and the elbow there is only
one bone in the arm, but between the elbow and the wrist there are
two. In the wrist there are eight small bones. They are bound (связаны)
together, but their large number allows the wrist to bend freely. Next
come the bones of the hand itself. In the body or palm of the hand
there are five long bones - one for each finger and one for the thumb.
Each of the fingers has three bones, and the thumb has two. Thus we
have twenty-seven bones in the framework of the hand and wrist alone.
Упражнение 13. 1) Прочтите и переведите текст А. Абзац 5 переведите письменно. 2) Найдите в тексте А ответы на следующие вопросы и зачитайте их.
1. Is the backbone the most important part of the body? 2. What classes do the naturalists divide all the animals into? 3. What does the skull include? 4. The bones of the trunk include the spinal column, the ribs and the breastbone, don't they? 5. How does the wrist work?
3) Составьте письменно план текста А.
Упражнение 14. Подберите к латинским словам английские эквиваленты.

Упражнение 15. Подберите пары синонимов.
vertebral column, injury, cage, damage, harm, box, backbone
Упражнение 16. Подберите пары антонимов.
to
include, inside, immovable, in front of, lower, behind, invertebrate,
to exclude, movable, vertebrate, outside, upper, higher
Упражнение 17. Переведите следующие предложения. Определите, какими частями речи являются выделенные слова.
1. The form of the skull depends upon the form of the bones. The bones form the framework of the body. 2. The number of the bones in the hand and wrist alone is 27. The bones in the human skeleton number 223. There is a number of movable bones in the skull. 3. The face is the ventral part of the skull. Medicine faces many problems.
Упражнение 18. Измените следующие предложения согласно образцу. Переведите их на русский язык.
Образец: We have special atlases on anatomy in our library.
There are special
atlases on anatomy in our library. 1. We have 27 bones in the
framework of the hand and wrist alone. 2. Each hand has four fingers
and one thumb. 3. We have no special names for ulna and radius in the
modern English language.
Упражнение 19. Переведите следующие предложения, обращая внимание на оборот there is.
1.
There is the skull at the upper end of the backbone. 2. There are many
illustrated books on Human Anatomy. 3. There are three bones in each
finger. 4. There is no backbone in invertebrate animals. 5. There are
special hospitals for children in every town.
Упражнение 20. Поставьте сказуемые в следующих предложениях в отрицательной форме, переведите предложения.
Образец: I went to see them yesterday.
I did not go to
see them yesterday. 1. The professor asked many questions at the
seminar. 2. I got many text-books from the library. 3. I entered the
Institute last year. 4. We shall help him with his studies. 5. He knows
Human Anatomy well.
Упражнение 21. Задайте вопросы, ответами на которые были бы следующие предложения.
1.
Yes, they do. The bones form the skeleton of the body. 2. Yes, they
did. Naturalists divided all animals into two classes. 3. Yes, they
will. The first-year students will study the structure of the human
body this year. 4. Yes, they do. The bones of the trunk include the
spinal column, the ribs and the breastbone.
Упражнение 22. Прочтите предложения, поставив глаголы, данные в скобках, в соответствующих временах группы Indefinite и согласуйте их с формой подлежащего и контекстом.
1. The trunk (to consist) of
the chest, the abdomen and the back. 2. The arms (to join) the body in
front of the backbone. 3. Galen was the first who (to describe)
completely and accurately the structure of the body. 4. The upper
cavity, the thorax, (to include) the heart and the lungs. 5. Tomorrow
the doctor (to come) and (to examine) you. 6. We (to begin) to study
the bones of the upper and lower limbs last week.
Упражнение 23. Переведите на английский язык.
1. Позвоночные животные образуют класс высших животных. 2. Беспозвоночные животные составляют класс низших животных.
3. Большое количество костей в запястье позволяет ему свободно двигаться. 4. Ребра защищают сердце, легкие и другие органы грудной клетки. 5. Плечо, предплечье и кисть образуют верхнюю конечность.
Упражнение 24. Опишите части тела, используя рис. 1. и следующие выражения.
The
skull includes... The trunk consists of ... The arms form the body at
... The bones form... There are ... bones in ... The spinal canal
contains ...
Часть II Слова к части II

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Прочтите и догадайтесь о значении следующих слов, используя знание русского и латинского языков. Проверьте себя по словарю.
general, separate, naturally, abdomen, bilaterally, symmetrical, substance, canal, spinal, nervous, diaphragm, dorsal, pharynx
Упражнение 2. Подберите к латинским словам английские эквиваленты.

Упражнение 3. Подберите пары синонимов.
brain case, to include, to separate, chamber, to contain, skull, cavity, to distinguish
Упражнение 4. Подберите пары антонимов.
the latter, the former, long, at the upper end, short, at the bottom
Упражнение 5. Прочитайте и запомните перевод следующих внешне похожих слов, часто встречающихся в научной литературе. Переведите предложения с этими словами.
last последний из ряда или по времени, предыдущий
the latest последний, недавний
the latter последний из двух (ранее упомянутых)
1. We remember the last lesson at school. 2. They were the last to come. 3. I like to listen to the latest news. His latest operation on the heart was yesterday. 4. The thorax encloses the heart and the lungs, the latter are on each side of the heart.
Упражнение 6. Переведите со словарем. Обратите внимание на изменение значения слова в зависимости от контекста.

Упражнение 7. Просмотрите
текст В (время - 10 мин): 1) скажите, в каких абзацах кратко изложено
содержание текста «А» и в каких дается новая информация. 2) найдите
предложения: а) с оборотом there is, there are. Объясните, как вы будете переводить предложения, в которых отсутствует обстоятельство места; б) с глаголом-сказуемым в форме Indefinite в действительном залоге. 3) Переведите предложения.
Text В
The
human body is obviously separable into the head, the trunk and the
limbs. In the head, the brain-case or skull is distinguishable from the
face. The trunk includes the chest or thorax, and the abdomen. Of the
limbs there are two pairs - the upper, or arms, and the lower, or legs;
and the legs and arms again are separable into several parts - the
thigh, the leg and the toes in the lower limb and the upper arm, the
forearm, the wrist and the fingers in the upper limb.
The whole body, is bilaterally symmetrical. There are special bones in the trunk which are bound (связаны)
together by a very strong and tough substance into a long column,
which lies nearer the dorsal (or back) than ventral (or front) part of
the body The bones are called (называются) the vertebrae. They separate a long narrow canal, the spinal canal, which lies upon the dorsal side.
The
spinal canal contains a long white cord - the spinal cord - which is
an important part of the nervous system. The diaphragm divides the
ventral chamber into two cavities - the thorax and abdomen. The
alimentary canal transverses these cavities from one end to the other
and pierces the diaphragm. In the abdomen there are also two kidneys,
which lie against each side of the vertebral column, the ureters, the
bladder, the liver, the pancreas and the spleen. The thorax encloses
the heart and two lungs. The latter lie one on each side of the heart.
The
dorsal chamber, or cavity of the skull, opens into the spinal canal.
It contains the brain, which is continuous with the spinal cord. The
brain and the spinal cord together constitute the cerebrospinal system.
The ventral chamber, or cavity of the face encloses mouth and pharynx,
into which the upper end of the alimentary canal (gullet or
oesophagus) opens.
Упражнение 8. Прочтите каждое суждение. Найдите в тексте В предло- жения, более полно выражающие мысль данного суждения, и прочтите их.
1.
The parts of the body are the head, the trunk and the limbs. 2. The
vertebral column divides the trunk symmetrically. 3. The spinal canal
contains a cord. 4. The diaphragm divides the trunk into two cavities.
5. The alimentary canal transverses them. 6. The oesophagus opens into
the pharynx.
Часть III
Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 1
Упражнение 1. Укажите предложения, которые следует переводить, начи- ная: а) с обстоятельства места; б) со сказуемого. Переведите их.
1.
There is a long white cord in the spinal canal. 2. There are two pairs
of limbs in the human skeleton. 3. There are three groups of vertebrae
according to their position. 4. There are differences in the structure
of vertebrae. 5. There exist two vertebral segments: anteriour and
posterior.
(Ответы: a) 1, 2, 4. б) 3, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 16 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 2. Образуйте форму инфинитива от следующих глагольных форм.
possessing, separated, made up, is, built, allows, turning, bent, containing, will bind
LESSON TWO
THE MUSCLES
1. Времена группы Continuous (Active Voice) (? 11)
2. Модальные глаголы can, must, may (? 17)
3. Функции и перевод слова that (those) (? 34)
Часть I Слова к части I


Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Найдите в каждом ряду глагол во временах группы Contin- uous (см. таблицу в ? 11 Грамматического справочника).
1.
was placing; placed; is placed; 2. bound; bind; is binding 3. were
bent; was bending; bent; 4. joins; is joining; were joined; 5. are not
included; will be including; includes; 6. is distinguishing; are
distinguishing; distinguishes
Упражнение 2. Поставьте след. предложения в отрицательную форму.
Образец: We are working at the laboratory now.
We are not working at
the laboratory now. 1. They were discussing the functions of brain for
two hours running. 2. We shall be studying the bones of the palm for
the whole day. 3. He is taking his examination in history now. 4. I was
writing my report when she entered the library hall.
Упражнение 3. Переведите следующие предложения, определите времен- ную форму глагола-сказуемого.
1. Smooth or unstriated muscles contract without any volition.
2. Blood vessels are contracting when they respond to the temperature.
3. The
bones of our body make up the skeleton. 4. They were conducting their
experiment from five to seven. 5. Students will learn the framework of
the chest in the first term. 6. We shall be studying the functions of
the heart during the whole lesson.
Упражнение 4. Найдите модальные глаголы в следующих предложениях. Переведите предложения на русский язык.
1.
The lesson is over, you may go home. 2. The character of the joints
distinguishes the degree of the motion which we can perform. 3. Smooth
muscles can contract slowly. 4. We may divide animals into vertebrates
and
invertebrates. 5. Student Petrov should stay at home as his leg still
aches. 6. Future doctors must know human anatomy very well.
Упражнение 5. Заполните пропуски модальными глаголами can, must, may.
1.
You ... come for consultations on physics any time from 5 to 8. 2. We
... know all the functions of the lungs. 3. ... I ask a question? 4.
She ... come as she is ill. 5. Who ... describe the tones of the trunk?
6. The joints ... move by the contraction of muscles.
Упражнение 6. Переведите следующие предложения. Определите какую функцию выполняют слова that/those (см. ? 34 Грамматического спра- вочника).
1. The doctor says that he knows this patient. 2. The bones of the lower extremities articulate with the pelvic bones, those of the upper extremities extend from the shoulder girdle. 3. Through the centre of the vertebral column runs the canal that contains the spinal cord. 4. We liked that lecture very much. 5. The function of the liver is different from that of the spleen. 6. That was the book he wanted.
Упражнение 7. Прочтите следующие слова и сочетания слов. Переведи- те их.
b) a layer of muscles, 50 per cent of the total body weight, a characteristic feature of the cardiac muscle
Упражнение 8. Познакомьтесь со значениями данных ниже суффиксов: ar, ive, ous, ion и приставки en. Прочтите и переведите производные слова.
1. en- + основа прилагательного/существительного/, глагола = глагол: large большой - to enlarge увеличиваться); to close закрывать - to enclose окружать, ограничивать.
to enable, to encircle, to encourage, to enrage
2. -ar - суффикс прилагательных, обозначающих принадлежность, или существительных, обозначающих лицо: muscle мышца - muscular мышечный; to beg умолять - beggar нищий, попрошайка.
nuclear, liar, lobular, circular
3. глагол + -ive = прилагательное: to act действовать - active активный.
demonstrative, connective, effective
4. -ous (-eous, -ious) - суффикс прилагательных, имеющих значение «обладающий качеством», обозначенным основой: to continue продолжаться) - continuous непрерывный; glory слава - glorious великолепный.
various, dangerous, infectious
5. -ion (-ation, -tion, -sion, -ssion) - суффиксы существительных, обозначающих действие или процесс, состояние или качество, результат действия: to separate отделять - separation отделение.
foundation, observation, motion, fermentation, foundation, classification, decision, submission
Упражнение 9. Прочтите и переведите следующие однокоренные группы слов.
1.
muscle, muscular, musculature, musculation; 2. to close, to enclose,
close, closely, closed, closing; 3. to contract, contracted,
contracting, contractile, contraction; 4. to vary, variant, various,
variable, variation, variety; 5. to connect, connecting, connection,
connective
Упражнение 12. Просмотрите текст А. Скажите, на сколько частей можно разделить текст и как можно озаглавить каждую часть.
Text A Types of Muscles
1. The
word «muscle», according to one theory, comes from a Latin word that
means «little mouse»: that is, when a man's muscles are contracting
they look as if a little mouse runs about under his skin. According to
another theory the word «muscle» comes from a Greek expression that
means «to enclose», that is, layers of muscles enclose the body. We
know that the muscles constitute approximately 50 per cent of the total
body weight, slightly more in the average male than the female.
Tendons, fasciae and the various organs themselves depend on the
muscular system and the function of muscle cells.
2. There are three main types of muscular tissue that we identify and classify on the basis of structure and functions:
1) smooth or visceral muscle,
2) striated or skeletal muscle,
3) cardiac muscle.
3. Smooth
muscles can contract slowly. They make up the walls of the internal
organs such as those of the blood vessels, and the digestive tract.
Since we identify the internal organs as viscera, we sometimes call
smooth

Fig. 2. Types of muscles
muscles
visceral muscles. The visceral muscles react relatively slowly to
changes within the body and do so without the intervention of the will.
The
walls of the blood vessels are contracting or expanding when they
respond to certain chemicals in the blood or in response to the effect
of temperature but we cannot deliberately cause them to lift our arm or
open our mouth. For this reason, we may call them involuntary muscles.
Smooth muscle tissue consists of long cells. Smooth muscle fibres are
bound (связаны) into bundles by connective tissue which contain blood vessels and nerves.
4. Striated
muscle tissue consists of large fibres in the form of bundles.
Striated muscles are most necessary for manipulation of the bones of
the skeleton. Those are the muscles necessary for walking, running,
turning the head and so on. That's why we sometimes call them skeletal
muscles. This type of muscle tissue includes the large muscle masses of
the body, the muscles of the arms, legs, back etc.1 It includes all those muscles which must react quickly to changes in the environment, i.e.2 those that become active through an effort of will. For this reason, we call striated muscles voluntary muscles.
5. Cardiac
(heart) muscle is, in a sense, a cross between the previous two. A
characteristic feature of cardiac muscle is that fibres have neither a
beginning nor an end. In other words, the heart is simply a huge net of
muscles in which all elements are continuous with each other. Cardiac
muscles («heart» - Greek) have the strength and force of contraction of
the skeletal muscle. Cardiac muscle is under complete involuntary
control. In that, it resembles visceral muscle.
Notes
1. etc. (Lat. et cetera) [it'setra] = and so on - и так далее
2. i.e. (Lat. id est) - читается: that is, namely - то есть
Упражнение 13. I) Прочтите и переведите текст А. Абзацы 4 и 5 переведите письменно. 2) Найдите в тексте А ответы на следующие вопросы и зачи- тайте их.
1.
How many types of muscular tissue are there? 2. How do we sometimes
call smooth muscles? 3. What is another name of striated
muscles? 4. What is the difference between the cardiac and skeletal muscles?
Упражнение 14. Подберите к латинским словам английские эквиваленты.

Упражнение 15. Подберите пары антонимов.
voluntary, beginning, separated, to include, the former, to exclude, the latter, connected, end, involuntary
Упражнение 16. Дайте синонимы к следующим словам и словосочетаниям.
injury, backbone, brain case, to be placed, to include
Упражнение 17. Прочтите
следующие предложения и определите, какой частью речи являются
выделенные слова, найдите их значение в словаре. Переведите предложения.
1. The word «muscle» means «little mouse» in Latin.
Упражнение 18. Прочтите предложения, поставив глаголы, данные в скобках, в нужное по смыслу время группы Continuous. Переведите предложения.
1.
The students (to work) in the physical laboratory from 9 to half past
10 yesterday. 2. When he came they (to classify) the bones of the upper
extremities. 3. The walls of the blood vessels (to expand) when they
respond to certain chemicals in the blood. 4. We (to discuss) the
characteristic features of cardiac muscles now.
Упражнение 19. Замените времена группы Indefinite временами группы Continuous, дополнив предложения обстоятельствами времени: now, at 11 o'clock, when you came, from ... to, all the day, где необходимо. Переведите предложения.
1.
First-year students work in the anatomy museum. 2. He will make a
report on the muscular system. 3. She prepared the text «Voluntary
and
Involuntary Muscles» at home. 4. We translated 5 sentences from this
text. 5. Last Monday we had a practical lesson on the structure and
functions of smooth muscles.
Упражнение 20. Ответьте на вопросы по данному образцу:
Образец: Why can't you go home? (to attend the lecture)
I cannot go home, because I must attend the lecture. 1. Why can't you consult a doctor? (to go to the Institute) 2. Why can't you give me your book? (to return it to the library) 3. Why can't she finish her test? (to prepare for the examination)
Упражнение 21. Переведите следующие предложения с модальными глаголами: can, may.
1. The joints between bones can move more or less easily.
Упражнение 22. Переведите следующие предложения, определите функции слов that (those).
1.
The special feature of that textbook on anatomy is that it has many
pictures. 2. One of the most interesting problems in medicine is that
of pathogenesis. 3. Note that in the middle the bone consists of very
compact tissue. 4. Will you name the diseases that are not infectious?
5. Metabolic diseases are those in which certain physiological
processes become disturbed.
Упражнение 23. Переведите следующие предложения на английский язык.
1. По структуре и функции мышцы можно разделить на три группы. 2. Гладкие мышцы сокращаются непроизвольно. 3. Соединитель- ная ткань гладких мышц включает нервы и кровеносные сосуды. 4. Поперечно-полосатые или скелетные мышцы реагируют на изменения в окружающей среде. 5. Волокна сердечной мышцы непрерывны.
Часть II
Слова к части II
produce [prs'djuus] v производить, uterus ['juutsrss] п матка
образовывать, давать elongate ['elongeit] v удлинять(ся)
consist [ksn'sist] v (of) состоять (из) vary ['vesri] v изменять(ся), варьи- tongue [tATj] n язык ровать


Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Прочтите следующие слова в единственном и множествен- ном числе:

Упражнение 2. Переведите следующие предложения со словосочетаниями as well (as).
1. Smooth muscles form the coat of some internal organs as well as a
part of the capsule of the spleen. 2. Smooth muscles form the coat of
some internal organs and a part of the capsule of the spleen as well. 3. You are to know physiology as well as anatomy.
Упражнение 3. Просмотрите
текст В (время - 10 мин). 1) Скажите, каково строение
поперечно-полосатых и гладких мышечных тканей. 2) Найдите предложения,
где употребляются: а) глаголы-сказуемые в форме Continuous; б) слова that (those). 3) Переведите эти предложения.
Text В
Skeletal and Smooth Muscles
Muscles
are the active part of the motor apparatus: their contractions are
producing various movements, when they are active. Functionally we
divide all muscles into two groups: voluntary and involuntary muscles.
Voluntary
muscles consist of striated muscle tissue and contract by the will of
the man. This group includes all the muscles of the head,
trunk
and extremities, i.e., the skeletal muscles, as well as those of some
internal organs (tongue, larynx, etc.). The skeletal muscles are the
organs of the muscular system. There are more than 400 skeletal muscles
in the human organism: in adults they make up about two-fifths of the
total body weight. Each skeletal muscle has an arterial, venous,
lymphatic and nervous supply. Muscles must always act in groups.
Skeletal muscles are complex in structure. They consist of muscle fibres of different length (up to
Smooth
muscles form the muscular coat of internal organs such as esophagus,
stomach and intestines, bladder, uterus and so on. They also form the
part of the capsule and the trabeculae of the spleen; they are present
as single cells or as little cylindrical bundles of cells in the skin.
They also form the walls of arteries, veins and some of the larger
lymphatics. Smooth muscles are not rich in blood vessels, as are
striated muscles. A smooth muscle is capable of spontaneous contraction
and can contract in two ways. Firstly, individual cells may contract
completely and secondly, a wave of contractions may pass from one end
of the muscle to the other. Smooth muscle cells are usually elongated
cells. In the skin and intestines they are long and thin, but in the
arteries they are short and thick. They vary in length from 12-15 mm in
small blood vessels to
Muscles
have both motor and sensory nerve fibres. Impulses (signals) about the
state of the muscle reach the brain along the sensory fibres. The
nerve impulses which cause the muscle to contract come from the brain
along the motor fibres. Injury to the nerves which innervate muscles
causes disturbances in voluntary movements (muscular paralysis).
Упражнение 5. Прочтите каждое суждение. Найдите в тексте предложения, более полно выражающие мысль данного суждения, и прочтите их.
1. The skeletal muscles are the organs of muscles system. 2. Skeletal muscles are complex in structure. 3. Smooth muscles form the muscular coat of internal organs, blood vessels and skin. 4. Smooth muscles are capable of contraction. 5. Smooth muscle cells have some characteristic features. 6. Muscles have nerve fibres.
Часть III
Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 2
Упражнение 1. Укажите, в каких предложениях глагол стоит в форме Con- tinuous.
1.
The muscles are contracting under stimulation. 2. Striated muscle
tissue consists of large fibres. 3. The walls of the blood vessels are
contracting or expanding in response to a stimulus. 4. Striated muscles
are necessary for manipulating the bones of the skeleton.
(Ответ: 1, 3. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 11 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 2. Укажите и переведите предложения с модальными глаголами.
1.
The muscles which we can control are called the voluntary muscles. 2.
We do not control smooth and cardiac muscles. 3. Each type of muscles
must perform definite functions. 4. Involuntary muscles control all the
processes of the body. 5. We may divide all muscles into two groups.
(Ответ: 1, 3, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 17 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 3. Укажите, в каких предложениях слово that переводится а) «что»; б) «который»; в) замещает существительное.
1.
We call the muscles that form internal organs are called visceral
muscles. 2. We know that the cardiac muscle forms the heart. 3. The
structure of smooth muscles differs from that of cardiac muscles.
(Ответ: a) 2; 6) 1; в) 3. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 34 Грамматического справочника.)
LESSON THREE
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
1. Времена группы Perfect (Active Voice) (? 12)
2. Степени сравнения прилагательных (? 3)
3. Функции и перевод слов because, because of (? 37)
Часть I
Слова к части I

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Назовите основные формы следующих глаголов.
to keep, to flow, to mean, to think, to come, to give
Упражнение 2. Найдите в каждом ряду глагол во временах группы Perfect (см. таблицу в ? 12 Грамматического справочника).
1. called;
has called; is calling; 2. had thought; think; is thought; 3. shall have
come; came; comes; 4. have given; gave; will give; 5. distinguish; has
distinguished; distinguishes
Упражнение 3. Определите время и форму глагола-сказуемого в следующих предложениях.
1.
We have just learned the general structure of the body. 2. The bones
of the skull protect the brain structure from injury. 3. All the bones
of the body are of different types. 4. Muscles are constantly assisting
in the body movement. 5. The doctor had already examined the girl's
heart when the professor came in. 6. We shall have got the books in
anatomy by tomorrow morning.
Упражнение 4. Прочтите следующие группы слов. Найдите прилагательные в сравнительной и превосходной степени.
more flexible bony tissue, lower arm, less compact bone, inner portion, the longest bone, the most difficult test
Упражнение 5. Прочтите и переведите следующие предложения; опреде- лите, какую функцию выполняют слова because и because of.
1.
Penicillin is an important antibiotic because of its antiseptic
properties. 2. Many infectious diseases are dangerous because it is
difficult to treat them. 3. The false ribs received this name because
they join the seventh rib at the point before they reach the sternum.
4. Acetabulum got its name because of its resemblance to a rounded cup
which the Romans used for acetum.
Упражнение 6. Прочтите следующие слова и переведите их.

Упражнение 7. Отработайте чтение следующих предложений.

Упражнение 8. Запомните значения нижеприведенных суффиксов. Про- чтите и переведите производные слова.
1. прилагательное + -гу = наречие: gradual постепенный - gradually постепенно.
anatomically, functionally, finally, freshly
2. -ist - встречается в существительных, обозначающих людей по профессии, занятию, убеждениям.
ecologist, chemist, anatomist, physiologist
3. -ate [eit] - суффикс глагола.
to communicate, to circulate, to separate, to graduate
4. -ate [it] (-ete, -ite, -ute) - суффикс прилагательных и существительных.
graduate, delegate, ultimate, accurate, complete, minute
5. -ward (s) - встречается в прилагательных, наречиях, предлогах, обозначая направление.
towards, upward, downwards, eastward, inward, backward, forward
Упражнение 9. Прочтите и переведите следующие гнезда слов.
1.
pure, impure, purity, impurity; 2. to weigh, weight, weightless,
weighty; 3. to circulate, circulatory, circulation; 4. artery,
arterial, arteri-ole, arteriosclerosis; 5. to separate, separately,
separation; 6. to nourish, nourishment
Упражнение 10. Прочтите и переведите следующие словосочетания.
molecular
weight, to put on (to gain) weight, to lose weight, systemic
circulation, circulating system, poor circulation, venous pulse blood,
thoracic cavity
Упражнение 11. Просмотрите текст А. Разделите текст на 4 части и выразите основную мысль каждой из них.
Text A
The Circulatory (Cardiovascular) System
1. The
cardiovascular system is the system of blood circulation. By the
cardiovascular system we mean the heart, the arteries, the veins and
the capillaries of the human body.
2. The centre of the circulatory system is the heart. The human heart is a cone-shaped organ, about 5 inches1 long and 3 1/2 inches broad. It weighs about 10 ounces2 in the adult male,
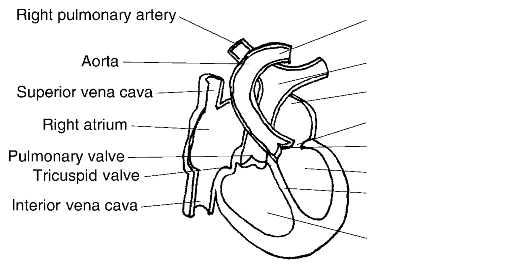
Left
pulmonary artery Pulmonary artery
Left atrium
Mitral valve Aortic valve Left ventricle Interventricular septum
Right ventricle
Fig. 3. Diagram of the heart
3. Blood
vessels that receive blood from the ventricle and lead it away from
the heart and towards other organs are arteries («air duct» - Greek).
The vessels received this name because the early anatomists assumed
that they had been empty in dead persons and had carried air.The artery
that takes up the blood from the right ventricle and carries it to the
lungs is the pulmonary artery («lungs» - Latin). The pulmonary artery
divides in two - one branch leads to the right lung, the other - to the
left. The arteries continue to divide and subdivide and form smaller
and smaller vessels with thinner and thinner walls. The smallest
arteries are the arterioles and these finally divide into capillaries
(«hairlike» - Latin). We name them so because of their fineness, though
actually they are much finer than hairs.
4. Gradually
the capillaries begin to join into larger vessels. Such larger blood
vessels that carry blood to the heart from the organs are the veins.
The smallest of these are the venules.
5. The
particular vein into which the capillaries and venules of the lungs
finally unite is the pulmonary vein. The pulmonary vein carries the
freshly oxygenated blood to the left auricle. The pulmonary artery and
pulmonary vein make up the pulmonary circulation.
6. The
contraction of the left ventricle forces the blood through a one-way
valve into the aorta («to lift up» - Greek). The aorta is the largest
artery in the body. It moves upward at first (the ascending aorta), but
then arches over dorsally (the arch of the aorta). In its downward
course, the aorta passes through the diaphragm.
7. The
blood is a red fluid, which coagulates when escapes from a blood vessel.
It consists of a colourless fluid, plasma or serum, and many millions
of minute bodies, the corpuscles.
Упражнение 12. Подберите к латинским словам английские эквиваленты.

Упражнение 13. Подберите пары синонимов.
substance, to supply, to nourish, because of, because, minute, tiny, to provide, to obtain, due to, fine, as, matter, to feed
Упражнение 14. Подберите пары антонимов.
larger, upward, ascending, colourless, thick, colourful, thin, descending, downward, smaller
Упражнение 15. Переведите следующие предложения. Определите, какими частями речи являются выделенные слова.
1. The number and even nature of the clots in the veins and arteries differ according to their size. 2. Under the microscope we can see the membrane which consists of a number of separate cells. 3. Blood includes minute bodies, which give the blood its colour. 4. The heart makes 70-80 contractions a minute.
Упражнение 16. Переведите следующие предложения. Определите времен- ную форму глагола-сказуемого.
1.
The heart is beating in the experimental animals even when we destroy
the nerve supply. 2. The vena cava brings deoxygenated blood which has
passed through the body to the right atrium. 3. During diastole, the
atrium of the heart is filling with blood from the venae cavae and the
pulmonary vein. 4. We were discussing the anatomy of the heart at the
English lesson yesterday. 5. We shall still be working at this problem
for another week. 6. The teacher corrected the tests which the students
had written the day before.
Упражнение 17. Поставьте прилагательные в следующих предложениях в сравнительную или превосходную степень.
1. The veins
are (large) than capillaries. 2. The aorta is the (large) artery which
distributes the blood throughout the body. 3. I know the
structure of the heart (good) than that of the lungs. 4. Anatomy is (difficult) subject for me. 5. The human heart weighs (little) than a pound.
Упражнение 18. Найдите в каждой колонке прилагательное в сравнительной степени.
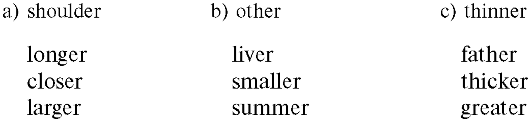
Упражнение 19. Переведите следующие предложения, выбрав подходящее по смыслу слово в скобках.
1.
The capillaries got their names (because, because of) they resemble
hairs. 2. The blood reaches the arteries (because, because of) the
contraction of the heart. 3. The two blood streams do not readily mix
in the ventricle (because, because of) the muscular meshwork within its
cavity. 4. (Because, because of) arteries carry blood away from the
heart, they must be strong enough to withstand the high pressure of the
pumping action of the heart. 5. If we stimulate the nerve in the ear
by electricity, the ear becomes blanched (because, because of) the
arteries contract.
Упражнение 20. Переведите на английский язык.
1. Сердечно-сосудистая система включает сердце, артерии, вены и капилляры. 2. Кровь возвращается к сердцу по венам (посредством вен). 3. Правая и левая части сердца состоят из двух камер: предсердия и желудочка. 4. При сокращении левого желудочка кровь проталкивается в аорту. 5. Стенки капилляров такие тонкие, что питательные вещества и кислород проходят через них в ткани.
Упражнение 21. Опишите сердечно-сосудистую систему, используя рис. 3.
Часть II Слова к части II
close [klous] а близкий, закрытый tiny ['taini] а очень маленький, кро- constitute ['konstitjut] v образовышечный
вать, составлять dilate [dai'leit] v расширять(ся)


Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Переведите следующие словосочетания.
1.
on the one side, on the other side, on the opposite side; 2. due to,
in due time, with due respect; 3. according to the rule
Упражнение 2. Переведите следующие предложения. Определите какой частью речи являются выделенные слова.
1. The walls of the arteries and veins are thicker than those of the capillaries. The former are less permeable for fluid. 2. There are no blood capillaries in certain parts of the body. These are the epidermis, epithelium and some others. 3. We call the valve that separates the chambers, the atrium and the ventricle the mitral valve. 4. Both the superior and inferior venae cavae empty into the right atrium. Both carry venous blood.
Упражнение 3. Просмотрите текст В (время 10 мин). 1) Скажите, что является предметом обсуждения. 2) Найдите предложения, где употребляются: а) глаголы-сказуемые во времени Perfect; б) прилагательные в сравнительной и превосходной степени; в) слова because, because of. 2) Переведите эти предложения.
Text В
Almost
all parts of the body are vascular. Minute and very close-set canals,
which have opened into one another traverse them and constitute a
small-meshed network. The canals or rather tubes have distinct but very
delicate walls. The walls contain a membrane that includes a number of
thin epithelial cells, which are bound (связаны)
together at their edges. There is a small oval nucleus in each of
these cells. These tubes are the blood capillaries. They vary in
diameter from 7 to 12 μηι. But there are certain parts of the body in which these blood capillaries
have
been absent. These are the epidermis and epithelium, the nails and
hairs, the substance of the teeth and the transparent cornea of the
eye.
Tiny rings of
muscles, precapillary sphincters, regulate the flow of blood into
capillaries. The question of nervous control of the precapillary
sphincters still remains the subject of the study.
The
capillary tubes contain the red fluid, blood. They join on opposite
sides and form larger tubes, with thicker walls, which are the smallest
arteries on the one side, and veins, on the other. These again join on
to larger arteries and veins, which ultimately communicate by a few
principal arterial and venous trunks with the heart. The mere fact that
the walls of these vessels are thicker than those of the capillaries
constitutes an important difference between the capillaries and the
small arteries and veins.
The
most important difference between these vessels and the capillaries,
however, is that their walls are not only thicker, but also more
complex. They have got several coats, one, at least, of which has been
muscular. The number and even nature of these coats differ according to
the size because the vessels are not the same in the veins as in
arteries, though the smallest veins and arteries resemble each other.
The
venous system starts with the venules into which the capillaries
empty. Small veins join and form larger ones. The larger veins join and
form the venae cavae. The superior vena cava collects the blood from
the head, neck, arms, and thorax, and the inferior vena cava, from the
legs and abdomen. Both empty into the right atrium.
Pressure in the venous system is low. In the vein at the level of the heart the pressure would be more than 5-7 mm Hg.1
It is evident that in the erect position blood that returns to the
heart from the feet has to overcome the force of gravity through a
distance of about
Notes
Упражнение 5. Найдите в тексте предложения, более полно выражающие мысль каждого данного суждения, и прочтите их.
1.
The capillaries form a small-meshed network. 2. The blood capillaries
are absent in some parts of the body. 3. There are some differences
1 5-7 mm Hg = 5-7 millimeters of Mercury
2 4 ft =
between the veins, arteries and capillaries. 4. The veins are more immune to diseases than the arteries. 5. Phlebitis is due to some infection.
Часть III
Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 3 Упражнение 1. Укажите, где глагол to have не переводится.
1.
We have attended English lessons since September. 2. The heart is a
hollow organ and has four chambers. 3. I have never been to Yaroslavl.
4. The capillaries have thin walls.
(Ответ: 1, 3. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 12 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 2. Переведите прилагательные и определите их степень сравнения.
1.
slightest; 2. most coloured; 3. more delicate; 4. more permeable; 5.
less infectious; 6. normal; 7. much more complex; 8. less transparent;
9. important; 10. much thicker; 11. much lower
(Ответ: положительная степень - 6, 9; сравнительная степень -
3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 11; превосходная степень - 1, 2. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 3 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 3. Укажите, в каких предложениях слово because переводится «так как», «потому что». Переведите эти предложения на русский язык.
1.
The heart pumps about five litres of blood in one minute because it
beats 60-80 times a minute and ejects about 130 cubic centimetres of
blood at each beat. 2. The woman's heart beats 6 or 8 times a minute
faster than that of the man because of the smaller size of her heart.
3. The mouse's heart flutters at 500 beats per minute because of its
tiny size.
4. The
frog's heart beats 30 times per minute in warm weather because
cold-blooded animals live at a much lower level of internal chemical
activity.
(Ответ: 1, 4. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 37 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 4. Определите, в каких предложениях выделенное слово является сказуемым. Переведите эти предложения.
1. The heart beats 72 times a minute. 2. The heart beats were weak. 3. The heart pumps the blood through the circulatory system. 4. The
heart is a pump that forces the blood through the circulatory system. 5. Rest is necessary after hard work. 6. The dark glasses rest my eyes.
(Ответ: 1, 3, 6. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 10 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 5. Переведите следующие предложения.
1. They obtained good results. 2. The fluid reduces friction which results from the heart movement.
LESSON FOUR
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
1. Времена группы Indefinite, Continuous, Perfect (Passive Voice) (? 14)
2. Функции и перевод слова one (ones) (? 36)
3. Существительные в функции определения (? 1)
Часть I
Слова к части I

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Прочтите следующие пары предложений и переведите их на русский язык.
1.
We call three major types of blood vessels arteries, veins and
capillaries. - Smaller branches of arteries are called arterioles. 2.
The heart pumps the blood into the lung by circulatory system. - From
the left heart the blood is pumped into the aorta. 3. Pulmonary artery
divides into two branches. - The upper extremity is divided into the
shoulder, the upper arm, the forearm and the hand. 4. The right carotid
artery distributes blood to all parts of the right side of the neck,
face, head and brain. - The blood from the aorta is distributed
throughout the body.
Упражнение 2. Прочтите следующие предложения. Определите время и залог сказуемого. Переведите предложения.
1. These textbooks will be distributed among all the students of our group. 2.
Упражнение 3. Переведите предложения. Определите какую функцию выполняет слово one (ones).
1.
There are four chambers in the heart: two smaller ones, the auricles,
and two larger ones, the ventricles. 2. One often describes the heart
as consisting of a base and an apex. 3.
Упражнение 4. Прочтите следующие предложения. Замените выделенные существительные словами-заменителями one (ones). Переведите предложения.
1. Here are some books, which book do you want? 2. This text is very difficult to translate without a dictionary; give me another text. 3. My watch is not working well. I must buy a new watch. 4. These exercises are much easier than the exercises we translated at the last lesson.
Упражнение 5. Переведите следующие словосочетания. Назовите суще- ствительные, выполняющие функцию (левого) определения.
blood
circulation, one-way valve, cone-shaped organ, striated muscle tissue,
smooth muscle cells, heart valves action, heart beat rate, tissue
oxygen supply, heart blood output
Упражнение 6. Переведите предложения, содержащие группы существи- тельных. Помните, что основное слово стоит последним в ряду слов и перед ним нет ни артикля, ни предлога.
1. The blood-pressure
measurement method is very simple. 2. The heart wall is composed of two
layers. 3. The arterioles divide into smaller tissue capillaries which
are near the body cells.
Упражнение 7. Прочтите следующие слова. Переведите их.

Упражнение 8. Напишите данные слова в 3 столбика в соответствии с чтением суффикса -ed как [t], [d], [id] и переведите их.
removed,
exhaled, distinguished, involved, inhaled, circulated, diffused,
breathed, called, produced, included, provided, connected
Упражнение 9. Отработайте чтение 4-го абзаца текста А.
Упражнение 10. Познакомьтесь с разными значениями суффикса -ing. Переведите производные слова.
1. глагол + -ing = существительное: to read читать - reading чтение.
feeling, breathing, functioning (of the system), (the) sustaining (of life)
2. -ing - встречается в прилагательных, развившихся из причастий настоящего времени: healing целебный.
striking, stunning, demanding, misleading, understanding
Упражнение 11. Прочтите и переведите данные гнезда слов.
1.
to respire, respiration, expiration, inspiration, respiratory,
inspiratory; 2. to produce, product, production, productive, producing;
3. to in-
hale,
inhalation, to exhale, exhaled, exhaling; 4. breath, to breathe,
breathing, breathless, breathlessness; 5. to pass, passage, passing,
passage-way.
Упражнение 12. Переведите следующие словосочетания.
expiratory
centre, respiratory mechanism, waste product, metabolic product, the
air conducting passage-ways, to inhale (breathe in) oxygen, to exhale
carbon dioxide, surrounding tissues
Упражнение 13. Прочтите данные группы слов и переведите их.
1. through, throughout, though, although; 2. case, cause, course; 3. some, same, sum; 4. since, science
Упражнение 14. Просмотрите текст А. Назовите тему и основные положения текста.
Text A The respiratory system
1. Respiration occurs in all living things, both plants and animals.The рroper
function of this system is perhaps the most important one in the
sustaining of life. Interruption of breathing for only a few minutes by
suffocation or strangulation causes death. In the human organism,
respiration consists of those processes by which the body cells and
tissues make use of oxygen and by which carbon dioxide or the waste
products of respiration are removed.
2. Inhaled
air contains about 20 per cent oxygen and four hundredths of one per
cent carbon dioxide. Exhaled air consists of approximately 16 per cent
oxygen and 4 per cent carbon dioxide. Nitrogen, which makes up about 79
per cent of the atmosphere, is not involved in the breathing process.
When air is inhaled into the lungs, a portion of the oxygen is passing
into the blood and is being circulated through the body. At the same
time, carbon dioxide is being diffused out of the blood into the lungs
and exhaled.
3. Air
is breathed through either the mouth or nose into the oral cavity, or
pharynx. It then passes through the voice box, or larynx, into the
windpipe, or trachea. The trachea ultimately divides into two smaller
tubes, bronchi, one is going to each lung. The bronchi divide into tiny
passage-ways that are named bronchioles, which lead directly to minute
air sacs, or alveoli. The exchange of life-giving gases is effected
through the walls of the alveoli.
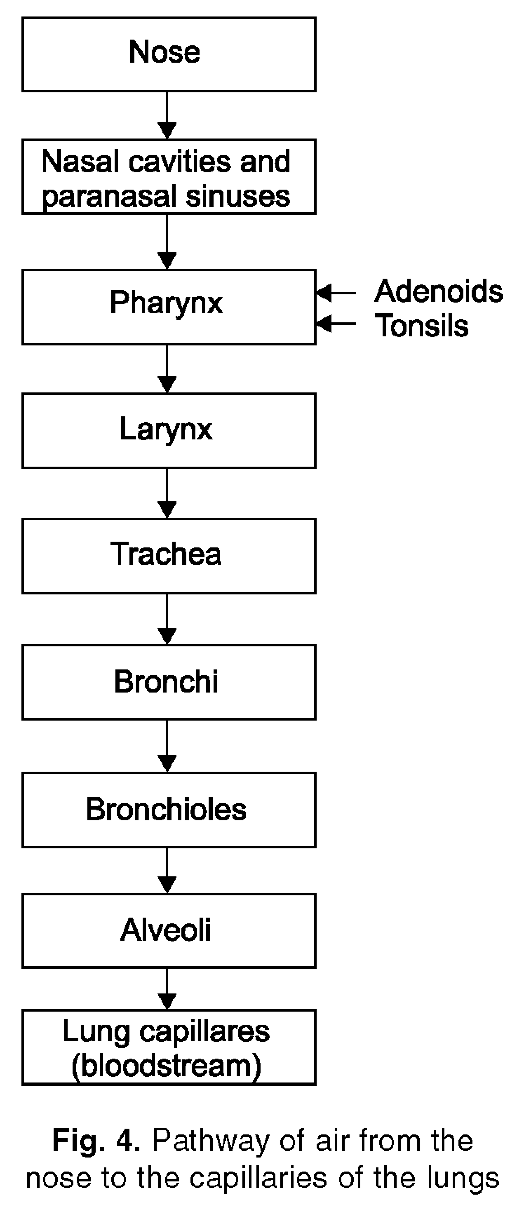

5. Other
structures which are connected with the system include: the laryngeal
tonsils, which are masses of tissue in the nasopharynx or posterior
portions of the nasal passages (adenoids are infected or diseased
laryngeal tonsils); the sinuses, cavities in the bones in the front
part of the skull that provide resonance to the voice, and the pleura, a
doublewalled membrane which surrounds the lungs.
6. When the diaphragm contracts and flattens, it contributes to the extension of the vertical diameter of the
thoracic
cavity. Air is constantly renewing in the lungs. The capacity of the
air passages is increasing. Any muscular effort, e.g. even standing up,
increases the number of respirations.
Упражнение 15. 1) Прочтите и переведите текст А. Абзацы 5 и 6 переведите письменно. 2) Найдите в тексте А ответы на следующие вопросы и зачитайте их.
1.
What gases are involved in breathing? 2. What parts of the respiratory
system does the air pass on its way to the alveoli? 3. What are the
other structures connected with the system? 4. Does the diaphragm
contribute to the extension of the vertical diameter of the thoracic
cavity? 5. Any muscular effort increases the number of respirations, doesn't it?
3) Составьте план текста А.
Упражнение 16. Подберите к латинским словам английские эквиваленты.

Упражнение 17. Подберите пары синонимов.
to
consist of, to take part in, fine, air passage, to occur, respiratory
tract, to happen, minute, to be involved in, to be made of
Упражнение 18. Образуйте пары антонимов к данным словам, используя приставку ех-, и переведите их.
to inhale, inspiration, to include
Упражнение 19. Образуйте форму множественного числа от данных латинских слов.
trachea, broncus, alveolus, cilium, pleura
Упражнение 20. Выберите верный перевод выделенных слов.
1. Each lung is surrounded by a double-folded membrane, the pleura. (окружает, окружило, окружено) 2. The tonsils are located in the oropharynx. (были расположены, расположат, расположены) 3. Numerous questions were being discussed at the lesson. (обсуждались, обсуждают, будут обсуждены) 4. The concept of respiration was based directly upon the work of Lavoisier. (была основана, основывают, основана) 5. The total number of alveoli in the lung has been estimated as 750 millions. (насчитывают, насчитали, насчитал)
Упражнение 21. Переведите следующие предложения. Запомните перевод данных глаголов, требующих после себя определенных предлогов.
to refer to, to speak of, to take care of, to send for, to wait for, to think of
1.
Respiration is usually thought of as the mechanical process of
breathing. 2. Disease germs are sometimes referred to as bugs. 3. Those
patients have been taken care of by the nurses. 4. By the discovery of
tubercule bacillus Robert Koch had been already much spoken about. 5. This lecture has long been waited for.
Упражнение 22. Переведите предложения, используя разные способы перевода страдательного залога.
1.
During the experiment all the work was being done automatically. 2.
The lungs are separated from other organs of the body in a movable
rigid-box - the chest cavity. 3. The boy with pneumonia was given
necessary treatment.
Упражнение 23. Переведите предложения, определите, где слово one не переводится.
1. One must
consider respiration essentially as exchange of gases - one in the lungs
and one in the tissues. 2. Pneumonia may be caused by one of the
different kinds of bacteria (germs), pneumococcus. 3. The thoracic
cavity that consists of ribs and muscles is the one for heart, lungs
and other viscera. 4. The lungs are built of alveoli and through the
bronchi, larynx, pharynx, mouth cavity and nasal one they expire carbon
dioxide (CO2) and inspire oxygen.
Упражнение 24. Переведите следующие словосочетания.
1.
life-giving gas, life-giving gas exchange; 2. tissue masses, tissue
masses structures; 3. respiration waste products, respiration waste
products removal; 4. carbon dioxide, carbon dioxide exhalation; 5.
doublewalled membrane, double-walled lung membrane; 6. blood
capillaries, blood capillaries dense network; 7. thoracic cavity
volume, thoracic cavity volume increase; 8. body cell oxygen, body cell
oxygen supply.
Упражнение 25. Переведите на английский язык.
1. Дыхание свойственно всему живому - как животным, так и растениям. 2. В процессе дыхания ткани поглощают кислород, а углекислый газ выводится из организма. 3. Воздух, который мы вдыхаем, содержит около 20% кислорода. 4. Бронхи делятся на мелкие воздухоносные пути, называемые бронхиолами. 5. Прекращение дыхания даже на несколько минут приводит к смерти.
Часть II Слова к части II

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Прочтите и переведите следующие слова. Проверьте себя по словарю.
maximum, production, pleural, passively, position, elasticity, tract, pulmonary, ventilation
Упражнение 2. Подберите пары синонимов.
interior, per minute, to take place, because, to occur, since, internal, each minute, a minute
Упражнение 3. Образуйте от данных слов антонимы, используя приставки ех-, un-, in-.
interior, decrease, inspiratory, important
Упражнение 4. Прочтите и запомните перевод слов rest, activity.
rest 1. остаток: the rest of the students, the rest of blood, for the rest в остальном; 2. покой: at rest в состоянии покоя, a resthome дом отдыха
activity 1. неисчисл. деятельность: respiratory activity; активность: political activity of the masses; 2. обычн. pl. деятельность (в опред. области): his social (political) activities
Упражнение 5. Прочтите и запомните следующие устойчивые словосоче- тания с предлогом at.
at all вообще, совсем at rest в состоянии покоя at first сначала at times временами, иногда
at last наконец at the same time в то же самое время
at least no крайней (меньшей) мере
Упражнение 6. Просмотрите
текст В (время 10 мин). 1) Скажите, на сколько частей можно разделить
текст. 2) Найдите предложения, где употребля- ются: а)
глаголы-сказуемые в Passive Voice; б) слово one (ones); в) существительные в функции определения. 3) Переведите эти предложения.
Text В Respiration
The
term «respiration» means the exchange of gases (oxygen and carbon
dioxide) which takes place between the living organism and the
environment. One must consider that in higher organisms this exchange
takes place at several different levels. An initial exchange must occur
between the air in the lungs, from which the oxygen is being
continually taken up and into which carbon dioxide is being continually
poured, and the external air. This is the process of external
respiration.
The
composition of the air inside the lungs is different from that of the
air which we inhale. The content of alveolar air is very constant,
especially the one of carbon dioxide, the partial pressure of which is
normally
The exchange
of gases varies according to the size and activity of the organism. In
man at rest the absorption of oxygen reaches about
The
movement of air into the lungs is brought about by an increase in the
volume of the thoracic cavity with the action of the respiratory
muscles. The lungs follow this movement passively. Some of the
inspiratory muscles have a fixed point on the ribs; when the ribs are
being raised the muscles increase the anteroposterior and transverse
diameters of the thoracic cavity (costal respiration). Another
important muscle is the diaphragm, a thin dome-shaped «sheet», which
closes the lower part of the thorax and separates it from the abdomen.
The diaphragm contracts and flattens; it contributes in this way to the
extension of the vertical diameter of the thoracic cavity and raises
the ribs (abdominal respiration). At the time of expiration, the thorax
returns to its initial
position, and air is expelled through the same tracts that had been used by fresh air during inspiration.
In
an individual at rest the number of inspirations per minute is 10 to
15; the pulmonary ventilation, or the volume of air which passes
through the respiratory system each minute, is about
Упражнение 8. Прочтите данные суждения. Найдите в тексте предложения, более полно выражающие мысль этих суждений.
1.
The term «respiration» means the exchange of gases. 2. An initial
exchange between the air in the lungs and the external air is called
external respiration. 3. The exchange of gases varies according to the
size and activity of the organism. 4. The content of alveolar air is
very constant. 5. The diaphragm contracts and flattens.
Часть III
Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 4
Упражнение 1. Переведите предложения с глаголом-сказуемым в страда- тельном залоге.
1.
Oxygen is being continually taken up from the lungs. 2. The exchange
of gases varies according to the size and activity of the organism.
3. Some of the respiratory muscles have a fixed point on the ribs. 4. Air is expelled through the tracts that have been used by fresh air during inspiration. 5. The heart wall is composed of two layers.
(Ответ: 1, 4, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 14 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 2. Прочтите предложения, где слово one - числительное. Переведите эти предложения.
1.
The lungs are two in number and one of them is in the right half of
the thoracic cavity. 2. One must know that smoking is harmful. 3. The
right lung is separated from the left one by the mediastinal septum.
4. There
is one movable bone in the skull. 5. The right and left pleural
cavities are serous sacs with visceral layers and parietal ones.
(Ответ: 1, 4. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 36 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 3. Опишите органы дыхания, используя рис. 4.
LESSON FIVE
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
Часть I
Слова к части I

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Заполните пропуски неопределенными местоимениями some, any, по и их производными.
1.
Are there ... grammar exercises in this textbook? 2. Give the patient
... analgetic. 3. Can ... show me the way to the Rectorate? 4. ... was
allowed to visit the boy because of the quarantine. 5. My eyeglasses are bad, I can't see ... now. 6. You may ask ... to help you.
Упражнение 2. Переведите следующие предложения с неопределенными местоимениями some, any, по и их производными.
1.
The diseases of the respiratory system depend in some way on its
anatomy and functions. 2. The laws of disease are as definite and
wellknown as those of any other biological process. 3. The earliest
symptoms of bronchitis must be known to everyone. 4. Anybody may catch a
respiratory disease at some time or other. 5. No student has been
absent from the lecture today.
Упражнение 3. В следующих предложениях определите придаточные предложения: определительные, дополнительные и обстоятельственные. Переведите предложения.
1. While oxygen is being taken into the blood, carbonic acid gas, or carbon dioxide passes from the blood into the lungs and is breathed out. 2. If you hold your breath, the carbon dioxide immediately begins to accumulate in the blood. 3. The tonsils can be removed in later life, provided the infection seems severe. 4. The right lung that is slightly larger of the two is divided into three lobes. 5. The teacher explains that the diaphragm contracts and descends with each inspiration. 6. When the lungs are full, the diaphragm relaxes.
Упражнение 4. Переведите предложения согласно образцу; обратите внимание на перевод местоимения it.
Образец: Water is liquid. Вода - жидкость.
It is necessary for life. Она необходима для жизни. It is necessary for health to drink distilled water. Для здоровья необходимо пить дистиллированную воду.
1. Medical students study anatomy. It
is difficult for them. It is difficult for them to study it. 2. The
amount of air which the body needs varies from time to time. It is
necessary for the body. It is necessary for the body to regulate it. 3.
Blood is a red fluid. It is easy to see it when it escapes from a
blood vessel. 4. Pneumonia is inflammation of the lungs. It is
dangerous for life. It is easy to diagnose it. 5. The larynx contains
the vocal cords. It is surrounded by pieces of cartilage for support.
It is possible to examine it with special instruments.
Упражнение 5. Переведите следующие предложения. Определите, в каких предложениях слово it не переводится.
1.
It is possible to remove one lobe of the lung without any damage to
the rest. 2. The upper part of the respiratory system conducts air and
produces the voice; it consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea
and bronchi. 3. It is known that internal respiration is the exchange
of gases. 4. Cold on the surface of the body can change the amount of
blood in the nose or lungs when it is needed there. 5. It is by means
of the organs of respiration that air is taken into the lungs and
oxygen is given to the blood.
Упражнение 6. Прочтите следующие слова. Переведите их.

Упражнение 7. Отработайте чтение следующих предложений:
Упражнение 8. Запомните значение суффикса -ic. Образуйте прилагательные от следующих существительных.
-ic (-ical) образует от основ существительных относительные прилагательные, которые обозначают принадлежность или признак: pelvis - pelvic; physiology - physiological, physiologic.
history, chemistry, mechanism, toxicity, spleen
Упражнение 9. Прочтите и переведите следующие гнезда слов.
1.
to bound, boundless, boundary; 2. to weigh, weight, weighing, weighed;
3. wide, to widen, width, widely; 4. long, length, to lengthen
Упражнение 10. Прочтите и переведите следующие словосочетания.
pelvic girdle, specific (atomic, molecular) weight, to refer a patient to a specialist, reference book, a wide variety of
Упражнение 11. Просмотрите текст А и скажите, какие органы брюшной полости описаны в данном тексте.
Text A The Abdomen
The abdomen is the largest cavity of the body. It is bounded above by the thorax or chest and below by two pelvic bones which meet in front. From the cavity of the thorax it is separated by the great muscle of respiration - the diaphragm. Laterally and in front it is enclosed by the lower ribs and abdominal muscles. Behind, it is supported by the spinal column.
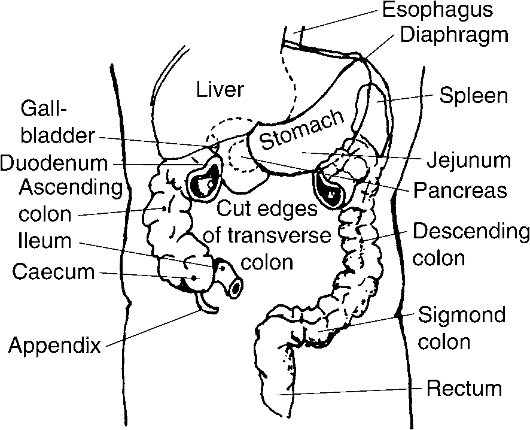
Fig. 5. The digestive system
The
organs of the abdominal cavity are the liver, the gall-bladder, the
stomach, the intestines, the pancreas, the spleen, the kidneys and the
bladder.
The
liver lies under the right ribs and extends across to the left of the
epigastrium. The liver is a large organ that weighs about
The gall-bladder lies beneath the right lobe of the liver. The gallbladder serves as a bile reservoir.
The
stomach lies under the left ribs and extends across to the right. It
is known that its smaller end situates in the epigastrium. The stomach
serves as a container of food, which is partly digested in it. The size
and shape of the stomach vary with any amount of food that is consumed
and the extent of contraction of its wall. The stomach when it is
filled with food is usually compared with a chemical retort. Its
capacity is some 1-2 litres.
The
intestines («internal» - Latin) occupy chiefly the central portions of
the abdominal cavity. From the stomach the food passes in small
portions into the small intestine where it undergoes further mechanical
and chemical changes. As the contents of the small intestine cannot
move back they may freely pass into the large intestine.
The «small» and «large» refers to the width, rather than the length. The small intestine is only 1.5 to
it leaves the stomach and it narrows somewhat thereafter. The large intestine is up to
Упражнение 12. Прочтите и переведите письменно следующие предложе- ния из текста А.
1.
The liver plays a very important part in the vital activity of the
organism. It secretes bile which participates in the digestive process
and has a defensive function, i.e. some toxic substances are detoxified
in the liver. 2: From the stomach the food passes in small portions
into the small intestine where it undergoes further mechanical and
chemical changes.
3. The small intestine is only 1.5 to
Упражнение 13. Прочтите и переведите текст А. Найдите в тексте ответы на следующие вопросы и зачитайте их.
1.
Where is the largest cavity of the body situated? 2. What organs does
the abdominal cavity contain? 3. What are the characteristics of the
liver?
4. What
does the gall-bladder serve for? 5. What are the characteristics of
the stomach? 6. How do we distinguish «small» and «large» intestines?
Упражнение 14. Составьте план текста А.
Упражнение 15. Подберите пары синонимов.
spinal column, to participate, beneath, thorax, chest, under, to take part, backbone
Упражнение 16. Подберите пары антонимов.
above, in front of, small, lower, to the left, to pass in; upper (higher), to the right, to leave, behind, below, large
Упражнение 17. Переведите следующие предложения на русский язык. Оп- ределите тип придаточных предложений (см. ? 29 Грамматического справочника)
1. After the food leaves the stomach it is acted on by several digestive enzymes. 2.
The stomach is a bag the walls of which are largely made up of
involuntary or smooth muscle fibres. 3. The liver is a large and
extremely important organ whose work is somewhat intermediate between
digestion and nutrition. 4. The esophagus is a 9 to
Упражнение 18. Переведите следующие предложения. Определите функции слова it (см. ? 35 Грамматического справочника)
1.
It must be noted that the role of the stomach is to prepare the food
chemically and mechanically. 2. When a group of organs performs a
varified series of functions we call it a system. 3. It is the gastric
glands in the stomach that secrete gastric juice, which is acid and
acts on meals. 4. It is through the capillary network of the villi that
digested foods pass to enter the bloodstream. 5. It is possible to
refer painful intestines to bacterial or amoebic infection of the
gastrointestinal tract. 6. After the food is properly prepared it is
absorbed into the lymph vessels and blood vessels.
Упражнение 19. Переведите на английский язык.
1. Диафрагма - это большая мышца, которой грудная полость отделяется от брюшной. 2. Известно, что печень, расположенная в правом подреберье, является одним из самых крупных органов. Она выполняет несколько жизненно важных функций. 3. Именно в печени обезвреживаются некоторые токсичные вещества. 4. Толстый кишечник на 1-1,5 дюйма шире, чем тонкий.
Упражнение 20. Опишите органы пищеварения, используя рис. 5.
Часть II Слова к части II

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Образуйте от данных слов прилагательные, используя суффиксы -al, -ive, -ous, и переведите их.
abdomen, intestine, mucus, to digest, defence, fibre, chemistry, mechanic, serum
Упражнение 2. Прочтите и запомните перевод следующих слов и слово- сочетаний.

Упражнение 3. Просмотрите текст В (10 мин). 1) Скажите, с точки зрения какой науки дается описание пищеварительной системы. 2) Найдите и переведите предложения, где употребляются: а) слово «it»; б) местоиме- ния some, any; в) слова through, result. 3) Найдите в тексте придаточные предложения и переведите их.
Text В
The Digestive System
The
digestive system consists of the digestive tract and digestive glands.
The digestive tract is some 8-10 m long and is divided into the
following parts: oral cavity, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small
intestine and large intestine. The structures of the different parts of
the tract have some special features.
The
wall of the greater part of the digestive tract consists of three
coats: internal - mucous, middle - muscular, and the external - serous.
The mucous coat is lined with the epithelium outside which is a
connective tissue with a thin layer of smooth muscle fibres. The mucous
coat is pink in colour because it has many blood vessels. The numerous
small glands in this coat secrete a viscous coat of the digestive
tract. It facilitates the movement of food and protects the mucous coat
from the damage by solid particles of food and various chemical
substances. One must remember that the mucous coat of the digestive
tract begins with the esophagus, contains lymph nodules which also have
a protective function.
The greater
part of the muscular coat of the digestive tract consists of two
layers: an internal layer with circular muscle fibres and an external
layer with longitudinal muscle fibres. The wall of the pharynx and the
superior part of the esophagus, and the tongue and the soft palate all
contain striated muscle tissue. It is the muscular coat of the other
parts of the digestive tract that consists of smooth muscle tissue.
Contractions of the muscular coat move food along the digestive tract.
The
serous coat that covers the digestive organs in the abdominal cavity
is called the peritoneum. The peritoneum has two layers, visceral and
parietal. In the esophagus the serous layer is lacking and the outer
coat is fibrous in nature.
The
digestive glands secrete digestive juices that contain enzymes and
some other substances which take part in the chemical processes of
digestion.
In
addition to the small glands in the mucous coat of the digestive
tract, there are also large glands: the salivary glands, the liver and
the pancreas. Though these glands are situated outside the digestive
tract, they communicate with it through ducts.
Any
part of the digestive tract and the digestive glands are equipped with
nerve fibres and their endings. The nerves of the digestive glands
regulate the secretion of digestive juices. It is known that the
nervous system not only regulates the activity of each organ, but also
coordinates their activities.
Упражнение 5. Прочтите каждое суждение. Найдите в тексте В предло- жения, более полно выражающие мысль данного суждения, и прочтите их.
1.
The digestive tract is divided into some parts. 2. The viscous coat of
the digestive tract facilitates the movement of food. 3. The muscles
of different types form the walls of the intestine. 4. The serous coat
doesn't cover all the organs of the digestive system. 5. Enzymes take
part in digestion. 6. Salivary glands, liver and pancreas are situated
outside the digestive tract. 7. The nervous system regulates and
coordinates the work of the digestive organs.
Часть III
Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 5
Упражнение 1. Найдите предложения с усилительной конструкцией it is ... that и переведите их.
1. It is known that the abdomen is the largest cavity of the body. 2. It is the liver that weighs about
(Ответ: 2, 4, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ?35 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 2. Найдите и переведите предложения, в которых any имеет значение «любой».
1.
Any lymph nodule of the mucous coat has a protective function. 2. Are
there any blood vessels in the mucous coat? 3. Unlike the organs of the
abdominal cavity the esophagus does not possess any serous layer.
4. Any
digestive glands secrete digestive juices that contain special
enzymes. 5. Are there any large glands in the digestive system?
(Ответ: 1, 4. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 7 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 3. Найдите и переведите определительные придаточные пред- ложения.
1.
The upper portion of the stomach which is called the fundus is at the
top. 2. The stomach when it is full becomes pear-shaped. 3. The gastric
juice is unusual for a body fluid as it is strongly acid. 4. The
enzymes that the digestive juices contain take an active part in the
process of digestion.
5. Nutrients are substances that help your body to grow and develop. (Ответ: 1, 4, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 29 Грамматического справочника.)
LESSON SIX
THE URINARY SYSTEM
1. Эквиваленты модальных глаголов (? 17)
2. Употребление глагола в настоящем времени в значении будущего в условных и временных придаточных предложениях (? 30)
3. Функции и перевод слов since, as (?? 37, 38)
Часть I
Слова к части I

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Напишите следующие предложения в а) Past Indefinite; б) Future Indefinite согласно образцу.
Образец: He must pass the examination in anatomy.
He had to pass the examination in anatomy.
He will have to pass
the examination in anatomy. 1. The students may take all necessary
textbooks from the Institute library. 2. He can help you with your
translation. 3. You must repeat the material of the lectures before the
examination. 4. They cannot translate these articles without a
dictionary.
Упражнение 2. Заполните пропуски модальными глаголами can, may, must, should.
Упражнение 3. Замените в следующих предложениях модальные глаголы их эквивалентами.
1.
The doctor says that you may walk. 2. The vitamins are substances
which must be found in the diets of animals in order that they can
utilize the organic foodstuffs to best advantage. 3. When the appetite
is impaired and nausea and vomiting are common, meals must be small and
be given at frequent intervals. 4. With the disappearance of symptoms
the patient with infective hepatitis may leave his bed for purposes of
toilet.
Упражнение 4. Переведите следующие предложения. Определите время глагола-сказуемого в главных и придаточных предложениях.
1. When
dehydration occurs from excessive vomiting, parenteral feeding will be
used. 2. If the diagnosis is correct, the patient will be
properly
treated. 3. If coma develops, the patient will be transferred to
hospital as soon as possible. 4. If some infectious fever is diagnosed,
the patient is moved to the hospital in an ambulance. 5. If you hold
your breath, carbon dioxide will immediately begin to accumulate in the
blood.
Упражнение 5. Прочтите и переведите следующие предложения. Опреде- лите, какую функцию выполняет слово as.
Упражнение 6. Переведите следующие предложения. Определите, какую функцию выполняет слово since.
1. Since penicillin was discovered a vast amount of information has been accumulated concerning its use. 2. Senna is a favourite cathartic, since it can be made up into a sweet mass. 3. Since the liver of polikilothermic animals is less demanding than that of mammals, the liver of the frog is generally used for different kinds of investigations. 4. I have studied English since 2001.
Упражнение 7. Отработайте чтение следующих предложений.
The 'urinary 'system is the /system | which ex'cretes the 'largest 'part of the 'waste 'products of the \body. It con'sists of the /kidneys, | right and \left
|, the /ureters |, a 'tube from 'each /kidney |, which con'veys the
'urine to the \ bladder, | the /urethra |, a 'tube | which leads from
the /bladder |, along which the 'urine is 'passed 'out of the \body.
Упражнение 8. Запомните значение нижеприведенных суффиксов и пре- фиксов. Образуйте и переведите производные слова согласно модели.
1. -ment - образует существительные от глаголов: to move двигаться) - movement движение.
to nourish кормить, питать, to improve улучшать(ся), to develop развиваться)

b) -en - образует глаголы от именных основ: deep глубокий -to deepen углубляться).
strength сила, moist влага, less меньше, straight прямой, length длина
Упражнение 9. Прочтите и переведите следующие гнезда слов.
1.
excrete, secrete, excretion, secretion, excretory, secretory; 2.
urine, urinary, urethra, ureter, urea; 3. pelvis, pelvic; 4. number, to
number, numerous, numberless
Упражнение 10. Просмотрите текст А и скажите, какие части мочевой системы описаны в тексте.
Text A The Urinary System
1. The
uriuary system is the system which excretes the largest part of the
waste products of the body. It consists of the kidneys, right and left,
the ureters, a tube from each kidney which conveys the urine to the
bladder, the urethra, a tube that leads from the bladder, along which
the urine is passed out of the body.
2. The
kidneys («renes» - Latin) are placed one on each side in the lumbar
region of the spine, on the posterior abdominal wall, at the level of
the twelfth thoracic and first-second lumbar vertebrae. A kidney weighs
about
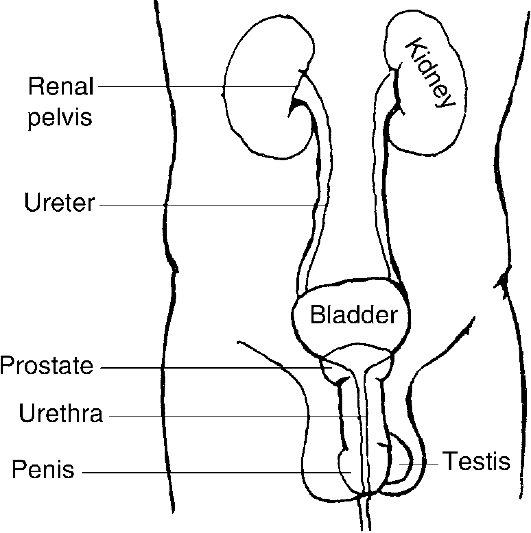
Fig. 6. The organs of the urinary system
lion
small tubes, which have to excrete products of metabolism and control
the concentrations of most of the constituents of body fluids. These
small tubules make up the parenchyma of the kidney. They are very fine
and may be of various shape. Since dissolved (растворенные) wastes may be excreted by diffusion through the various cell membranes there is little evidence that such excretion occurs.
3. The inner margin of the kidney is known as the hilus. At the hilus the ureter which conveys urine is a tube about
4. The
bladder is a reservoir for urine. It is situated in the cavity of the
pelvis. The bladder has three parts: the superior part or apex, the
middle part or body, and the inferior part or fundus. The wall of the
bladder consists of three coatings - mucous, muscular and connective
tissue. The mucous membrane of the bladder forms numerous folds. If the
bladder fills, the folds of the mucous coat will straighten out. The
muscular coat consists of three layers of smooth muscles which are able
to extend in different directions. It should be known that the
capacity of the bladder of an adult is about 350-500 ml.
Упражнение 11. Прочтите и переведите текст А. Третий абзац переведите письменно.
Упражнение 12. Найдите в тексте А ответы на следующие вопросы и зачитайте их.
1.
What are the parts of the urinary system? 2. Where are the kidneys
placed? 3. What are the functions of the fine tubes which make up the
parenchyma of the kidney? 4. What route does the ureter pass?
Упражнение 13. Составьте план текста А.
Упражнение 14. Подберите пары синонимов.
to consist of, to excrete, fine, capacity, fundus, volume, bottom, to be made up of, to pass out, minute
Упражнение 15. Подберите пары антонимов.
to ascend, large, the same, to discover, inferior, superior, to cover, small, various, to descend
Упражнение 16. Переведите предложения. Определите, какой частью речи являются выделенные слова. Найдите их значение в словаре.
1. The tubules which make up the parenchyma of the kidney are very fine. 2. The weather was fine on holidays. 3. As the bladder fills the folds of the mucous coat straighten out. 4. All higher animals have a backbone or vertebral column as it is called. 5. Smooth muscles form the muscular coat of internal organs such as esophagus, stomach and so on. They are also present as single cells or as cylindrical bundles of cells in the skin. 6. The muscular substance of the heart is known as myocardium.
Упражнение 17. Найдите модальные глаголы и их эквиваленты в следующих предложениях. Переведите предложения.
1.
All nitrogenous waste products must be thrown off by the body first
because they are useless, second because in some instances they are
poisonous.
2. Many
substances can affect the kidney epithelium so as to render it more or
less reduced in ability to excrete urine. 3. Physiotherapeutic
treatment of patients with chronic pyelonephritis should be advisable
only in combination with medicamental therapy. 4. The kidney has to put
back into the bloodstream all the materials that the body needs. 5.
The process of filtration in the kidney is dependent upon the character
of the membrane which may vary in permeability. 6. The effect of
complex therapy in patients with chronic pyelonephritis may be only
achieved when urodynamics is restored.
Упражнение 18. Переведите следующие предложения. Запомните значение слов as, since.
1.
As the blood courses through the capillary glomeruli, the kidney cells
take up water, salts and waste bodies. 2. Pathogenetic therapy
includes such antiinflammatory preparations, as salicylates,
dichlorophene, lydasa, aloe.
3. The wastes are substances which are taken in with the foods or as foods.
4. The
phenomena of coagulation have received great attention from
physiologists since the earliest times. 5. Since the arterioles of each
renal artery are small, blood passes through them slowly, but
constantly. 6. Since plasma sodium concentration remained unchanged,
the experiments establish the ability of cadmium to increase tubular
sodium reabsorption.
Упражнение 19. Переведите следующие предложения. Объясните, в каких случаях форма глагола-сказуемого в настоящем времени переводится будущим временем.
1.
After the kidney cells remove the end products of food from the blood
these substances are washed out of the tubules into the pelvis of
the
kidney down the ureter into the bladder. 2. When the man smells
something that he likes to eat, the gastric juice will be poured out in
large quantities. 3. If the kidney is diseased and cannot excrete
urine, the amount of urea in the blood is increased. 4. When no nerve
impulses go to the heart-muscle, it will not beat regularly and
rhythmically. 5. When the sympathetic nerve in the neck of a rabbit is
cut, the blood vessels in the ear on that side become very much
dilated.
Упражнение 20. Переведите на английский язык.
1. Большая часть продуктов распада вьгаодится из организма почками. 2. Паренхима почки состоит из 1 000 000 маленьких трубочек, которые могут быть различной формы. 3. По мере того как мочевой пузырь наполняется, складки слизистой оболочки расправляются. 4. Емкость мочевого пузыря составляет в среднем 350-500 мл.
Упражнение 21. Назовите органы мочевыделительной системы, используя рис. 6.
Часть II Слова к части II

Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Подберите пары синонимов.
waste products, much, amount, stop, also, a good deal, cease, waste matters, too, quantity
Упражнение 2. Подберите пары антонимов.
large, to join, concave, inner, outwards, to separate, outer, convex, inwards, minute
Упражнение 3. Переведите следующие предложения. Запомните значение слов certain, cause, to regard.
1.
The chief function of the kidneys is to separate fluid and certain
solids from the blood. 2. The kidneys may be regarded as filters
through which the whole blood of the body passes, and which remove from
the blood a substance that is called urea together with other
impurities. 3. If the kidneys cease to work from any cause, the blood
will become poisonous.
Упражнение 4. Прочтите
текст В (10 мин). 1) Скажите, на сколько частей можно разделить текст и
какова тема каждой из них. 2) Найдите предло- жения, где: а) даны
эквиваленты модальных глаголов; б) слова since, as; в)
глагол-сказуемое в придаточных времени и условия употребляется в форме
настоящего времени, которая переводится будущим временем. 3) Переведите предложения.
Text В The Kidneys
Kidneys
are a pair of glands which are situated close to the spine in the
upper part of the abdomen. They are on a level with the last dorsal and
upper two lumbar vertebrae. They are kept in this position by a
quantity of fat, loose connective tissue, in which they are embedded,
and the large vessels which have to supply them with blood.
Structure. In size each kidney is about
Since the
outer margin of the kidney is convex, the inner is concave. It presents a
deep depression, which is known as the hilus, where the vessels enter
its substance. At the hilus the renal vein lies in front of the renal
artery, the former joins the inferior vena cava, and the latter springs
from the aorta almost at a right angle.
Vertical
section through a kidney allows to disclose three concentric zones.
The outer light-coloured zone is the renal cortex, within this is the
darker renal medulla and within this again is a space - the renal sinus
which is normally occupied by fibrous sac, the renal pelvis. The
cortex extends inwards in a series of renal columns which divide the
medulla into a number of renal pyramids.
Within
the cortex each minute artery presents a vascular knot, a glomerulus.
Each glomerulus projects into the end of its corresponding renal
tubule, which is separated by a thin layer of cells, glomerular
(Bowman's) capsule;
glomerulus
plus capsule forms a renal (Malpighian) corpuscle. A renal corpuscle
with tubules and blood vessels is called a renal unit, or nephron.
Function. One
chief function of the kidneys is to separate fluid and certain solids
form the blood. The glomeruli are to filter from the blood the
non-protein portion of the plasma. It is estimated that in 24 hours the
total human glomeruli will be able to filter between 150 and
The
kidneys are to be regarded as filters through which the whole blood of
the body passes and which remove from the blood a substance, urea,
together with other impurities, which together constitute the urine.
The cleansed blood passes on in its vessels, and the urine drains into
the ureters and finally into the bladder. If the kidneys cease to work
the blood will become poisonous because of the accumulation of the
waste matters.
Упражнение 5. Прочтите каждое суждение. Найдите в тексте предложе- ния, более полно выражающие мысль данных суждений, и прочтите их.
1.
Kidneys are situated close to the spine. 2. The vessels enter the
substance of the kidney at the hilus. 3. The renal cortex, renal
medulla and renal sinus are three concentric zones of the kidney. 4.
The kidneys may be regarded as filters.
Часть III
Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 6
Упражнение 1. Найдите и переведите предложения, где сказуемое стоит в прошедшем времени.
1.
The renal blood vessels can be constricted or dilated. 2. The patient
was allowed to take this analgetic. 3. The boy will be able to walk by
himself. 4. The inflow of blood had to be diminished when the renal
blood vessels were constricted.
(Ответ: 2, 4. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 17 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 2. Найдите и переведите предложения, где глагол to have выражает долженствование.
1.
The bowels have the function to secrete the end products of digestion.
2. The lungs have to excrete carbon dioxide and water. 3. The
boy
has been recently examined in a surgical department for intestinal
pains. 4. Carbon dioxide is a gas which has to be eliminated from the
body.
(Ответ: 2, 4. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 17 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 3. Найдите и переведите предложения, где выделенные гла- голы-сказуемые переводятся будущим временем.
1. When a person suffers from a severe pain he has to consult a doctor.
2. If there is any disfunction of the kidney, it will affect the process of urine formation. 3. When the renal blood vessels are dilated, the inflow of blood will increase. 4. If the renal blood vessels are constricted, less urine will be formed.
(Ответ: 2, 3, 4. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ? 30 Грамматического справочника.)
Упражнение 4. Найдите и переведите предложения, где as и since являются союзами.
1.
Waste products such as products of albuminous nutrition are excreted
by the kidneys. 2. Since water is taken into the body, some of it is
excreted through the lungs and perspiration. 3. The kidneys contain a
large number of nerve fibres as their work is regulated by the nervous
system. 4. As the renal blood vessels are dilated, the urine formation
is changed. 5. Since last week there was no protein or sugar in the
urine analysis. 6. Some waste materials are carried to the bladder and
excreted as urine.
(Ответ: 2, 3, 4. Если вы ошиблись, повторите ?? 37, 38 Грамматического справочника.)